CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
AF1225000
-
CHEMICAL NAME :
-
Acetic acid
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
64-19-7
-
BEILSTEIN REFERENCE NO. :
-
0506007
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
199806
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
69
-
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C2-H4-O2
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
60.06
-
WISWESSER LINE NOTATION :
-
QV1
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Standard Draize test
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Administration onto the skin
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Open irritation test
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Administration onto the skin
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rabbit
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Standard Draize test
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Administration onto the skin
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rabbit
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Rinsed with water
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Administration into the eye
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rabbit
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
1470 ug/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Gastrointestinal - changes in structure or function of esophagus Gastrointestinal - ulceration or bleeding from small intestine Gastrointestinal - ulceration or bleeding from large intestine
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TCLo - Lowest published toxic concentration
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Inhalation
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
816 ppm/3M
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Sense Organs and Special Senses (Olfaction) - effect, not otherwise specified Sense Organs and Special Senses (Eye) - effect, not otherwise specified Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - other changes
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Rectal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - child
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
281 uL/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Gastrointestinal - alteration in gastric secretion Liver - liver function tests impaired Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - changes in tubules (including acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis)
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Unreported
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
308 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
3310 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LCLo - Lowest published lethal concentration
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Inhalation
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
16000 ppm/4H
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LC50 - Lethal concentration, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Inhalation
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
5620 ppm/1H
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Sense Organs and Special Senses (Eye) - conjunctive irritation Sense Organs and Special Senses (Eye) - effect, not otherwise specified Blood - other changes
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
525 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rabbit
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
600 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Administration onto the skin
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rabbit
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
1060 uL/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Subcutaneous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rabbit
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
600 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Rectal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rabbit
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
600 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
22680 mg/kg/9W-C
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - food intake (animal) Nutritional and Gross Metabolic - weight loss or decreased weight gain
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TCLo - Lowest published toxic concentration
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Inhalation
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
5070 ug/m3/24H/95D-C
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Kidney, Ureter, Bladder - other changes in urine composition Blood - changes in leukocyte (WBC) count Biochemical - Enzyme inhibition, induction, or change in blood or tissue levels - true cholinesterase
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
DOSE :
-
700 mg/kg
-
SEX/DURATION :
-
lactating female 18 day(s) post-birth
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Reproductive - Effects on Newborn - behavioral
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intratesticular
-
DOSE :
-
400 mg/kg
-
SEX/DURATION :
-
male 1 day(s) pre-mating
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Reproductive - Fertility - male fertility index (e.g. # males impregnating females per # males exposed to fertile nonpregnant females)
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Sex chromosome loss and nondisjunction
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Sex chromosome loss and nondisjunction
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Cytogenetic analysis
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Unscheduled DNA synthesis
