L-γ-Glutamyl-S-nitroso-L-cysteinylglycine

L-γ-Glutamyl-S-nitroso-L-cysteinylglycine structure
|
Common Name | L-γ-Glutamyl-S-nitroso-L-cysteinylglycine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 57564-91-7 | Molecular Weight | 336.322 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N4O7S | Melting Point | >170ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of L-γ-Glutamyl-S-nitroso-L-cysteinylglycineNitrosoglutathione (GSNO), a exogenous NO donor and a substrate for rat alcohol dehydrogenase class III isoenzyme, inhibits cerebrovascular angiotensin II-dependent and -independent AT1 receptor responses[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | S-nitrosoglutathione |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), a exogenous NO donor and a substrate for rat alcohol dehydrogenase class III isoenzyme, inhibits cerebrovascular angiotensin II-dependent and -independent AT1 receptor responses[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO, 250 μM) prevents 90% of the response to 0.1 μM 5-HT and 40% of the response to 1.0 μM 5-HT in rings treated with LY-83583, indicating an effect of GSNO that was independent of guanylate cyclase activity[5]. |
| In Vivo | Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO, 8 mg/kg) significantly decreases systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures in PE-induced rats from day 14 through day 20[3]. Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO, 0.2 and 0.6 mg/kg) significantly inhibits superoxide production and suppressed NF-κB activation, iNOS induction, and 3-nitrotyrosine expression, butup-regulates endothelial NOS expression in the flap vessels[4]. Animal Model: Male Lewis rats[4]. Dosage: 0.2 and 0.6 mg/kg. Administration: Slow intravenous injection via the opposite femoral vein into each rat. Result: Animals treated with 0.2 mg of GSNO per kilogram before reperfusion had an intermediate survival rate (40.2 ± 4.9%). Although 0.6 mg/kg of GSNO showed a better rescuing effect than 150 mg/kg of NAC, there was no significant difference between the groups. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >170ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N4O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 336.322 |
| Exact Mass | 336.073975 |
| PSA | 213.55000 |
| LogP | -0.26 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.656 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MC0558000 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Down regulation of NO signaling in Trypanosoma cruzi upon parasite-extracellular matrix interaction: changes in protein modification by nitrosylation and nitration.
PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9 , e0003683, (2015) Adhesion of the Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes, the causative agent of Chagas' disease in humans, to components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) is an important step in host cell invasion. The sig... |
|
|
Lipopolysaccharides Promote S-Nitrosylation and Proteasomal Degradation of Liver Kinase B1 (LKB1) in Macrophages in Vivo.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 19011-7, (2015) LKB1 (liver kinase B1) plays important roles in tumor suppression, energy metabolism, and, recently, in innate immune responses. However, how LKB1 is regulated under physiological or pathological cond... |
|
|
S-nitrosylation triggers ABI5 degradation to promote seed germination and seedling growth.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 8669, (2015) Plant survival depends on seed germination and progression through post-germinative developmental checkpoints. These processes are controlled by the stress phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA). ABA regula... |
| L-γ-Glutamyl-S-nitroso-L-cysteinylglycine |
| glycine, N-(N-L-γ-glutamyl-S-nitroso-L-cysteinyl)- |
| Glycine, L-γ-glutamyl-S-nitroso-L-cysteinyl- |
| S-Nitroso-L-glutathione |
| S-NITROSOGLUTATHIONE |
| MFCD00214341 |
| EINECS 248-170-7 |
 CAS#:70-18-8
CAS#:70-18-8![4,7-dimethyl-1,2,5-oxadiazolo[3,4-d]pyridazine 1,5,6-trioxide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/451/116303-47-0.png) CAS#:116303-47-0
CAS#:116303-47-0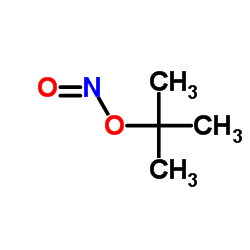 CAS#:540-80-7
CAS#:540-80-7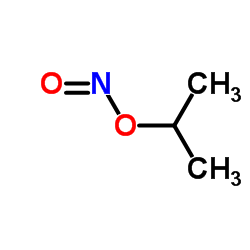 CAS#:541-42-4
CAS#:541-42-4 CAS#:109-95-5
CAS#:109-95-5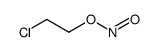 CAS#:10288-17-2
CAS#:10288-17-2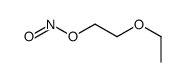 CAS#:41051-51-8
CAS#:41051-51-8 CAS#:10311-10-1
CAS#:10311-10-1 CAS#:110-46-3
CAS#:110-46-3 CAS#:59-89-2
CAS#:59-89-2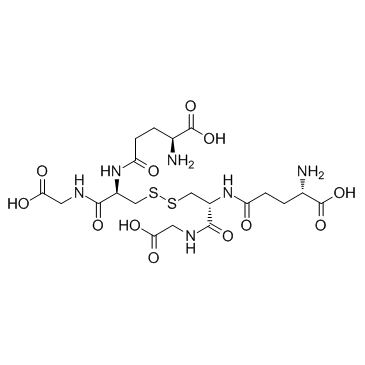 CAS#:27025-41-8
CAS#:27025-41-8 CAS#:67776-06-1
CAS#:67776-06-1 CAS#:599-71-3
CAS#:599-71-3![(2S)-2-amino-5-[[(2R)-3-(benzenesulfonylsulfanyl)-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/304/97512-84-0.png) CAS#:97512-84-0
CAS#:97512-84-0 CAS#:1116-54-7
CAS#:1116-54-7 CAS#:13081-14-6
CAS#:13081-14-6
