| Description |
Dencichin is a non-protein amino acid originally extracted from Panax notoginseng, and can inhibit HIF-prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD-2) activity.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
PHD-2[1]
|
| In Vitro |
Dencichin (β-ODAP, 10 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM and 200 μM) increases HRE expression by 1.3±0.09, 2.5±0.07, 4.2±0.15 and 1.3±0.07 fold respectively compared to control. Dencichin has intermolecular interactions with PHD-2[1]. Dencichin (10 μM, 100 μM, 1 mM) significantly inhibits cell proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins accumulation of HBZY-1 cells, and reduces the secretion of collagen I (Col I), collagen IV (Col IV), and fibronectin (FN)[2].
|
| In Vivo |
Dencichin improves metabolism disorder in diabetic nephropathy (DN) secondary to type II diabetes mellitus (DM) model. Dencichin (80, 160 mg/kg/day, p.o.) significantly prevents the up-regulation of TCH, TG, LDL, and HbAlc and the down-regulation of HDL in DN rats induced by STZ injection. Dencichin also attenuates renal injury induced in the DN secondary to type II DM model. Dencichin alleviates pancreas damage in the STZ-induced DN model. Dencichin regulates protein expression in the TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway in STZ-induced DN models[2].
|
| Cell Assay |
Cells are cultured in 6-well plates with glucose (LG) or high glucose control (HG) and then treated with valsartan (1.0 × 10-3 M) or Dencichin (1.0 × 10-5 M, 1.0 × 10-4 M and 1.0 × 10-3 M) for 24 h before analysing the activation of FN, Col I, and Col IV expression by ELISA and analysing MMP-9 and TIMP-1 expression by immunofluorescence. Each experiment is repeated at least three times throughout the study[2].
|
| Animal Admin |
Male SD rats weighted approximately 200 ± 20 g (eight weeks old) are kept at 23 ± 2°C. The rats are randomLy allotted into two groups: normal group (n = 16) and diabetic nephropathy (DN) group (n = 60). The normal rats fed with normal diet and vehicle fall into the normal control group (NC, n = 8) and the normal rats fed with normal diet and Dencichin fall into the Dencichin control group (De C, n = 8). The rats in the diabetic group are fed the high-sugar-high-fat diet (composition: Common breeding material 54.6%, lard oil 16.9%, sucrose 14%, casein 10.2%, gunk 2.1%, maltodextrin 2.2%). Five weeks later, DN is induced by administering of 40 mg/kg STZ though intraperitoneal injection, and the normal rats are treated with vehiclecitrate buffer (0.1 M, pH 4.2). Next, the DN rats (n = 32) are assigned into four groups and oral administered with metformin hydrochloride (a positive control) at 80 mg/kg/day, (DN+Met, n = 8), which is dissolve into distilled water to make a 2 mg/mL solution before use; vehicle control for the DN control group (DN, n = 8), or Dencichin. The Dencichin group is divided into a high Dencichin group (160 mg/kg/day; DN+De H, n = 8) and a low Dencichin group (80 mg/kg/day; DN+De L, n = 8), which are dissolved into distilled water to make a 5 mg/mL and 2.5 mg/mL solution before use and oral administered at the dosage once per day. Blood glucose is measured each month. 8 w after administering with Dencichin, the rats are killed[2].
|
| References |
[1]. Eslavath RK, et al. β-N-oxalyl-L-α, β- diaminopropionic acid induces HRE expression by inhibiting HIF-prolyl hydroxylase-2 in normoxic conditions. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;791:405-411. [2]. Jie L, et al. Dencichine ameliorates kidney injury in induced type II diabetic nephropathy via the TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 5;812:196-205.
|
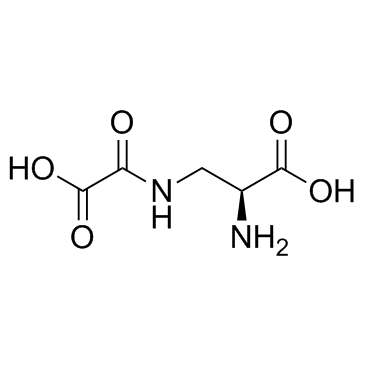
 CAS#:61277-72-3
CAS#:61277-72-3
