| Description |
Vasicinone is a quinazoline alkaloid isolated from the Adhatoda vasica plant. Vasicinone is a potential agent for Parkinson's disease and possibly other oxidative stress-related neurodegenerative disorders[1].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
Vasicinone (1~30 µM; 24 hours; SH-SY5Y cells) significantly reverses the paraquat-induced reduction in cell viability[1]. Vasicinone (10 and 15 μM; 24 hours; SH-SY5Y cells) abates the paraquat-induced injury of SH-SY5Y cells by suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway, dose-dependently reduces the percentage of apoptotic cells and is capable of rescuing paraquat-induced apoptotic death[1]. Vasicinone (10 and 15 μM; SH-SY5Y cells) attenuates the paraquat-induced accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and attenuates the paraquat-induced expression of apoptotic proteins[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y cells Concentration: 1~30 µM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Significantly reversed the paraquat-induced reduction in cell viability. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y cells Concentration: 10 and 15 µM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Abated the paraquat-induced injury of SH-SY5Y cells by suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y cells Concentration: 10 and 15 µM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Dose-dependently reduced the percentage of apoptotic cells.
|
| References |
[1]. Ju DT, et al. Effect of Vasicinone against Paraquat-Induced MAPK/p53-Mediated Apoptosis via the IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT Pathway in a Parkinson's Disease-Associated SH-SY5Y Cell Model. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1655. Published 2019 Jul 19.
|
![1-[1(S),3-dihydroxypropyl]quinazolin-4(1H)-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/043/391249-56-2.png) CAS#:391249-56-2
CAS#:391249-56-2![2,3-Dihydropyrrolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-9(1H)-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/084/530-53-0.png) CAS#:530-53-0
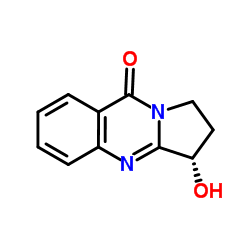
CAS#:530-53-0 CAS#:328571-50-2
CAS#:328571-50-2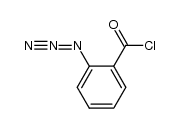 CAS#:34897-85-3
CAS#:34897-85-3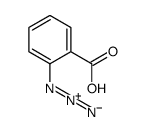 CAS#:31162-13-7
CAS#:31162-13-7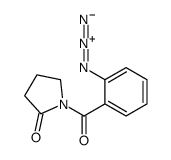 CAS#:125659-45-2
CAS#:125659-45-2![3-bromo-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-9-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/213/71540-68-6.png) CAS#:71540-68-6
CAS#:71540-68-6 CAS#:72710-66-8
CAS#:72710-66-8 CAS#:28144-70-9
CAS#:28144-70-9
