N,N'-Diacetyl-L-cystine
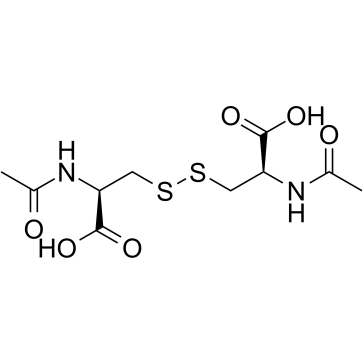
N,N'-Diacetyl-L-cystine structure
|
Common Name | N,N'-Diacetyl-L-cystine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5545-17-5 | Molecular Weight | 324.374 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 715.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N2O6S2 | Melting Point | 55-72ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 386.5±32.9 °C | |
Use of N,N'-Diacetyl-L-cystineN,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine (DiNAC) is the disulphide dimer of N-acetylcysteine with immunomodulating properties. N,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine is a potent, orally active modulator of contact sensitivity/delayed type hypersensitivity reactions in rodents. N,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine also has antiatherosclerotic effects in Watanabe-heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit (WHHL) rabbits[1][2]. |
| Name | (ac-cys-oh)2 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine (DiNAC) is the disulphide dimer of N-acetylcysteine with immunomodulating properties. N,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine is a potent, orally active modulator of contact sensitivity/delayed type hypersensitivity reactions in rodents. N,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine also has antiatherosclerotic effects in Watanabe-heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit (WHHL) rabbits[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Immunomodulator[1] |
| In Vivo | N,N'-Diacetyl-L-cystine (DiNAC; 0-973.11 μg/kg; oral administration; daily; for 12 weeks; WHHL rabbits) treatment reduces by 50% thoracic aorta atherosclerosis, without affecting plasma lipid levels[1]. Animal Model: Male heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit (WHHL) rabbits (10-22 weeks)[1] Dosage: 0 μg/kg, 9.73 μg/kg, or 973.11 μg/kg Administration: Oral administration; daily; for 12 weeks Result: Reduced by 50% thoracic aorta atherosclerosis, without affecting plasma lipid levels. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 715.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 55-72ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N2O6S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 324.374 |
| Flash Point | 386.5±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 324.044983 |
| PSA | 183.40000 |
| LogP | 0.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.583 |
| Storage condition | -15°C |
| Stability | Moisture Sensitive |
| HS Code | 29225090 |
|---|
|
~98% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Oba, Makoto; Tanaka, Kazuhito; Nishiyama, Kozaburo; Ando, Wataru Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 76, # 10 p. 4173 - 4177 |
|
~0% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Stamler, Jonathan S.; Loscalzo, Joseph Analytical Chemistry, 1992 , vol. 64, # 7 p. 779 - 785 |
|
~% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Biological Chemistry, , vol. 94, p. 244 Archives of Biochemistry, , vol. 18, p. 379 |
|
~22% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Watzig; Dette; Aigner; Wilschowitz Pharmazie, 1994 , vol. 49, # 4 p. 249 - 252 |
|
~% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Inorganic chemistry, , vol. 39, # 8 p. 1728 - 1734 |
|
~% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Biochemical Journal, , vol. 25, p. 619 Rikagaku Kenkyusho Iho, , vol. 8, p. 647,650 Chem. Zentralbl., , vol. 100, # II p. 2770 |
|
~% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Biochemical Journal, , vol. 25, p. 619 Rikagaku Kenkyusho Iho, , vol. 8, p. 647,650 Chem. Zentralbl., , vol. 100, # II p. 2770 |
|
~% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Photochemistry and Photobiology, , vol. 71, # 3 p. 273 - 280 |
|
~% 
N,N'-Diacetyl-L... CAS#:5545-17-5 |
| Literature: Canadian Journal of Chemistry, , vol. 76, # 6 p. 789 - 794 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
|
Influence of N,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine on D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide induced immunological liver failure in mice.
Yao Xue Xue Bao 39(10) , 782-6, (2004) To study the therapeutic effects of N,N'-diacetyl-L-cystine (DiNAC) on immunological liver failure.Serum ALT, AST and T cell subsets in peripheral blood of the experimental animals during the trial pe... |
|
|
Immunomodulation with DiNAC-- a new approach to the treatment of atherosclerosis?
Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 11(5) , 717-20, (2002) Not all antioxidants reduce atherosclerosis. This may be because atherosclerosis has an autoimmune, inflammatory pathogenesis. As probucol is both an antioxidant and an immunomodulatory drug, it may b... |
|
|
The new oral immunomodulating drug DiNAC induces brachial artery vasodilatation at rest and during hyperemia in hypercholesterolemic subjects, likely by a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism.
Atherosclerosis 196(1) , 275-82, (2008) To investigate if the immunomodulator drug DINAC (1) affects arterial dimensions in asymptomatic patients with hypercholesterolemia, (2) has effects on leucocyte markers of inflammation and (3) has in... |
| N,N`-Diacetyl-L-cystine |
| N,N'-Diacetyl-L-cystine |
| N,N'-diacetyl-cystine |
| N-acetyl-L-cystine |
| ACETYL-L-CYSTINE |
| DiNAC |
| L-Cystine, N,N'-diacetyl- |
| Cystine, N,N'-diacetyl-, L- |
| diacetylcysteine |
| L-Cystine,N,N'-diacetyl |
| N,N''-Diacetyl-L-cysteine |
| N-ACETYL CYSTINE |



![trans-[Pt(OH)2(c-C6H11NH2)(NH3)] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/455/1034767-14-0.png)


 CAS#:7664-41-7
CAS#:7664-41-7