Linalool oxide
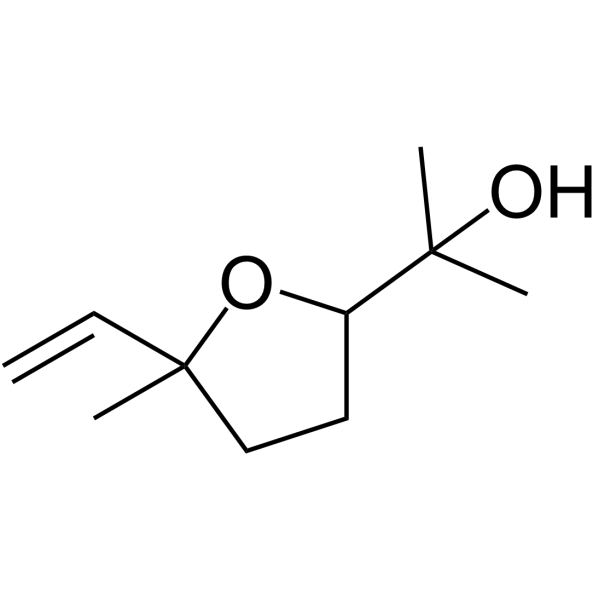
Linalool oxide structure
|
Common Name | Linalool oxide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 60047-17-8 | Molecular Weight | 170.24900 | |
| Density | 0.945 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 188°C | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 63°C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Linalool oxideLinalool oxide is a secondary metabolite in elongating wheat plants with antinociceptive and anticonvulsant effects. Linalool oxide shows anxiolytic activity[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 2-(2-Hydroxy-2-Propyl)-5-Methyl-5-Vinyltetrahydrofuran |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Linalool oxide is a secondary metabolite in elongating wheat plants with antinociceptive and anticonvulsant effects. Linalool oxide shows anxiolytic activity[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.945 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 188°C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 170.24900 |
| Flash Point | 63°C |
| Exact Mass | 170.13100 |
| PSA | 32.76000 |
| LogP | 1.88100 |
| Index of Refraction | n20/D 1.452 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H314 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | C |
| Risk Phrases | 22-34 |
| Safety Phrases | S23-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 1760 8 / PGIII |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | OI7782000 |
| HS Code | 2932190090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 2932190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932190090 other compounds containing an unfused furan ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:20.0% |
|
Red:far-red light conditions affect the emission of volatile organic compounds from barley (Hordeum vulgare), leading to altered biomass allocation in neighbouring plants.
Ann. Bot. 115 , 961-70, (2015) Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) play various roles in plant-plant interactions, and constitutively produced VOCs might act as a cue to sense neighbouring plants. Previous studies have shown that VOC... |
|
|
Linalool oxide: generalist plant based lure for mosquito disease vectors.
Parasit. Vectors 8 , 581, (2015) Lack of effective vaccines and therapeutics for important arboviral diseases such as Rift Valley fever (RVF) and dengue, necessitates continuous monitoring of vector populations for infections in them... |
|
|
Behavioural response of female Culex pipiens pallens to common host plant volatiles and synthetic blends.
Parasit. Vectors 8 , 598, (2015) Most mosquito species need to obtain sugar from host plants. Little is known about the chemical cues that Culex pipiens pallens use during their orientation to nectar host plants. In this study, we in... |
| EINECS 262-038-6 |
| Linalool oxide |
| MFCD00053543 |
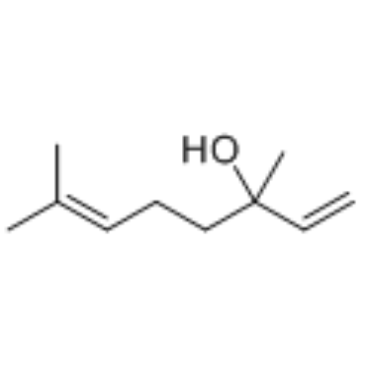 CAS#:78-70-6
CAS#:78-70-6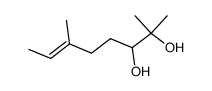 CAS#:78631-57-9
CAS#:78631-57-9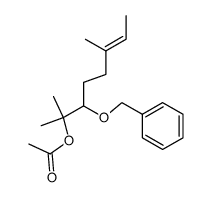 CAS#:78631-58-0
CAS#:78631-58-0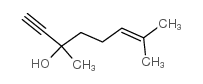 CAS#:29171-20-8
CAS#:29171-20-8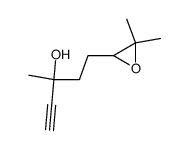 CAS#:74026-67-8
CAS#:74026-67-8 CAS#:111-66-0
CAS#:111-66-0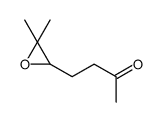 CAS#:16262-93-4
CAS#:16262-93-4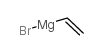 CAS#:1826-67-1
CAS#:1826-67-1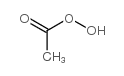 CAS#:79-21-0
CAS#:79-21-0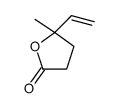 CAS#:1073-11-6
CAS#:1073-11-6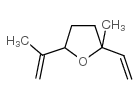 CAS#:13679-86-2
CAS#:13679-86-2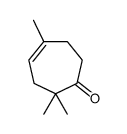 CAS#:19822-67-4
CAS#:19822-67-4
