| Description |
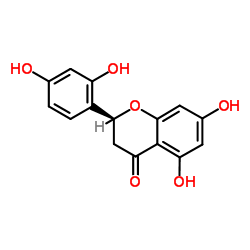
Steppogenin is a potent inhibitor of HIF-1α and DLL4, with IC50 values of 0.56 and 8.46 μM, respectively. Steppogenin can be sued for the research of angiogenic diseases, such as those involving solid tumors[1].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
IC50: 0.56 ± 0.043 μM (HIF-1α), 8.46 ± 1.08 μM (DLL4)[1]
|
| In Vitro |
Steppogenin (0-10 μM, 24 h) 以剂量依赖性方式抑制 HEK293T 细胞缺氧条件下 HIF-1α 的转录活性和血管内皮细胞 (ECs) 中 VEGF 诱导的 DLL4 表达[1]。 Steppogenin (0-3 μM,6 h) 在缺氧条件下抑制 HIF-1α 靶基因(VEGF、GLUT1、CXCR4 和 CA9)的 mRNA 表达[1]。 Steppogenin (0-3 μM,16 h) 抑制 HIF-1α 蛋白水平,并抑制 VEGF、CXCR4 和 CA9 的蛋白水平[1]。 Steppogenin (0-3 μM,24 h) 抑制缺氧诱导的血管 EC 增殖和迁移以及 VEGF 诱导的 EC 球体发芽[1]。 RT-PCR[1] Cell Line: A549 cells Concentration: 0, 0.3, 1, 3 μM Incubation Time: 6 h Result: Suppressed the mRNA expression of HIF-1α target genes (VEGF, GLUT1, CXCR4, and CA9) under hypoxic conditions. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: HEK293T, A549, ARPE19 cells Concentration: 0, 0.3, 1, 3 μM Incubation Time: 16 h Result: Significantly suppressed HIF-1α protein levels in a dose-dependent manner. reduced nuclear expression of HIF-1α under hypoxic conditions. Inhibited protein levels of VEGF, CXCR4, and CA9 compared with the levels detected in the vehicle control group. Suppresseed VEGF-induced DLL4 protein expression.
|
| In Vivo |
Steppogenin (2 mg/kg,腹腔注射,一次) 抑制肿瘤生长和血管生成[1]。 Steppogenin (2 mg/kg,腹腔注射,一次) 在肝脏和脾脏中的分布最高 (分别为 25.5 倍和 9.74 倍 AUC 比率),T1/2 显著更高[1]。 Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Steppogenin in male C57BL/6 J mice[1]. Cmax (ng/mL) Tmax (h) T1/2 (h) AUC8h (ng/mL∗h) AUC∞ (ng/mL∗h) AUC ratio Plasma 448 ± 113 0.25 0.49 ± 0.14 283 ± 98.9 284 ± 97.8 1 Tumor 635 ± 114 0.3 ± 0.1 1.87 ± 0.87 1078 ± 494 1252 ± 547 4.58 Liver 4319 ± 1063 0.25 1.72 ± 0.26 6733 ± 1300 6967 ± 1200 25.5 Lung 521 ± 181 0.25 0.36 ± 0.12 261 ± 96.1 280 ± 106 1.02 Heart 285 ± 15.2 0.25 0.2 107 ± 44.3 176.9 0.65 Kidney 1225 ± 463 0.25 0.33 ± 0.01 628 ± 234 624.7 ± 238 2.35 Spleen 6110 ± 2954 0.25 0.47 ± 0.01 2443 ± 1155 2663 ± 1289 9.74 Brain 309 ± 95.7 0.25 1.36 ± 0.46 191 ± 67 241 ± 75.4 0.88 Animal Model: C57BL/6 J mice (6-week-old, male, Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) allograft tumor model)[1] Dosage: 2 mg/kg Administration: IP, once Result: Significantly suppressed tumor growth. Animal Model: C57BL/6 J mice (6-week-old, male, Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) allograft tumor model)[1] Dosage: 2 mg/kg Administration: IP, once (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Result: Showed the highest distribution to the liver and spleen (25.5-fold and 9.74-fold AUC ratio, respectively) with significantly higher T1/2. may not be accumulated even in the highly distributed tissues after the repeated administration of steppogenin.
|
| References |
[1]. Cha S, et al. Steppogenin suppresses tumor growth and sprouting angiogenesis through inhibition of HIF-1α in tumors and DLL4 activity in the endothelium. Phytomedicine. 2023 Jan;108:154513.
|