Conduritol B Epoxide (Conduritol Epoxide)
Modify Date: 2024-01-06 17:33:48
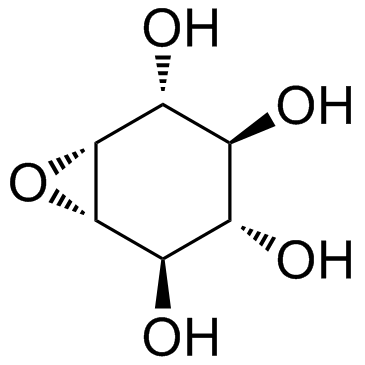
Conduritol B Epoxide (Conduritol Epoxide) structure
|
Common Name | Conduritol B Epoxide (Conduritol Epoxide) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6090-95-5 | Molecular Weight | 162.141 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 360.5±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O5 | Melting Point | 157-159ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 171.8±27.9 °C | |
Use of Conduritol B Epoxide (Conduritol Epoxide)Conduritol B epoxide is an irreversible covalently bound acid β-glucosidase (GCase) inhibitor, with IC50s of 1 and 100 μM for β-glucosidase and α-glucosidase respectively. |
| Name | Conduritol B Epoxide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Conduritol B epoxide is an irreversible covalently bound acid β-glucosidase (GCase) inhibitor, with IC50s of 1 and 100 μM for β-glucosidase and α-glucosidase respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 1 μM (β-glucosidase), 100 μM (α-glucosidase) |
| In Vitro | Treating N2a and Conduritol B epoxide-N2a cells with G6 gave GC reductions to 7% and 26% of untreated levels, respectively. G6 treated Conduritol B epoxide-N2a also has significantly decreased GS. Co-treatment of G6 and dantrolene of Conduritol B epoxide-N2a cells lead to a similar degree of GC and GS reduction as G6 alone, indicating a specific effect of G6 on inhibition of substrate accumulation, Conduritol B epoxide-N2a cells have higher calcium levels than in N2a cells without caffeine at baseline. Conduritol B epoxide-N2a cells show a significant increase in cytosolic calcium levels compared to N2a cells. Conduritol B epoxide-N2a cells show a significant reduction in OCR as evidenced by approximately 50% in all the parameters, including rate of ATP production, basal respiration, and maximal respiration, compared to N2a cells, indicating reduced mitochondrial function in this nGD cell model. In dantrolene-treated Conduritol B epoxide-N2a cells, levels of Ryr3 are increased to 76% of WT level[1]. |
| In Vivo | Conduritol B epoxide treatment of 4L, 9H, 9V and WT mice (100 mg/kg/day, i.p.) from postnatal day 5 to 11 does not induce α-synuclein aggregates. Long-term daily Conduritol B epoxide treatment of 4L mice (100 mg/kg/day of Conduritol B epoxide from postnatal day 15 for 24 or 36 doses) leads to hind limb paralysis and small amounts of α-synuclein accumulation in the olfactory bulb, brainstem, and PVP near D3V (dorsal 3rd ventricle)[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Cells are homogenized in 1% sodium taurocholate/1% Triton X-100. GCase activity is determined fluorometrically using 4MU-Glucose as the substrate in 0.25% sodium taurocholate, 0.25% Triton X-100 and 0.1M citric-phosphate buffer (pH 5.6). Brain tissues are homogenized in 1X PBS and incubated in 5 µM brain phosphatidylserine and 0.1M citric-phosphate buffer (pH 5.6) for GCase activity assay using 4MU-Glucose as substrate. Protein concentrations are determined by BCA assay using BSA as standard. |
| Animal Admin | Gba1 point mutated 4L, 9H and 9V mice or WT mice are intraperitoneally injected with 100 mg/kg/day of Conduritol B epoxide. In short-term experiments, daily injections are initiated at postnatal day 5 and continued for 6 daily doses. The mice are sacrificed on day 12 or 2 months after last injection. In long-term experiments, 4L mice are injected daily beginning at postnatal day 15 for 24 or 36 daily doses and sacrificed the day after last injection. Mice are perfused with PBS and organs are harvested for enzyme activity, lipid and histological analyses. |
| References |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 360.5±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 157-159ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 162.141 |
| Flash Point | 171.8±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 162.052826 |
| PSA | 93.45000 |
| LogP | -0.49 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.732 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Conduritol B epoxide |
| UNII:NHM754Q310 |
| 7-Oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptane-2,3,4,5-tetrol, (1R,2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)- |
| (1R,2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-7-Oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptane-2,3,4,5-tetrol |
| CBE |
![(+)-(1S,2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-2,3,4,5-tetrakisbenzyloxy-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptane Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/252/110550-28-2.png) CAS#:110550-28-2
CAS#:110550-28-2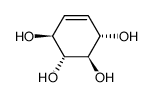 CAS#:138258-55-6
CAS#:138258-55-6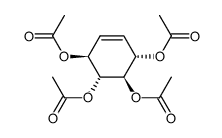 CAS#:4381-96-8
CAS#:4381-96-8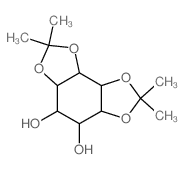 CAS#:40617-60-5
CAS#:40617-60-5 CAS#:120710-66-9
CAS#:120710-66-9 CAS#:120679-73-4
CAS#:120679-73-4 CAS#:85798-11-4
CAS#:85798-11-4 CAS#:102997-58-0
CAS#:102997-58-0
