L-(+)-Penicillamine
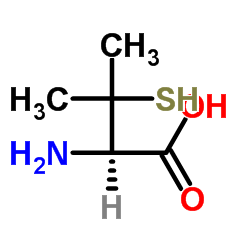
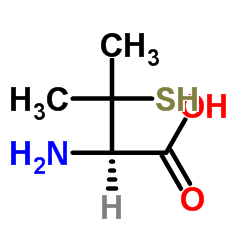
L-(+)-Penicillamine structure
|
Common Name | L-(+)-Penicillamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 52-66-4 | Molecular Weight | 149.211 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 251.8±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2S | Melting Point | 208-212ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 106.1±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of L-(+)-PenicillamineDL-Penicillamine [(±)-Penicillamine] is a copper chelating agent. DL-Penicillamine has antidotal effects in thallotoxicosis rats when co-treated with Prussian blue (HY-106594A). DL-Penicillamine can cause pyridoxine deficiency and then induce optic axial neuritis. DL-Penicillamine can also depress primary immune response[1][2][3]. |
| Name | penicillamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-Penicillamine [(±)-Penicillamine] is a copper chelating agent. DL-Penicillamine has antidotal effects in thallotoxicosis rats when co-treated with Prussian blue (HY-106594A). DL-Penicillamine can cause pyridoxine deficiency and then induce optic axial neuritis. DL-Penicillamine can also depress primary immune response[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | DL-Penicillamine (25 mg/kg; i.p.; twice daily, for 5 days) has antidotal effects in thallotoxicosis rats when co-treated with Prussian blue (HY-106594A)[2]. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats, NIH strain (intoxicated by i.p. injection of 32 mg/kg thallium (I) acetate)[2] Dosage: 25 mg/kg Administration: i.p.; twice daily, for 5 days Result: Decreased slightly the thallium content in blood, organs and brain. Increased the probability survival when co-treated with Prussian blue (50 mg/kg; p.o.). |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 251.8±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 208-212ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 149.211 |
| Flash Point | 106.1±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 149.051056 |
| PSA | 102.12000 |
| LogP | 0.93 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.528 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S26;S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YV9445000 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Nakajima, Suanne; Zhenwei, Miao; Sun, Ying; Tang, Datong; Xu, Guoyou; Porter, Brian; Or, Yat Sun; Wang, Zhe Patent: US2004/266668 A1, 2004 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 56 ; |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
|
Literature: Tatsuoka; Miyamoto Yakugaku Zasshi, 1949 , vol. 69, p. 294,297 Chem.Abstr., 1950 , p. 2513 Full Text Show Details Leach; Hunter Biochemical Preparations, 1953 , vol. 3, p. 111,114 Anm. 7 Full Text Show Details Crooks Chem.Penicillin, |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Tatsuoka; Miyamoto Yakugaku Zasshi, 1949 , vol. 69, p. 294,297 Chem.Abstr., 1950 , p. 2513 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Munro, Andrew P.; Williams, D. Lyn H. Journal of the Chemical Society. Perkin Transactions 2, 2000 , # 9 p. 1794 - 1797 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Kessler, David P.; Ghebre-Sellassie, Isaac; Knevel, Adelbert M.; Hem, Stanley L. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 2: Physical Organic Chemistry (1972-1999), 1981 , p. 1247 - 1251 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Schaefer, K.; Asmus, K.-D. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1981 , vol. 85, # 7 p. 852 - 855 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Merck and Co. Inc. Patent: US2516240 , 1946 ; |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Holmes, Anthony J.; Williams, D. Lyn H. Journal of the Chemical Society. Perkin Transactions 2, 2000 , # 8 p. 1639 - 1644 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Penicillamine CAS#:52-66-4 |
| Literature: Surdhar, Parminder S.; Mezyk, Stephen P.; Armstrong, David A. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1989 , vol. 93, # 8 p. 3360 - 3363 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Identification and Characterization of EDTA Test Strip Interfering Substances Using a Digital Color Detector.
Clin. Lab. 61 , 785-91, (2015) Rapid test strips for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) can be used to verify correct specimen types for clinical assays which require, or cannot be performed on, plasma collection tubes containi... |
|
|
Paternal breed effects on expression of IGF-II, BAK1 and BCL2-L1 in bovine preimplantation embryos.
Zygote 23 , 712-21, (2015) The effects of the paternal breed on early embryo and later pre- and postnatal development are well documented. Several recent studies have suggested that such paternal effects may be mediated by the ... |
|
|
All-trans retinoic acid prevents oxidative stress-induced loss of renal tight junction proteins in type-1 diabetic model.
J. Nutr. Biochem. 26 , 441-54, (2015) We previously reported that diabetes decreased the expression of renal tight junction (TJ) proteins claudin-5 in glomerulus, and claudin-2 and occludin in proximal tubule through an oxidative stress d... |
| 2-Amino-3-mercapto-3-methylbutanoic acid |
| 3-mercapto-L-valine |
| 3-Sulfanyl-L-valine |
| EINECS 200-147-2 |
| L-Penicillamine |
| DL-β,β-Dimethylcysteine |
| (R)-penicillamine |
| DL-β-Mercaptovaline |
| DL-Penicillamine |
| DL-Beta,Beta-Dimethylcysteine |
| DL-.β.-Mercaptovaline |
| (2R)-2-amino-3-mercapto-3-methyl-butyric acid |
| (2R)-2-amino-3-mercapto-3-methylbutanoic acid |
| MFCD00004856 |
| L-Valine, 3-mercapto- |

