Nicotinic acid
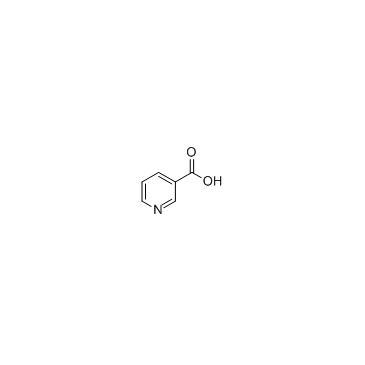
Nicotinic acid structure
|
Common Name | Nicotinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59-67-6 | Molecular Weight | 123.11 | |
| Density | 1.473 | Boiling Point | 292.5±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H5NO2 | Melting Point | 234-238 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 130.7±19.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Nicotinic acidNiacin (Vitamin B3) is a water-soluble vitamin and is part of the vitamin B group.Target: OthersNiacin (also known as vitamin B3 and nicotinic acid) is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NO2 and, depending on the definition used, one of the 20 to 80 essential human nutrients. Not enough niacin in the diet can cause nausea, skin and mouth lesions, anemia, headaches, and tiredness. Chronic Niacin deficiency leads to a disease called pellagra. The lack of niacin may also be observed in pandemic deficiency disease which is caused by a lack of five crucial vitamins: niacin,vitamin C, thiamin, vitamin D and vitamin A, and is usually found in areas of widespread poverty and malnutrition.Niacin has been used for over 50 years to increase levels of HDL in the blood and has been found to decrease the risk of cardiovascular events modestly in a number of controlled human trials. Niacin cannot be directly converted to nicotinamide, but both compounds could be converted to and are precursors of NAD and NADP in vivo.Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and tryptophan (via quinoline acid) are co-factors for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). NAD converts to NADP by phosphorylation in the presence of the enzyme NAD+ kinase. NADP and NAD are coenzyme for many dehydrogenases, participating in many hydrogen transfer processes. NAD is important in catabolism of fat, carbohydrate, protein, and alcohol, as well as cell signaling and DNA repair, and NADP mostly in anabolism reactions such as fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis.High energy requirements (brain) or high turnover rate (gut, skin) organs are usually the most susceptible to their deficiency. |
| Name | Nicotinic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Niacin (Vitamin B3) is a water-soluble vitamin and is part of the vitamin B group.Target: OthersNiacin (also known as vitamin B3 and nicotinic acid) is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NO2 and, depending on the definition used, one of the 20 to 80 essential human nutrients. Not enough niacin in the diet can cause nausea, skin and mouth lesions, anemia, headaches, and tiredness. Chronic Niacin deficiency leads to a disease called pellagra. The lack of niacin may also be observed in pandemic deficiency disease which is caused by a lack of five crucial vitamins: niacin,vitamin C, thiamin, vitamin D and vitamin A, and is usually found in areas of widespread poverty and malnutrition.Niacin has been used for over 50 years to increase levels of HDL in the blood and has been found to decrease the risk of cardiovascular events modestly in a number of controlled human trials. Niacin cannot be directly converted to nicotinamide, but both compounds could be converted to and are precursors of NAD and NADP in vivo.Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and tryptophan (via quinoline acid) are co-factors for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). NAD converts to NADP by phosphorylation in the presence of the enzyme NAD+ kinase. NADP and NAD are coenzyme for many dehydrogenases, participating in many hydrogen transfer processes. NAD is important in catabolism of fat, carbohydrate, protein, and alcohol, as well as cell signaling and DNA repair, and NADP mostly in anabolism reactions such as fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis.High energy requirements (brain) or high turnover rate (gut, skin) organs are usually the most susceptible to their deficiency. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.473 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 292.5±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 234-238 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H5NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 123.11 |
