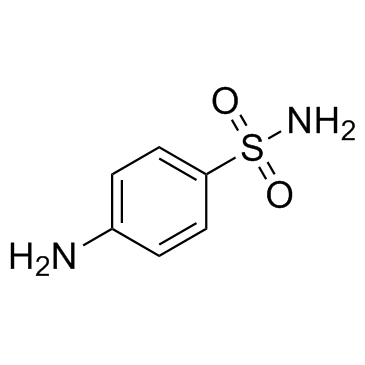
Sulfaquinoxaline
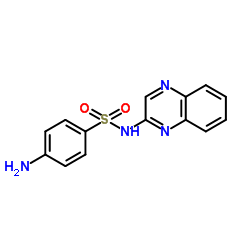
Sulfaquinoxaline structure
|
Common Name | Sulfaquinoxaline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59-40-5 | Molecular Weight | 300.336 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 557.0±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H12N4O2S | Melting Point | 247-2480C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 290.7±30.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of SulfaquinoxalineSulfaquinoxaline is an antimicrobial for veterinary use, with activity against a broad spectrum of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Sulfaquinoxaline is used to prevent coccidiosis and bacterial infections[1][2]. |
| Name | Sulfaquinoxaline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sulfaquinoxaline is an antimicrobial for veterinary use, with activity against a broad spectrum of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Sulfaquinoxaline is used to prevent coccidiosis and bacterial infections[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Bacterial, Parasite[1][2] |
| In Vivo | Sulfaquinoxaline shows the presence of all antimicrobial residues at concentration higher than the drugs' maximum residue limit (MRL) of 100 μg/kg until two days after discontinuation of the medication[2]. |
| Animal Admin | For the depletion studies, 240 1-day-old Cobb chicks are used. The chickens are housed in pens that contains 30 birds each (10 birds/m2) and are provided ad libitum access to water and non-medicated feed. The chickens are randomly allocated into four experimental groups, labeled from A to D, containing 80 birds each. Chickens in group A form the untreated control group, whereas those in groups B, C and D are treated with 10 mg/kg bw of enrofloxacin, Sulfaquinoxaline or oxytetracycline, respectively, which is administered via drinking water from the 32nd to 34th day of breeding[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 557.0±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 247-2480C |
| Molecular Formula | C14H12N4O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 300.336 |
| Flash Point | 290.7±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 300.068085 |
| PSA | 106.35000 |
| LogP | 1.58 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.718 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | WP2100000 |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|
~88% 
Sulfaquinoxaline CAS#:59-40-5 |
| Literature: Li, Jian; Chen, Jing; Gui, Chunshan; Zhang, Li; Qin, Yu; Xu, Qiang; Zhang, Jian; Liu, Hong; Shen, Xu; Jiang, Hualiang Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2006 , vol. 14, # 7 p. 2209 - 2224 |
|
~% 
Sulfaquinoxaline CAS#:59-40-5 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 14, # 7 p. 2209 - 2224 |
|
~% 
Sulfaquinoxaline CAS#:59-40-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 66, p. 1957 |
|
~% 
Sulfaquinoxaline CAS#:59-40-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 66, p. 1957 |
|
~% 
Sulfaquinoxaline CAS#:59-40-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 66, p. 1957 |
|
~% 
Sulfaquinoxaline CAS#:59-40-5 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, , p. 2129,2132 US2675379 , ; |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009090 other sulphonamides VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:35.0% |
|
Fast determination of 22 sulfonamides from chicken breast muscle using core-shell nanoring amino-functionalized superparamagnetic molecularly imprinted polymer followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1345 , 17-28, (2014) A novel, simple and sensitive method was developed for the simultaneous determination of 22 sulfonamides (SAs) in chicken breast muscle by using the dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction (d-μ-SPE) p... |
|
|
Evaluation of stationary phases packed with superficially porous particles for the analysis of pharmaceutical compounds using supercritical fluid chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1360 , 275-87, (2014) Superficially porous particles (SPP), or core shell particles, which consist of a non-porous silica core surrounded by a thin shell of porous silica, have gained popularity as a solid support for chro... |
|
|
Multi-residue Determination of Polar Veterinary Drugs in Livestock and Fishery Products by Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry.
J. AOAC Int. 98(1) , 230-47, (2015) Residues of 37 polar veterinary drugs belonging to six families (quinolones, tetracyclines, macrolides, lincosamides, sulfonamides, and others) in livestock and fishery products were determined using ... |
| sulfaquinoxaline |
| Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-2-quinoxalinyl- |
| Kokozigal |
| 4-Amino-N-[(2E)-2(1H)-quinoxalinylidene]benzenesulfonamide |
| sulquin |
| N1-2-quinoxalylsulfanilamide |
| MFCD00055406 |
| anti-k |
| EINECS 213-526-2 |
| N1-(2-Quinoxalyl)sulfanilamide |
| sulfacox |
| sulphaquinoxaline |
| italquina |
| 4-Amino-N-(2-quinoxalinyl)benzenesulfonamide |
| Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-[(2E)-2(1H)-quinoxalinylidene]- |
| sulfaline |
| 4-Amino-N-(quinoxalin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide |
| Compound 3-120 |
| avicocid |
| SUQUIN |
![Acetamide,N-[4-[(2-quinoxalinylamino)sulfonyl]phenyl]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/369/6632-67-3.png)


 CAS#:681235-15-4
CAS#:681235-15-4
