| Description |
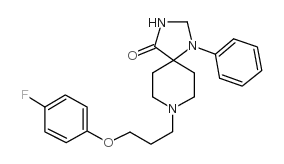
Spiramide (AMI-193) is a potent and selective antagonist of 5-HT2 and dopamine D2 receptor, with Kis of 2 nM and 3 nM, respectively. Spiramide has >2000-fold selectivity for 5-HT2 versus 5-HT1C (Ki=4300 nM) receptors. Spiramide exhibits antipsychotic activity[1][2][3].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
5-HT2 Receptor:2 nM (Ki)
D2 Receptor:3 nM (Ki)
5-HT1A Receptor:50 nM (Ki)
D1 Receptor:2530 nM (Ki)
5-HT1C Receptor:4300 nM (Ki)
|
| In Vitro |
Spiramide retains affinity for 5-HT1A sites (Ki=50 nM) and also binds at dopamine D2 sites (Ki=3 nM), but possesses low affinity for dopamine D1 sites (Ki=2530 nM)[1].
|
| In Vivo |
AMI-193 (0.003-0.01 mg/kg; i.m.) dose-dependently decreases response rate in monkeys under a fixed-interval (FI) schedule of stimulus termination[2]. AMI-193 (0.003-0.01 mg/kg; i.m.) attenuates the discriminative-stimulus effects of cocaine in drug-discrimination experiments[2]. AMI-193 (0.003-0.01 mg/kg; i.m.) reduces response rate under a second-order schedule of i.v. self-administration of cocaine (0.1 mg/infusion)[2]. Animal Model: Adult male squirrel monkeys (850-1300 g)[2] Dosage: 0.003, 0.01 mg/kg Administration: I.m. on Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday the following week Result: Decreased the response rate. The rate-decreasing effects were reversed by cocaine.
|
| References |
[1]. Ismaiel AM, et, al. Antagonism of 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminopropane stimulus with a newly identified 5-HT2- versus 5-HT1C-selective antagonist. J Med Chem. 1993 Aug 20;36(17):2519-25. [2]. Czoty PW, et, al. Behavioral effects of AMI-193, a 5-HT(2A)- and dopamine D(2)-receptor antagonist, in the squirrel monkey. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000 Oct;67(2):257-64. [3]. Kjellberg B, et, al. Partial restoration by a neuroleptic (spiramide) of items of grooming behaviour suppressed by amphetamine. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1974 Jul;210(1):61-6.
|
![1-Phenyl-1,3,8-triaza-spiro[4.5]decan-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/259/1021-25-6.png)