| Flash Point | 130.7±19.8 °C |
| PSA | 55.98000 |
| LogP | 0.15 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.571 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May be light sensitive. |
| Water Solubility | 1-5 g/100 mL at 17 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | 2810.0 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | QS3675000 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 29362990 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 causes ADAM10-dependent ectodomain shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Mol. Pharmacol. 87(3) , 533-42, (2015) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25D3) has a potential antiatherosclerotic effect through anti-inflammatory actions. We investigated how 1,25D3 regulates tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced lectin-like... |
|
|
Evidence for fatty acids mediating CL 316,243-induced reductions in blood glucose in mice.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 307(7) , E563-70, (2014) CL 316,243, a β3-adrenergic agonist, was developed as an antiobesity and diabetes drug and causes rapid decreases in blood glucose levels in mice. The mechanisms mediating this effect have not been fu... |
|
|
Protein enrichment of an Opuntia ficus-indica cladode hydrolysate by cultivation of Candida utilis and Kluyveromyces marxianus.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(5) , 1094-102, (2015) The cladodes of Opuntia ficus-indica (prickly pear cactus) have a low protein content; for use as a balanced feed, supplementation with other protein sources is therefore desirable. We investigated pr... |
| 3-Pyridinecarboxylic acid |
| Vitamin B3 |
| 5-22-02-00057 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) |
| 3-Pyridylcarboxylic acid |
| MFCD00006391 |
| P. P. Factor |
| Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid |
| Pyridine-β-carboxylic acid |
| P.P. factor-pellagra preventive factor |
| T6NJ CVQ |
| Nicotinamide |
| EINECS 200-441-0 |
| antipellagra vitamin |
| nicotinic acid |
| Niacin |
 CAS#:100-55-0
CAS#:100-55-0 CAS#:108-99-6
CAS#:108-99-6 CAS#:2398-81-4
CAS#:2398-81-4 CAS#:500-22-1
CAS#:500-22-1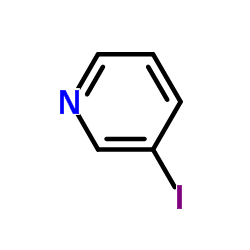 CAS#:1120-90-7
CAS#:1120-90-7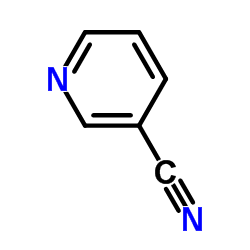 CAS#:100-54-9
CAS#:100-54-9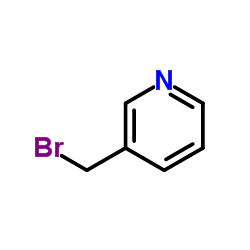 CAS#:69966-55-8
CAS#:69966-55-8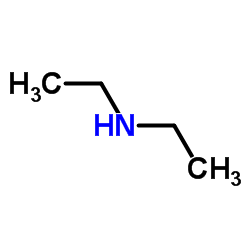 CAS#:109-89-7
CAS#:109-89-7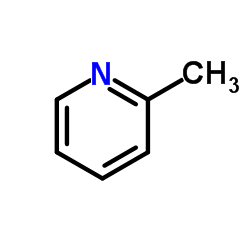 CAS#:109-06-8
CAS#:109-06-8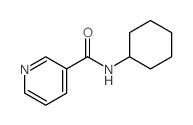 CAS#:10354-56-0
CAS#:10354-56-0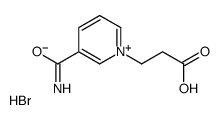 CAS#:109822-09-5
CAS#:109822-09-5 CAS#:5006-66-6
CAS#:5006-66-6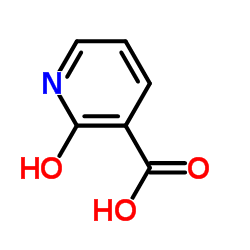 CAS#:609-71-2
CAS#:609-71-2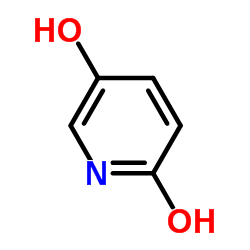 CAS#:5154-01-8
CAS#:5154-01-8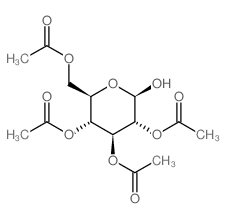 CAS#:3947-62-4
CAS#:3947-62-4 CAS#:10030-92-9
CAS#:10030-92-9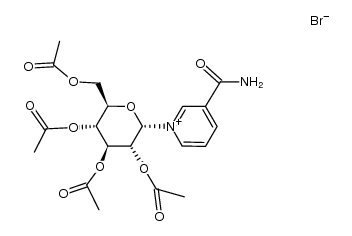 CAS#:60764-06-9
CAS#:60764-06-9![[3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-(5-carbamoylpyridin-1-yl)oxan-2-yl]methyl acetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/099/7151-92-0.png) CAS#:7151-92-0
CAS#:7151-92-0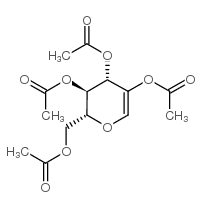 CAS#:3366-47-0
CAS#:3366-47-0
