Betaine Hydrochloride
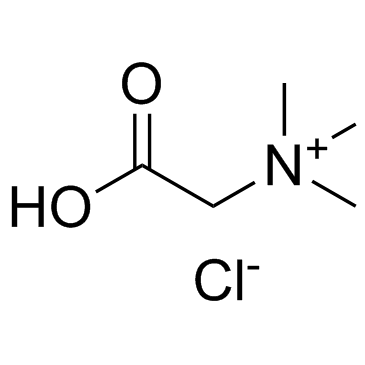
Betaine Hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Betaine Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 590-46-5 | Molecular Weight | 153.607 | |
| Density | 1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H12ClNO2 | Melting Point | 241-242 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Betaine HydrochlorideBetaine hydrochloride is a natural compound found in many foods and also an active methyl-donor which can maintain normal DNA methylation patterns. |
| Name | Betaine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Betaine hydrochloride is a natural compound found in many foods and also an active methyl-donor which can maintain normal DNA methylation patterns. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | It is found that proliferation of HeLa cells is inhibited significantly upon exposure to increasing Betaine hydrochloride levels with the MTT test (p<0.05). The percentage of S phase cells in the low dose groups (<5 mg/mL) are distinctly higher than in high dose groups, and the rates of Sub-G1 phase are the opposite (p<0.05). A high concentration of Betaine hydrochloride (>5.0 mg/mL) significantly promotes the apoptosis of HeLa cells (p<0.01). SOD activities of the low dose groups are slightly higher than the control group (p<0.05), and there are obvious synchronicity and correlation among the expression of promoting apoptosis genes Bax, P53, Caspase 3 and apoptosis suppression gene Bcl-2. In response to an apoptosis-inducing stimulus, p53 and cyclin D1 can be activated with blockage of the cell cycle at G1/S or S/G2 checkpoints[1]. |
| In Vivo | Liver-to-body weight ratio is attenuated by Betaine hydrochloride supplementation. When Betaine hydrochloride is added to the alcohol-containing liquid diet, both hepatic triglyceride (TG) accumulation and liver injury are significantly reduced. Betaine hydrochloride supplementation attenuates epididymal fat pad mass loss induced by chronic alcohol feeding. Betaine hydrochloride supplementation prevents the depletion of S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAM) and reduces the increase in S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), thereby improving the methylation state of the adipose tissue[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Cytotoxic effects of Betaine hydrochloride are evaluated by MTT assays. Briefly, 5×103 HeLa or MCF-10A cells/well are seeded in a 96-well plate and cultured overnight. Then, different concentrations of Betaine hydrochloride (from 0 to 100 mg/mL) are added to each well, and the MTT assay is performed at 24, 48, 72 and 96 h after incubation. Cu/Zn-SOD activities are detected using the superoxide dismutase Assay Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Male C57BL/6 mice weighing 25±0.5 g are used in this study. Animals are randomly assigned to four groups (n=6 to 8 per group) and pair-fed a modified Lieber-DeCarli alcohol (AF) or isocaloric maltose dextrin control liquid diet (PF) for 5 weeks with a stepwise feeding procedure. The ethanol content starts at 30% of total calories and gradually increases up to 36% in the last week. Betaine hydrochloride is administered as a supplement in the liquid diets (both PF and AF) at a concentration of 0.5% (w/v), simultaneously with the alcohol. All animals have access to diet and water ad libitum. At the end of the experiment, the mice are killed after being deprived of food for 4 h, and the plasma, liver and epididymal fat pad samples are harvested for assays[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 241-242 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H12ClNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 153.607 |
| Exact Mass | 153.055649 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| Water Solubility | 64.7 g/100 mL (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi, Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S39-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BP3136000 |
| HS Code | 2923900090 |
|
~% 
Betaine Hydroch... CAS#:590-46-5 |
| Literature: US2006/9656 A1, ; Page/Page column 2-3 ; |
|
~95% 
Betaine Hydroch... CAS#:590-46-5 |
| Literature: Yamanaka, Hiroki; Yamashita, Seiji; Fukunishi, Koushi; Kuwabara, Masaki; Ishihara, Takashi; Nomura, Mototeru Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 1991 , vol. 52, # 2 p. 185 - 194 |
|
~% 
Betaine Hydroch... CAS#:590-46-5 |
| Literature: DE269751 ; Fortschr. Teerfarbenfabr. Verw. Industriezweige, vol. 11, p. 119 |
|
~19% 
Betaine Hydroch... CAS#:590-46-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, , vol. 52, # 2 p. 185 - 194 |
|
~% 
Betaine Hydroch... CAS#:590-46-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, , vol. 52, # 2 p. 185 - 194 |
|
~% 
Betaine Hydroch... CAS#:590-46-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, , vol. 52, # 2 p. 185 - 194 |
|
~% 
Betaine Hydroch... CAS#:590-46-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, , vol. 52, # 2 p. 185 - 194 |
| HS Code | 2923900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2923900090 other quaternary ammonium salts and hydroxides。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Sulfur amino acid metabolism in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 96 , 256-66, (2015) The present study was aimed to investigate the metabolomics of sulfur amino acids in Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats, an obese type 2 diabetic animal model. Plasma levels of total cysteine, homocyste... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
| (Trimethylammonio)acetate hydrochloride |
| EINECS 209-683-1 |
| Acinorm |
| lycine hydrochloride |
| ACIDOL |
| Betaine Hydrochloride |
| Achylin |
| Betaine, hydrochloride |
| Pluchine |
| BET HCL |
| 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethylmethanaminium chloride |
| Acidin |
| Methanaminium, 1-carboxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-, chloride (1:1) |
| Euacid |
| MFCD00011903 |
| Achyin |
| Carboxy-N,N,N-trimethylmethanaminium chloride |
| betainium chloride |
| Acidine |
| Muriat |
| carboxymethyl-trimethyl-ammonium chloride |
| (Trimethylammonio)acetathydrochlorid |
| betaine chloride |
| betain hydrochloride |
| Betaine (hydrochloride) |



 CAS#:53684-57-4
CAS#:53684-57-4 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9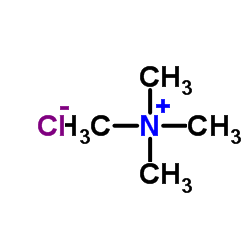 CAS#:75-57-0
CAS#:75-57-0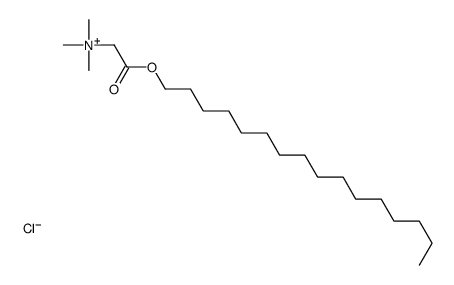 CAS#:52132-48-6
CAS#:52132-48-6
