Asunaprevir
Modify Date: 2024-01-07 16:11:34
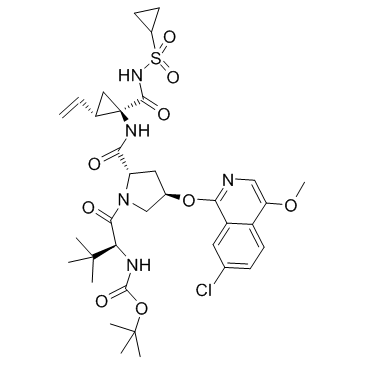
Asunaprevir structure
|
Common Name | Asunaprevir | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 630420-16-5 | Molecular Weight | 748.286 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C35H46ClN5O9S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of AsunaprevirAsunaprevir is a potent hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3 protease inhibitor, with IC50 of 0.2 nM-3.5 nM. |
| Name | tert-butyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S,4R)-4-(7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yl)oxy-2-[[(1R,2S)-1-(cyclopropylsulfonylcarbamoyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropyl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Asunaprevir is a potent hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3 protease inhibitor, with IC50 of 0.2 nM-3.5 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.2 nM-3.5 nM (HCV NS3 protease) |
| In Vitro | In multiple experiments, populations of resistant colonies are markedly reduced when cells are treated with a combination of DCV and Asunaprevir[1]. Asunaprevir (ASV) inhibits the NS3 proteolytic activity of genotype 1a (H77 strain) and genotype 1b (J4L6S strain), with IC50s of 0.7 and 0.3 nM, respectively. The EC50s of ASV against replicons encoding the NS3 protease domains representing genotypes 1a, 1b, and 4a, range from 1.2 to 4.0 nM[2]. Replicon cells are maintained under selective pressure with asunaprevir at concentrations of 10 and 30 times the EC50 values (50 or 150 nM final concentrations, respectively). For genotype 1b resistance selection, replicon cells are maintained in the presence of asunaprevir at 10 or 30 times the EC50 values (30 or 90 nM final concentrations, respectively)[3]. Asunaprevir, administered at single or multiple doses of 200 to 600 mg twice daily, is generally well tolerated, achieving rapid and substantial decreases in HCV RNA levels in subjects chronically infected with genotype 1 HCV[4]. |
| In Vivo | Asunaprevir (ASV, 3-15 mg/kg, p.o.) displays a hepatotropic disposition (liver-to-plasma ratios ranging from 40- to 359-fold across species) in several animal species. Twenty-four hours postdose, liver exposures across all species tested are ≥110-fold above the inhibitor EC50 observed with HCV genotype-1 replicons[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Cytotoxicity is determined by incubating cells (3,000 to 10,000 cells/well) with serially diluted test compounds or DMSO for 5 days (MT-2 cells) or 4 days (all other cell types). Cell viability is quantitated using an MTS assay for MT-2 or a Cell-Titer Blue reagent assay for HEK-293, HuH-7, HepG2, and MRC5 cells, and 50% cytotoxic concentrations (CC50s) are calculated. For the HCV and BVDV replicon assays, CC50s are determined from the same wells that are later used to determine EC50s. |
