Trimetrexate
Modify Date: 2024-01-03 14:29:20
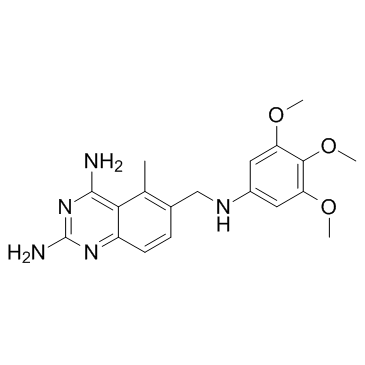
Trimetrexate structure
|
Common Name | Trimetrexate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 52128-35-5 | Molecular Weight | 369.41800 | |
| Density | 1.305g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 647ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N5O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 345.1ºC | |
Use of TrimetrexateTrimetrexate(CI-898) is a potent competitive inhibitor of bacterial, protozoan, and mammalian dihydrofolate reductase.IC50 value:Target: Antibiotic Trimetrexate therapy had minimal toxicity; transient neutropenia or thrombocytopenia occurred in 12 patients and mild elevation of serum aminotransferases in 4. We conclude that the combination of trimetrexate and leucovorin is safe and effective for the initial treatment of pneumocystis pneumonia in patients with AIDS and for the treatment of patients with intolerance or lack of response to standard therapies [1]. In noncomparative trials trimetrexate was effective in the treatment of P. carinii pneumonia (PCP) in patients with AIDS who were intolerant of or refractory to cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) and pentamidine treatment. In these patients, 2- to 4-week survival rates of 48 to 69% were reported. In a comparative trial in the initial therapy of PCP, trimetrexate was less effective than cotrimoxazole in moderate to severe disease as evidenced by a significantly higher failure rate [2]. trimetrexate plus leucovorin was effective, albeit inferior to TMP-SMZ, for moderately severe P. carinii pneumonia but was better tolerated than TMP-SMZ [3]. |
| Name | 5-methyl-6-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyanilino)methyl]quinazoline-2,4-diamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Trimetrexate(CI-898) is a potent competitive inhibitor of bacterial, protozoan, and mammalian dihydrofolate reductase.IC50 value:Target: Antibiotic Trimetrexate therapy had minimal toxicity; transient neutropenia or thrombocytopenia occurred in 12 patients and mild elevation of serum aminotransferases in 4. We conclude that the combination of trimetrexate and leucovorin is safe and effective for the initial treatment of pneumocystis pneumonia in patients with AIDS and for the treatment of patients with intolerance or lack of response to standard therapies [1]. In noncomparative trials trimetrexate was effective in the treatment of P. carinii pneumonia (PCP) in patients with AIDS who were intolerant of or refractory to cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) and pentamidine treatment. In these patients, 2- to 4-week survival rates of 48 to 69% were reported. In a comparative trial in the initial therapy of PCP, trimetrexate was less effective than cotrimoxazole in moderate to severe disease as evidenced by a significantly higher failure rate [2]. trimetrexate plus leucovorin was effective, albeit inferior to TMP-SMZ, for moderately severe P. carinii pneumonia but was better tolerated than TMP-SMZ [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.305g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 647ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N5O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 369.41800 |
| Flash Point | 345.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 369.18000 |
| PSA | 117.54000 |
| LogP | 3.97590 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|
|
~% 
Trimetrexate CAS#:52128-35-5 |
| Literature: FMC Corporation Patent: US5534518 A1, 1996 ; |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| Trimetrexato |
| Trimetrexate |
| CI-898 |
| Trimetrexatum |
| Jb-11 |