Ko 143
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 09:57:08
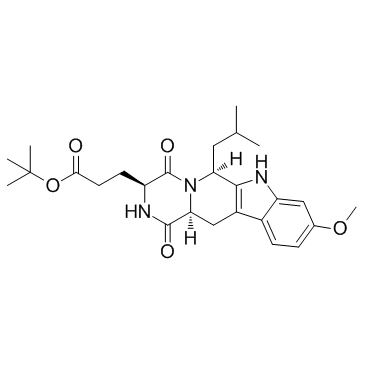
Ko 143 structure
|
Common Name | Ko 143 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 461054-93-3 | Molecular Weight | 469.573 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 689.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H35N3O5 | Melting Point | 147ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 371.0±31.5 °C | |
Use of Ko 143Ko 143 is a potent and selective ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 (ABCG2) inhibitor. |
| Name | Ko 143 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ko 143 is a potent and selective ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 (ABCG2) inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC90: 26 nM (BCRP) |
| In Vitro | Ko143 (10 nM) significantly decreases (2.5-fold) the IC50 of MTX for HEK G2 cells and mouse G2 cells. Ko143 (1-100 μM) metabolite does not inhibit the function of ABC Transporters[1]. Reversal of drug resistance in topotecan-selected mouse MEF3.8/T6400 cells and human IGROV1/T8 cells by FTC analogue Ko143. Ko143 is applied at zero, one, or eight times the EC90 concentration of 25 nM[2]. Ko143 inhibits BCRP-mediated transport of rosuvastatin in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) 2-BCRP421CC (wild type) cells and MDCK2-BCRP421AA (mutant type) cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Ko143 (10 mg/kg, p.o.) increases the oral availability of topotecan in mice[2]. Ko143 significantly affects the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in rats[3]. |
| Cell Assay | cells are plated at 400 or 1000/well in 96-well plates the night before addition of drugs. A concentration series of drug is applied along one plate axis and left for the duration of the assay. Plates are harvested after 4-5 days while untreated wells are still subconfluent. Relative cell proliferation is quantified with CyQuant or Sybr Green I fluorescent nucleic acid stains. Assays with human cell lines are performed in the presence of 0.1 μm PSC833 to inhibit confounding P-gp activity. |
| Animal Admin | Oral toxicity of FTC analogues in mice is tested by mixing 50 mg/mL stocks in DMSO 1:1 with Tween 80 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan mono-oleate) and diluting with 5% w/v glucose such that the final volume administered by oral gavage is 10 μL/g of body weight. Pairs of mice are administered oral doses of 50 mg/kg Ko132, Ko134, Ko143, or vehicle under light methoxyflurane anesthesia. Final tests of 50 mg/kg Ko134 or Ko143 are performed on additional pairs of unanesthetized animals to observe any behavioral effects. Further, another pair of mice receive the higher dose of 100 mg/kg Ko134. For i.p. toxicity tests, the FTC analogue stocks in DMSO are dispersed in at least 10 volumes of sterile corn oil such that the injected volume is 5 μL/g of body weight. After pilot tests at lower doses show no adverse effects, mice (4 per group) are administered vehicle or 10 mg/kg i.p. of Ko132, Ko134, or Ko143. The mice are observed continuously during the first hour after administration and then at increasing intervals for 2 weeks, after which they are sacrificed for histological examination of major organs and structures including brain, salivary glands, heart, lungs, liver, adrenal glands, kidneys, urinary tract, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, pancreas, stomach, intestines, cecum, colon, testes, epididymus, skin, head, trunk, and limbs. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 689.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 147ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C26H35N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 469.573 |
| Flash Point | 371.0±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 469.257660 |
| PSA | 100.73000 |
| LogP | 2.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.597 |
| Ko143 hydrate |
| 2-Methyl-2-propanyl 3-[(3S,6S,12aS)-6-isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydropyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl]propanoate |
| Ko-143 |