| Animal Admin | Mice (n=9 per group; overnight fast) receive Asunaprevir (ASV) by oral gavage (5 mg/kg; vehicle of PEG-400-ethanol, 9:1). Blood samples (-0.2 mL) are obtained by retro-orbital bleeding at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, 8, and 24 h after dosing. Within each group, three animals are bled at 0.25, 3, and 24 h, three at 0.5 and 6 h, and three at 1 and 8 h, resulting in a composite pharmacokinetic profile. Livers and brains are also removed from mice at the terminal sampling points. Rats (n=3 per group; overnight fast) receive ASV (amorphous free acid) by oral gavage (3, 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg) in PEG-400-ethanol (9:1). Serial blood samples (-0.3 mL) are obtained from the jugular vein predosing (0 h) and at 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, and 48 h postdosing. To assess tissue exposure, rats are orally administered ASV (5 or 15 mg/kg, same vehicle as above), and blood, liver, and heart samples from two rats/group are obtained at 0.17, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, 48, and 72 h after dosing. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C35H46ClN5O9S |
| Molecular Weight | 748.286 |
| Exact Mass | 747.270447 |
| PSA | 201.18000 |
| LogP | 4.02 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.616 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Asunaprevir (JAN/USAN) |
| 1,1-dimethylethyl [(1S)-1-{[(2S,4R)-4-(7-chloro-4methoxyisoquinolin-1-yloxy)-2-({(1R,2S)-1-[(cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl]-2-ethenylcyclopropyl}carbamoyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]carbonyl}-2,2-dimethylpropyl]carbamate |
| tert-butyl (S)-1-((2S,4R)-4-(7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yloxy)-2-((1R,2S)-1-(cyclopropylsulfonylcarbamoyl)-2-vinylcyclopropylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-ylcarbamate |
| 3-Methyl-N-{[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)oxy]carbonyl}-L-valyl-(4R)-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-N-{(1R,2S)-1-[(cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl]-2-vinylcyclopropyl}-L-prolinamide |
| Cyclopropanecarboxamide, N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-3-methyl-L-valyl-(4R)-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-L-prolyl-1-amino-N-(cyclopropylsulfonyl)-2-ethenyl-, (1R,2S)- |
| UNII-S9X0KRJ00S |
| CS-0674 |
| L-Prolinamide, N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-3-methyl-L-valyl-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-N-[(1R,2S)-1-[[(cyclopropylsulfonyl)amino]carbonyl]-2-ethenylcyclopropyl]-, (4R)- |
| Asunaprevir |
| N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-3-methyl-L-valyl-(4R)-4-((7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy)-N-((1R,2S)-1-((cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-vinylcyclopropyl)-L-prolinamide |
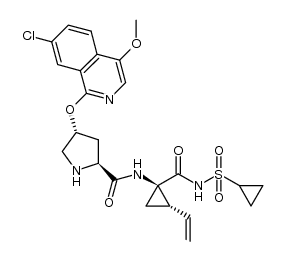 CAS#:1028252-93-8
CAS#:1028252-93-8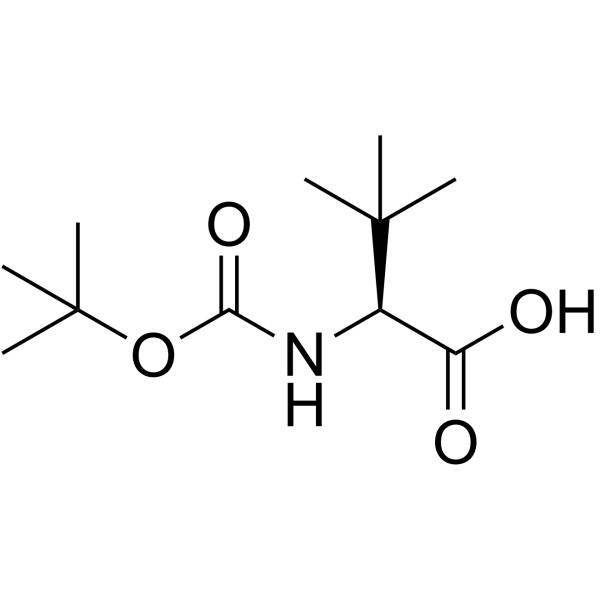 CAS#:62965-35-9
CAS#:62965-35-9 CAS#:1028252-17-6
CAS#:1028252-17-6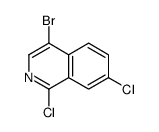 CAS#:953421-74-4
CAS#:953421-74-4 CAS#:630423-36-8
CAS#:630423-36-8 CAS#:1615-02-7
CAS#:1615-02-7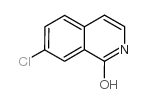 CAS#:24188-74-7
CAS#:24188-74-7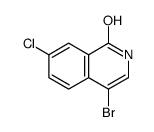 CAS#:1028252-13-2
CAS#:1028252-13-2