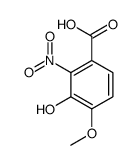
Cinnabarinic acid
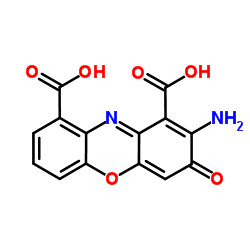
Cinnabarinic acid structure
|
Common Name | Cinnabarinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 606-59-7 | Molecular Weight | 300.223 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 536.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8N2O6 | Melting Point | >300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 278.4±30.1 °C | |
Use of Cinnabarinic acidCinnabarinic acid is a specific orthosteric agonist of mGlu4 by interacting with residues of the glutamate binding pocket of mGlu4, has no activity at other mGlu receptors. Cinnabarinic acid is an endogenous metabolite of the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan. Cinnabarinic acid induces cell apoptosis[1]. |
| Name | Cinnabarinic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cinnabarinic acid is a specific orthosteric agonist of mGlu4 by interacting with residues of the glutamate binding pocket of mGlu4, has no activity at other mGlu receptors. Cinnabarinic acid is an endogenous metabolite of the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan. Cinnabarinic acid induces cell apoptosis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
mGluR4 |
| In Vitro | Cinnabarinic acid (0-100 μM) does not activate mGlu1, mGlu2, mGlu5, mGlu6, mGlu7, and mGlu8 receptors as shown by measurements of [3H]InsP formation. In contrast, cinnabarinic acid acts as a partial agonist of mGlu4 receptors by increasing [3H]InsP formation by approximately 35% at 100 μM, which is 5-fold less efficacious than ACPT-I in activating mGlu4 receptors in HEK293 cells transiently transfected with rat mGlu1, -2, -4, -5, -6, -7, or -8 receptors[1]. Cinnabarinic acid (0-100 μM) reduces cAMP formation in a concentration-dependent manner with an excellent potency and efficacy. At 30 μM, cinnabarinic acid is effective at 30 μM, and substantially inhibits cAMP formation in cultured cerebellar granule cells[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 536.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8N2O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 300.223 |
| Flash Point | 278.4±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 300.038239 |
| PSA | 143.72000 |
| LogP | -0.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.780 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7 |
| Literature: Korshunova, Z. I.; Popova, E. B.; Glibin, E. N.; Ginzburg, O. F. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1991 , vol. 27, # 2.2 p. 314 - 319 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1991 , vol. 27, # 2 p. 369 - 376 |
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7 |
| Literature: Korshunova, Z. I.; Popova, E. B.; Glibin, E. N.; Ginzburg, O. F. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1991 , vol. 27, # 2.2 p. 314 - 319 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1991 , vol. 27, # 2 p. 369 - 376 |
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7 |
| Literature: Manthey, Michael K.; Pyne, Stephen G.; Truscott, Roger J. W. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1988 , vol. 53, # 7 p. 1486 - 1488 |
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7
Detail
|
| Literature: Korshunova, Z. I.; Popova, E. B.; Glibin, E. N.; Ginzburg, O. F. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1991 , vol. 27, # 2.2 p. 314 - 319 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1991 , vol. 27, # 2 p. 369 - 376 |
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7
Detail
|
| Literature: Korshunova, Z. I.; Popova, E. B.; Glibin, E. N.; Ginzburg, O. F. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1991 , vol. 27, # 2.2 p. 314 - 319 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1991 , vol. 27, # 2 p. 369 - 376 |
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7 |
| Literature: Butenandt et al. Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1957 , vol. 602, p. 72,79 |
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7
Detail
|
| Literature: Hick, Larry A.; Manthey, Michael K.; Truscott, Roger J. W. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 1991 , vol. 28, # 4 p. 1157 - 1160 |
|
~38% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7 |
| Literature: Pasceri, Raffaele; Siegel, David; Ross, David; Moody, Christopher J. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2013 , vol. 56, # 8 p. 3310 - 3317 |
|
~% 
Cinnabarinic acid CAS#:606-59-7
Detail
|
| Literature: Korshunova, Z. I.; Popova, E. B.; Glibin, E. N.; Ginzburg, O. F. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1991 , vol. 27, # 2.2 p. 314 - 319 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1991 , vol. 27, # 2 p. 369 - 376 |
|
Aminophenoxazinones as inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Synthesis of exfoliazone and chandrananimycin A.
J. Med. Chem. 56(8) , 3310-7, (2013) A range of 2-aminophenoxazin-3-ones has been prepared by oxidative cyclocondensation of 2-aminophenols, including the natural products exfoliazone and chandrananimycin A, both synthesized for the firs... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of 3-hydroxyanthranilic and cinnabarinic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography with photometric or electrochemical detection.
Anal. Biochem. 200(2) , 273-9, (1992) A convenient and rapid method for the simultaneous determination by HPLC of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid and the dimer derived by its oxidation, cinnabarinic acid, is described. Buffers or biological sam... |
|
|
Oxidation of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid to the phenoxazinone cinnabarinic acid by peroxyl radicals and by compound I of peroxidases or catalase.
Biochemistry 31(34) , 8090-7, (1992) Since 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (3HAA), an oxidation product of tryptophan metabolism, is a powerful radical scavenger [Christen, S., Peterhans, E., & Stocker, R. (1990) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. ... |
| 2-amino-3-oxophenoxazine-1,9-dicarboxylic acid |
| 2-Amino-3-oxo-3H-phenoxazine-1,9-dicarboxylic acid |
| 3H-Phenoxazine-1,9-dicarboxylic acid, 2-amino-3-oxo- |


![6-amino-3-[(2-carboxy-6-hydroxyphenyl)amino]-2,5-dioxo-1,3-cyclohexadiene-1-carboxylic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/010/112817-49-9.png)