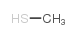


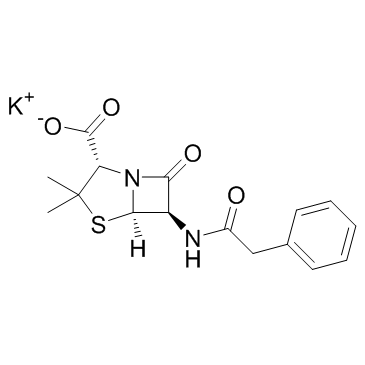
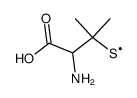

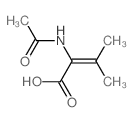

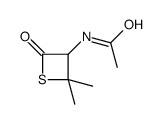 CAS#:108865-98-1
CAS#:108865-98-1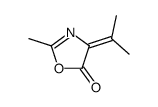 CAS#:4894-12-6
CAS#:4894-12-6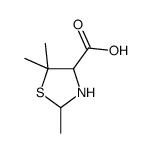 CAS#:18455-58-8
CAS#:18455-58-8 CAS#:72778-00-8
CAS#:72778-00-8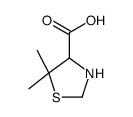 CAS#:22916-26-3
CAS#:22916-26-3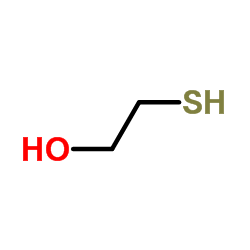 CAS#:60-24-2
CAS#:60-24-2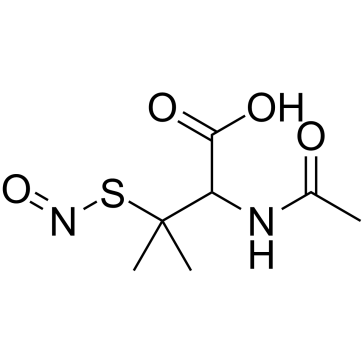 CAS#:67776-06-1
CAS#:67776-06-1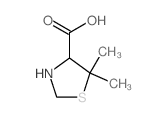 CAS#:15260-83-0
CAS#:15260-83-0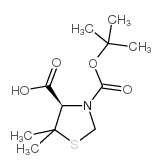 CAS#:117918-23-7
CAS#:117918-23-7