TOFA
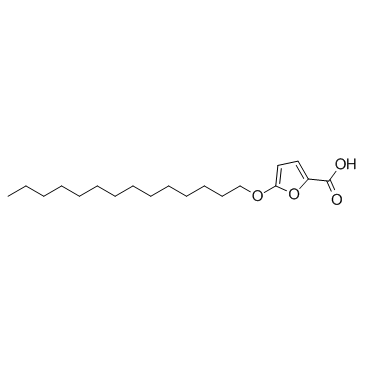
TOFA structure
|
Common Name | TOFA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 54857-86-2 | Molecular Weight | 324.455 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 441.7±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H32O4 | Melting Point | 112-115ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 220.9±23.2 °C | |
Use of TOFATOFA (RMI14514;MDL14514) is an allosteric inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase-α (ACCA ). |
| Name | 5-(tetradecyloxy)-2-furoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | TOFA (RMI14514;MDL14514) is an allosteric inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase-α (ACCA ). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | TOFA (5-tetradecyloxy-2-furoic acid) is cytotoxic to lung cancer cells NCI-H460 and colon carcinoma cells HCT-8 and HCT-15, with an IC50 at approximately 5.0, 5.0, and 4.5 μg/mL, respectively. TOFA at 1.0–20.0 μg/mL effectively blocks fatty acid synthesis and induces cell death in a dose-dependent manner[1]. TOFA is found to be cytotoxic to COC1 and COC1/DDP cells with IC50 values of ~26.1 and 11.6 µg/mL, respectively. TOFA inhibits the proliferation of the cancer cells examined in a time and dose dependent manner, arrests the cells in the G0/G1 cell cycle phase and induces apoptosis[2]. Acetyl-CoA-carboxylase-α (ACCA) is a key enzyme in the regulation of fatty acids synthesis. Inhibition of ACCA by TOFA decreases fatty acid synthesis and induces caspase activation and cell death in most PCa cell lines[3]. |
| In Vivo | TOFA inhibits COC1/DDP cell growth in ovarian tumor mouse xenografts. The tumor growth rate is signifi¬cantly inhibited by TOFA compared with the DMSO treated control mice (1649±356.3 vs. 5128±390.4 mm3. No toxicity is observed in the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney and intestinal tissues. By inhibiting ACC, TOFA may be a promising small molecule agent for ovarian cancer therapy[2]. |
| Cell Assay | NCI-H460, human lung cancer cells, and HCT-8 and HCT-15 cells (5,000/well) are seeded in 96-well plates overnight and then exposed to TOFA at indicated concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10, 20, 50 µg/mL) for 72 hours. Viable cells are detected using MTT assay[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Mice are treated with 50 μL DMSO (control group) or treated with TOFA (50 mg/kg). The drugs are injected intraperitoneally daily for two weeks. Tumor volumes are recorded every two days by measuring dimensions (length and width) with Vernier calipers. The mice are sacrificed four weeks after the final treatment. Tumor weights are measured by a scale[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 441.7±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 112-115ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H32O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 324.455 |
| Flash Point | 220.9±23.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 324.230072 |
| PSA | 59.67000 |
| LogP | 7.82 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.483 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2932190090 |
|
~% 
TOFA CAS#:54857-86-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, , vol. 70, # 10 p. 1095 - 1100 |
|
~% 
TOFA CAS#:54857-86-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, , vol. 70, # 10 p. 1095 - 1100 |
| HS Code | 2932190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932190090 other compounds containing an unfused furan ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:20.0% |
|
Pregnane X receptor activation and silencing promote steatosis of human hepatic cells by distinct lipogenic mechanisms.
Arch. Toxicol. 89 , 2089-103, (2015) In addition to its well-characterized role in the regulation of drug metabolism and transport by xenobiotics, pregnane X receptor (PXR) critically impacts on lipid homeostasis. In mice, both ligand-de... |
|
|
AMPK activation promotes lipid droplet dispersion on detyrosinated microtubules to increase mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7176, (2015) Lipid droplets (LDs) are intracellular organelles that provide fatty acids (FAs) to cellular processes including synthesis of membranes and production of metabolic energy. While known to move bidirect... |
|
|
De novo fatty acid biosynthesis contributes significantly to establishment of a bioenergetically favorable environment for vaccinia virus infection.
PLoS Pathog. 10(3) , e1004021, (2014) The poxvirus life cycle, although physically autonomous from the host nucleus, is nevertheless dependent upon cellular functions. A requirement for de novo fatty acid biosynthesis was implied by our p... |
| 5-Tetradecyloxy-2-furonic acid |
| TOFA |
| 2-Furancarboxylic acid, 5-(tetradecyloxy)- |
| 5-tetradecoxyfuran-2-carboxylic acid |
| 5-(Tetradecyloxy)-2-furoic acid |
| MFCD01726059 |
 CAS#:62443-38-3
CAS#:62443-38-3