2,3-dihydroxypropanoic acid
Modify Date: 2024-01-11 16:54:27
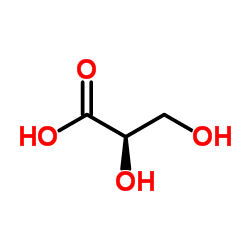
2,3-dihydroxypropanoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 2,3-dihydroxypropanoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6000-40-4 | Molecular Weight | 106.077 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 412.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 217.1±21.1 °C | |
Use of 2,3-dihydroxypropanoic acidD-Glyceric acid is an endogenous metabolite present in Urine that can be used for the research of Primary hyperoxaluria Type I and Glutaric Acidemia Type 2[1][2][3]. |
| Name | D-(+)-Glyceric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-Glyceric acid is an endogenous metabolite present in Urine that can be used for the research of Primary hyperoxaluria Type I and Glutaric Acidemia Type 2[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Endogenous metabolites is defined as those that are annotated by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes as substrates or products of the ~1900 metabolic enzymes encoded in our genome. It is clear in the body of literature that there are documented toxic properties for many of these metabolites[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 412.0±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 106.077 |
| Flash Point | 217.1±21.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 106.026611 |
| LogP | -1.92 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.515 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Propanoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxy-, (2R)- |
| EINECS 207-472-9 |
| D-(+)-Glyceric acid |
| (2R)-2,3-Dihydroxypropanoic acid |
| (R)-GLYCERIC ACID |
| 19D9ZZX4MH |
| Glyceric acid |
| R-glyceric acid |
| D-glyceric acid |