Auraptene
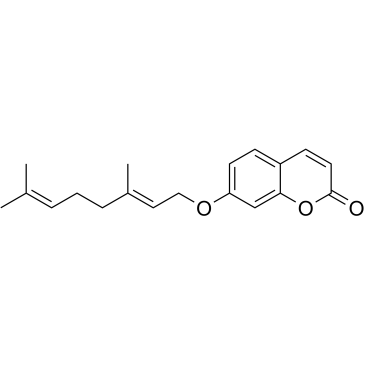
Auraptene structure
|
Common Name | Auraptene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 495-02-3 | Molecular Weight | 298.376 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 455.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22O3 | Melting Point | 66 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 195.4±23.3 °C | |
Use of AurapteneAuraptene is the most abundant naturally occurring geranyloxycoumarin. Auraptene is primarily isolated from plants in the Rutaceae family, such as citrus fruits. Auraptene decreases the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) as well as key inflammatory mediators, including IL-6, IL-8, and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand-5(CCL5)[1]. |
| Name | auraptene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Auraptene is the most abundant naturally occurring geranyloxycoumarin. Auraptene is primarily isolated from plants in the Rutaceae family, such as citrus fruits. Auraptene decreases the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) as well as key inflammatory mediators, including IL-6, IL-8, and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand-5(CCL5)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
MMP-2 |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 455.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 66 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 298.376 |
| Flash Point | 195.4±23.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 298.156891 |
| PSA | 39.44000 |
| LogP | 5.69 |
| Appearance of Characters | white to off-white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.549 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >20mg/mL |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
|
Suppression of mitochondrial respiration with auraptene inhibits the progression of renal cell carcinoma: involvement of HIF-1α degradation.
Oncotarget 6 , 38127-38, (2015) Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) progression resulting from the uncontrolled migration and enhanced angiogenesis is an obstacle to effective therapeutic intervention. Tumor metabolism has distinctive featur... |
|
|
Novel prodrugs for the treatment of colonic diseases based on 5-aminosalicylic acid, 4'-geranyloxyferulic acid, and auraptene: biological activities and analytical assays.
Curr. Drug Deliv. 9(2) , 112-21, (2012) A pro-drug is a substance administered in a pharmacologically inactive structure that, once administered, is metabolised in vivo into the corresponding active principle. The rationale for the design o... |
|
|
Development of a quantitative bioassay to assess preventive compounds against inflammation-based carcinogenesis.
Nitric Oxide 25(2) , 183-94, (2011) Reducing cancer incidence and mortality by use of cancer-chemopreventive agents is an important goal. We have established an in vitro bioassay that is able to screen large numbers of candidate chemica... |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 7-((3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl)oxy)-, (E)- |
| Coumarin, 7-[(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl)oxy]-, (E)- |
| Auraptene |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 7-[(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl)oxy]-, (E)- |
| 7-{[(2E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]oxy}-2H-chromen-2-one |
| 7-[[(2E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]oxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one 7-Geranyloxycoumarin Aurapten |
| 7-{[(2E)-3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-dien-1-yl]oxy}-2H-chromen-2-one |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 7-[[(2E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]oxy]- |
| 7-Geranyloxycoumarin |
| 7-{[(2E)-3,7-Diméthyl-2,6-octadièn-1-yl]oxy}-2H-chromén-2-one |
| aurapten |
 CAS#:93-35-6
CAS#:93-35-6 CAS#:6138-90-5
CAS#:6138-90-5 CAS#:5389-87-7
CAS#:5389-87-7 CAS#:1181223-78-8
CAS#:1181223-78-8![2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one,7-[[(2E)-3-(4,5-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-furanyl)-2-buten-1-yl]oxy]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/234/36413-91-9.png) CAS#:36413-91-9
CAS#:36413-91-9![7-[(E)-3-(5,5-dimethyl-4-oxooxolan-2-yl)but-2-enoxy]chromen-2-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/019/98066-12-7.png) CAS#:98066-12-7
CAS#:98066-12-7![Coumarin, 7-[ (6,7-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenyl)oxy]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/231/5980-09-6.png) CAS#:5980-09-6
CAS#:5980-09-6 CAS#:61347-54-4
CAS#:61347-54-4
