Acifluorfen
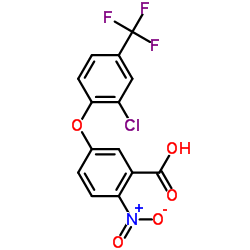
Acifluorfen structure
|
Common Name | Acifluorfen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50594-66-6 | Molecular Weight | 361.657 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 422.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H7ClF3NO5 | Melting Point | 161ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 209.2±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of AcifluorfenAcifluorfen, a protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PROTOX) inhibitor herbicide, promotes the accumulation of protoporphyrin IX (PPIX), and induces tumors in the rodent liver. Acifluorfen causes strong photooxidative destruction of pigments and lipids in sensitive plant species[1][2]. |
| Name | acifluorfen |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acifluorfen, a protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PROTOX) inhibitor herbicide, promotes the accumulation of protoporphyrin IX (PPIX), and induces tumors in the rodent liver. Acifluorfen causes strong photooxidative destruction of pigments and lipids in sensitive plant species[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | The effect of Acifluorfen on glutathione and ascorbate levels in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) cotyledon discs is investigated to assess the relationship between herbicide activity and endogenous antioxidants. Acifluorfen decreases the levels of glutathione and ascorbate over 50% in discs exposed to less than 1.5 hours of white light (450 microeinsteins per square meter per second). Acifluorfen also causes the rapid depletion of ascorbate in far-red light grown plants which are photosynthetically incompetent[2]. |
| In Vivo | Dietary treatment with 2500 ppm Acifluorfen for up to 13 weeks increases Cyp2b10 expression in the livers of wild-type mice, but not in CAR-knockout (CARKO) mice. Microscopically, Acifluorfen treatment-induces cytotoxic changes, including hepatocellular necrosis and inflammation, and causes regenerative changes accompanied by prolonged increases in the numbers of proliferating cell nuclear antigen-positive hepatocytes in WT mice[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 422.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 161ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C14H7ClF3NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 361.657 |
| Flash Point | 209.2±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 360.996490 |
| PSA | 92.35000 |
| LogP | 4.35 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.576 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H318-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R38;R41;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S24-S39-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 |
| RTECS | DG5643070 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| HS Code | 2918990027 |
|
~% 
Acifluorfen CAS#:50594-66-6 |
| Literature: Rohm and Haas Company Patent: US4031131 A1, 1977 ; |
|
~% 
Acifluorfen CAS#:50594-66-6 |
| Literature: Rohm and Haas Company Patent: US4395570 A1, 1983 ; |
|
~% 
Acifluorfen CAS#:50594-66-6 |
| Literature: Rohm and Haas Company Patent: US4031131 A1, 1977 ; |
|
~% 
Acifluorfen CAS#:50594-66-6 |
| Literature: Zeneca Limited Patent: US6342630 B1, 2002 ; Location in patent: Example 2 ; |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918990027 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990027 5-(2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)-2-nitrobenzoic acid。supervision conditions:s(import or export registration certificate for pesticides)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tarrif:6.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
[Determination of biphenyl ether herbicides in water using HPLC with cloud-point extraction].
Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban 41(1) , 148-52, (2010) To determine residues of multiple biphenyl ether herbicides simultaneously in water using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with cloud-point extraction.The residues of eight biphenyl ether... |
|
|
Increased expression of Fe-chelatase leads to increased metabolic flux into heme and confers protection against photodynamically induced oxidative stress.
Plant Mol. Biol. 86(3) , 271-87, (2014) Fe-chelatase (FeCh, EC 4.99.1.1) inserts Fe(2+) into protoporphyrin IX (Proto IX) to form heme, which influences the flux through the tetrapyrrole biosynthetic pathway as well as fundamental cellular ... |
|
|
Photochemistry and photoinduced toxicity of acifluorfen, a diphenyl-ether herbicide.
J. Environ. Qual. 31(1) , 268-74, (2002) Photochemistry studies can be helpful in assessing the environmental fate of chemicals. Photochemical reactions lead to the formation of by-products that can exhibit different toxicological properties... |
| EINECS 256-634-5 |
| 5-[2-Chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitrobenzoic acid |
| Acifluorfen ∆ |
| WNR BVQ DOR BG DXFFF |
| Acifluorofen |
| 5-(2-Chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)-2-nitrobenzoic acid |
| 5-(2-chloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-2-nitrobenzoic acid |
| 5-{[2-Chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]oxy}-2-nitrobenzoic acid |
| Benzoic acid, 5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitro- |
| 5-(2-Chloro-4-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-2-nitrobenzoic acid |
| Acifluorfen |
| MFCD00143541 |


 CAS#:100-02-7
CAS#:100-02-7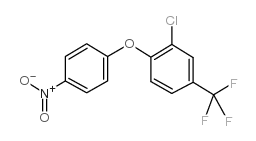 CAS#:42874-01-1
CAS#:42874-01-1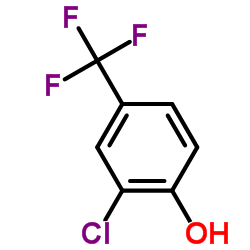 CAS#:35852-58-5
CAS#:35852-58-5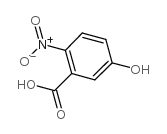 CAS#:610-37-7
CAS#:610-37-7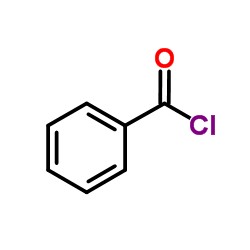 CAS#:98-88-4
CAS#:98-88-4![5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitrobenzoyl chloride structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/381/67446-83-7.png) CAS#:67446-83-7
CAS#:67446-83-7 CAS#:72178-02-0
CAS#:72178-02-0 CAS#:77501-90-7
CAS#:77501-90-7
