Lonidamine
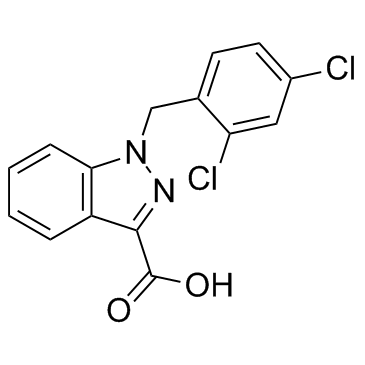
Lonidamine structure
|
Common Name | Lonidamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50264-69-2 | Molecular Weight | 321.158 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 537.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10Cl2N2O2 | Melting Point | 207-209°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 279.1±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of LonidamineLonidamine is an orally administered small molecule hexokinase inactivator.Target: OthersLonidamine is a derivative of indazole-3-carboxylic acid, which for a long time, has been known to inhibit aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. It seems to enhance aerobic glycolysis in normal cells, but suppress glycolysis in cancer cells. This is most likely through the inhibition of the mitochondrially bound hexokinase. Later studies in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells showed that lonidamine inhibits both respiration and glycolysis leading to a decrease in cellular ATP. Clinical trials of lonidamine in combination with other anticancer agents for a variety of cancers has begun. Lonidamine has been used in the treatment of brain tumours in combination with radiotherapy and temozolomide. Results showed that a combination of temozolomide and lonidamine at clinically achievable, low plasma concentrations, could inhibit tumour growth, and lonidamine could reduce the dose of temozolomide required for radiosensitization of brain tumours. From Wikipedia. |
| Name | lonidamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Lonidamine is an orally administered small molecule hexokinase inactivator.Target: OthersLonidamine is a derivative of indazole-3-carboxylic acid, which for a long time, has been known to inhibit aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. It seems to enhance aerobic glycolysis in normal cells, but suppress glycolysis in cancer cells. This is most likely through the inhibition of the mitochondrially bound hexokinase. Later studies in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells showed that lonidamine inhibits both respiration and glycolysis leading to a decrease in cellular ATP. Clinical trials of lonidamine in combination with other anticancer agents for a variety of cancers has begun. Lonidamine has been used in the treatment of brain tumours in combination with radiotherapy and temozolomide. Results showed that a combination of temozolomide and lonidamine at clinically achievable, low plasma concentrations, could inhibit tumour growth, and lonidamine could reduce the dose of temozolomide required for radiosensitization of brain tumours. From Wikipedia. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 537.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 207-209°C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10Cl2N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 321.158 |
| Flash Point | 279.1±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 320.011932 |
| PSA | 55.12000 |
| LogP | 4.32 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.678 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H351-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P281-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R60;R22;R40 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S22-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NK7886000 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~% 
Lonidamine CAS#:50264-69-2 |
| Literature: THRESHOLD PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. Patent: WO2005/120498 A2, 2005 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 18; 20 ; |
|
~% 
Lonidamine CAS#:50264-69-2 |
| Literature: THRESHOLD PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. Patent: WO2005/120498 A2, 2005 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 22 ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
A novel effect of DMOG on cell metabolism: direct inhibition of mitochondrial function precedes HIF target gene expression.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1847 , 1254-66, (2015) Abnormal accumulation of oncometabolite fumarate and succinate is associated with inhibition of mitochondrial function and carcinogenesis. By competing with α-ketoglutarate, oncometabolites also activ... |
|
|
Aerobic glycolysis tunes YAP/TAZ transcriptional activity.
EMBO J. 34 , 1349-70, (2015) Increased glucose metabolism and reprogramming toward aerobic glycolysis are a hallmark of cancer cells, meeting their metabolic needs for sustained cell proliferation. Metabolic reprogramming is usua... |
|
|
Male contraception: history and development.
Urol. Clin. North Am. 41(1) , 145-61, (2014) Although the twentieth century has seen great strides in the development of female contraception, not a single new agent has been introduced as an approved method for common use for male contraception... |
| 1-(2,4-Dichlorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxylic acid |
| 1H-Indazole-3-carboxylic acid, 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]- |
| DICA |
| Lonidaminum |
| Lonidamin |
| Lonidaminum [INN-Latin] |
| MFCD00866285 |
| Diclondazolic acid |
| Lonidamine |
| EINECS 256-510-0 |
| 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]indazole-3-carboxylic acid |
| 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-1H-indazole-3-carboxylic acid |
| Lonidamina |
| 1-(2,4-Dichlorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxylic acid Diclondazolic acid |
| Doridamina |
![1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]indazole-3-carbonyl chloride structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/271/874110-84-6.png) CAS#:874110-84-6
CAS#:874110-84-6