Dimethylcurcumin
Modify Date: 2024-01-03 21:53:11
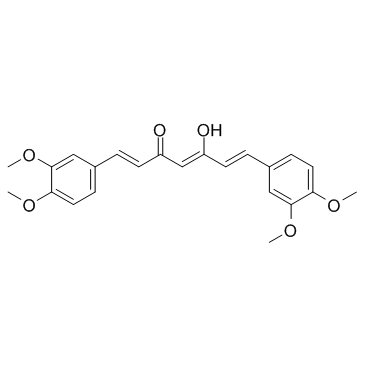
Dimethylcurcumin structure
|
Common Name | Dimethylcurcumin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 52328-98-0 | Molecular Weight | 396.433 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 588.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H24O6 | Melting Point | 129-130 °C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 201.8±23.6 °C | |
Use of DimethylcurcuminASC-J9 is an androgen receptor degradation enhancer that effectively suppresses castration resistant prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion. |
| Name | (1E,4Z,6E)-1,7-Bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-1,4,6-heptatrie n-3-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | ASC-J9 is an androgen receptor degradation enhancer that effectively suppresses castration resistant prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | ASC-J9 is able to degrade fAR and AR3 in a dose-dependent manner in various human PCa cells. ASC-J9 can also effectively suppress AR-targeted genes in CWR22Rv1-fARKD cells. ASC-J9 (5 or 10 µM) significantly suppresses the DHT-induced cell growth in all three PCa cell lines. ASC-J9 suppresses AR-targeted genes and cell growth by degradation of fAR and ectopic AR3 in C81 and C4-2 cells[1]. ASC-J9 selectively promotes AR degradation by disrupting the interaction between AR and AR coregulators. ASC-J9 reduces the AR aggregated AR-112Q in cells. ASC-J9 suppresses the aggregation of AR-112Q in SBMA PC12/AR-112Q cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | ASC-J9 (75 mg/kg, i.p.) degrades both fAR and AR3 in the xenografted tumors in vivo, and SC-J9-treated tumors has significantly decreased Ki67-positive cells[1]. ASC-J9 (50 mg/kg every 48 h, i.p.) substantially ameliorates the SBMA symptoms in AR-97Q mice, and ameliorates neuromuscular pathological findings. The ASC-J9-treated SBMA mice have relatively normal serum testosterone concentrations[2]. ASC-J9-treated mice show significantly smaller prostate tumor sizes when compared with those receiving classic ADT/castration with little serum androgen[3]. |
| Cell Assay | For the cell survival assay, the PC12/AR-112Q and PC12/AR-10Q cells are cultured as described previously and incubated cells in the presence of 10 μg/mL doxycycline for 24 h. Then the cells are treated with vehicle, 5 μM ASC-J9 or 10 μM ASC-J9, along with 1 nM DHT, and determined cell viability using Trypan blue staining at specific time intervals. |
| Animal Admin | CWR22Rv1 cells (1×106 cells per site) are injected into both anterior prostates of castrated nude mouse after 2 weeks of implantation. The mice are randomLy divided into two groups (four mice/eight tumors each group) and either receives 75 mg/kg ASC-J9 intraperitoneal injection or vehicle control every other day. After 4 weeks of treatment, all mice are killed to examine the tumor growth. Body weights and mice activity are measured weekly. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 588.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 129-130 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C23H24O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.433 |
| Flash Point | 201.8±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 396.157288 |
| PSA | 74.22000 |
| LogP | 4.05 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.608 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| ASC-J9 |
| (1E,4Z,6E)-1,7-Bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one |
| (1E,4Z,6E)-1,7-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyhepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one |
| 1,4,6-Heptatrien-3-one, 1,7-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-, (1E,4Z,6E)- |
| Dimethylcurcumin |
 CAS#:91998-04-8
CAS#:91998-04-8