Olvanil

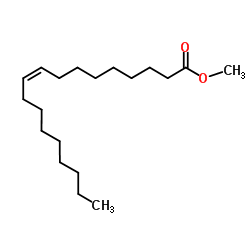
Olvanil structure
|
Common Name | Olvanil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58493-49-5 | Molecular Weight | 417.62 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 596.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H43NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 314.3±30.1 °C | |
Use of OlvanilOlvanil (NE-19550)is an agonist of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channels with an EC50 of 0.7 nM.Analgesic[1]. |
| Name | (Z)-N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]octadec-9-enamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Olvanil (NE-19550)is an agonist of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channels with an EC50 of 0.7 nM.Analgesic[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TRPV1:0.7 nM (EC50) |
| In Vitro | Olvanil affects C6 glioma cell proliferation (IC50 value of 5.5 μM)[2] |
| In Vivo | Olvanil is one capsaicin analog, which acts as an agonist at the vanilloid receptor. Olvanil may have causes an anxiogenic-like effect. Doses of 0, 0.2, 1.0 and 5.0 mg/kg Olvanil, respectively, yielded percent open arm entries at 5 min of 25±10.1, 19.3±7.1, 14.9±5.9 and 0±0[3]. Animal Model: Sprague-Dawley rats weighing approximately 200 g[3] Dosage: 0, 0.2, 1.0 and 5.0 mg/kg Administration: Injected intraperitoneally 30 min before the behavioral tests Result: The percent open arm times at 5 min were 12.9±8.1 for the 0 mg/kg dose, 8.9±4.2 for the 0.2 mg/kg dose, 15.2±7.9 for the 1 mg/kg dose and 0±0 for the 5 mg/kg dose. The mean number of entries into the closed arm at 5 min were 1.7±0.3, 3.3±0.8, 2.7±0.3 and 0.25±0.1 for doses of 0, 0.2, 1 and 5 mg/kg, respectively. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 596.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C26H43NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 417.62 |
| Flash Point | 314.3±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 417.324280 |
| PSA | 58.56000 |
| LogP | 7.69 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.509 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | RG2242130 |
|
Inhibition by capsaicin and its related vanilloids of compound action potentials in frog sciatic nerves.
Life Sci. 92(6-7) , 368-78, (2013) Although capsaicin not only activates transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) channels but also inhibits nerve conduction, the latter action has not yet been fully examined. The purpose of th... |
|
|
Identification of drug modulators targeting gene-dosage disease CMT1A.
ACS Chem. Biol. 7(7) , 1205-13, (2012) The structural integrity of myelin formed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is required for proper nerve conduction and is dependent on adequate expression of myelin genes includ... |
|
|
Activation of recombinant human TRPV1 receptors expressed in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells increases [Ca(2+)](i), initiates neurotransmitter release and promotes delayed cell death.
J. Neurochem. 102(3) , 801-11, (2007) The transient receptor potential (TRP) vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (TRPV1) is a ligand-gated, Ca(2+)-permeable ion channel in the TRP superfamily of channels. We report the establishment of the first... |
| 9-Octadecenamide, N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-, (9Z)- |
| N-vanillylamide |
| oleoyl vanillylamide |
| TCMDC-124289 |
| N-Vanillyloleamide |
| Vanillyloleamide |
| MFCD00673962 |
| (9Z)-N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)-9-octadecenamide |
| N-Vannilyloleoylamide |
| OLVANIL |
| (9Z)-N-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)octadec-9-enamide |