Neriifolin
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 11:36:29
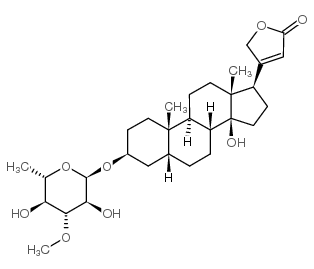
Neriifolin structure
|
Common Name | Neriifolin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 466-07-9 | Molecular Weight | 534.68100 | |
| Density | 1.274g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 700.079ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H46O8 | Melting Point | 218-225ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 224.862ºC | |
Use of NeriifolinNeriifolin, a CNS-penetrating cardiac glycoside, is an inhibitor of the Na+, K+-ATPase. Neriifolin can target beclin 1, inhibits the formation of LC3-associated phagosomes and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) development. Neriifolin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells[1][2. |
| Name | neriifolin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Neriifolin, a CNS-penetrating cardiac glycoside, is an inhibitor of the Na+, K+-ATPase. Neriifolin can target beclin 1, inhibits the formation of LC3-associated phagosomes and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) development. Neriifolin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells[1][2. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Neriifolin (0.1μg/mL; 48 hours) induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Neriifolin (0-8 μg/mL; 72 hours) reduces viability of HepG2 cells. Neriifolin also induces S and G2/M phase arrests of the cell cycle and stimulates apoptosis of HepG2 cells. Stimulation of HepG2 cells with Neriifolin induced activation of caspase-3, -8, and -9, and up-regulated expression of Fas and FasL proteins[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.274g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 700.079ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 218-225ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C30H46O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 534.68100 |
| Flash Point | 224.862ºC |
| Exact Mass | 534.31900 |
| PSA | 114.68000 |
| LogP | 3.11020 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.581 |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 26/27/28 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | FH4906100 |
| NERIIFOLIN |
| 17Beta-Neriifolin |
| xy)-14-hydroxy |
| digitoxigenin+thevetose |