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Mutation test systems - not otherwise specified
MUTATION DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Cytogenetic analysis
-
TEST SYSTEM :
-
Rodent - hamster Ovary
-
REFERENCE :
-
MUREAV Mutation Research. (Elsevier Science Pub. B.V., POB 211, 1000 AE Amsterdam, Netherlands) V.1- 1964- Volume(issue)/page/year: 240,195,1990 *** REVIEWS *** ACGIH TLV-STEL 37 mg/m3 (15 ppm) DTLVS* The Threshold Limit Values (TLVs) and Biological Exposure Indices (BEIs) booklet issues by American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH), Cincinnati, OH, 1996 Volume(issue)/page/year: TLV/BEI,1997 ACGIH TLV-TWA 25 mg/m3 (10 ppm) DTLVS* The Threshold Limit Values (TLVs) and Biological Exposure Indices (BEIs) booklet issues by American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH), Cincinnati, OH, 1996 Volume(issue)/page/year: TLV/BEI,1997 TOXICOLOGY REVIEW AMIHAB AMA Archives of Industrial Health. (Chicago, IL) V.11-21, 1955-60. For publisher information, see AEHLAU. Volume(issue)/page/year: 21,28,1960 TOXICOLOGY REVIEW ARTODN Archives of Toxicology. (Springer-Verlag, Heidelberger Pl. 3, D-1000 Berlin 33, Fed. Rep. Ger.) V.32- 1974- Volume(issue)/page/year: 39,299,1978 *** U.S. STANDARDS AND REGULATIONS *** EPA FIFRA 1988 PESTICIDE SUBJECT TO REGISTRATION OR RE-REGISTRATION FEREAC Federal Register. (U.S. Government Printing Office, Supt. of Documents, Washington, DC 20402) V.1- 1936- Volume(issue)/page/year: 54,7740,1989 MSHA STANDARD-air:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) DTLVS* The Threshold Limit Values (TLVs) and Biological Exposure Indices (BEIs) booklet issues by American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH), Cincinnati, OH, 1996 Volume(issue)/page/year: 3,2,1971 OSHA PEL (Gen Indu):8H TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) CFRGBR Code of Federal Regulations. (U.S. Government Printing Office, Supt. of Documents, Washington, DC 20402) Volume(issue)/page/year: 29,1910.1000,1994 OSHA PEL (Construc):8H TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) CFRGBR Code of Federal Regulations. (U.S. Government Printing Office, Supt. of Documents, Washington, DC 20402) Volume(issue)/page/year: 29,1926.55,1994 OSHA PEL (Shipyard):8H TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) CFRGBR Code of Federal Regulations. (U.S. Government Printing Office, Supt. of Documents, Washington, DC 20402) Volume(issue)/page/year: 29,1915.1000,1993 OSHA PEL (Fed Cont):8H TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) CFRGBR Code of Federal Regulations. (U.S. Government Printing Office, Supt. of Documents, Washington, DC 20402) Volume(issue)/page/year: 41,50-204.50,1994 *** OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE LIMITS *** OEL-AUSTRALIA:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3);STEL 15 ppm (37 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-AUSTRIA:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-BELGIUM:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3);STEL 15 ppm (37 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-DENMARK:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-FINLAND:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3);STEL 15 ppm (37 mg/m3);Skin JAN 1993 OEL-FRANCE:STEL 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-GERMANY:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-HUNGARY:TWA 10 mg/m3;STEL 20 mg/m3 JAN 1993 OEL-INDIA:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3);STEL 15 ppm (37 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-JAPAN:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-THE NETHERLANDS:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-THE PHILIPPINES:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-POLAND:TWA 5 mg/m3 JAN 1993 OEL-RUSSIA:TWA 10 ppm;STEL 5 mg/m3;Skin JAN 1993 OEL-SWEDEN:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3);STEL 15 ppm (35 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-SWITZERLAND:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3);STEL 20 ppm (50 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-THAILAND:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-TURKEY:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL-UNITED KINGDOM:TWA 10 ppm (25 mg/m3);STEL 15 ppm (35 mg/m3) JAN 1993 OEL IN BULGARIA, COLOMBIA, JORDAN, KOREA check ACGIH TLV OEL IN NEW ZEALAND, SINGAPORE, VIETNAM check ACGIH TLV *** NIOSH STANDARDS DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE DATA *** NIOSH RECOMMENDED EXPOSURE LEVEL (REL) : NIOSH REL TO ACETIC ACID-air:10H TWA 10 ppm;STEL 15 ppm REFERENCE : NIOSH* National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, U.S. Dept. of Health, Education, and Welfare, Reports and Memoranda. Volume(issue)/page/year: DHHS #92-100,1992 NIOSH OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE SURVEY DATA : NOHS - National Occupational Hazard Survey (1974) NOHS Hazard Code - 01568 No. of Facilities: 51469 (estimated) No. of Industries: 264 No. of Occupations: 150 No. of Employees: 486503 (estimated) NOES - National Occupational Exposure Survey (1983) NOES Hazard Code - 01568 No. of Facilities: 49403 (estimated) No. of Industries: 266 No. of Occupations: 169 No. of Employees: 907205 (estimated) No. of Female Employees: 322123 (estimated)
|





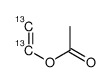 CAS#:106139-40-6
CAS#:106139-40-6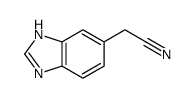 CAS#:110925-52-5
CAS#:110925-52-5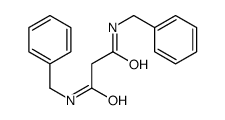 CAS#:10255-99-9
CAS#:10255-99-9 CAS#:1119-72-8
CAS#:1119-72-8 CAS#:110851-12-2
CAS#:110851-12-2![4-(6-METHOXYBENZO[D]THIAZOL-2-YL)-N,N-DIMETHYLANILINE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/093/10205-71-7.png) CAS#:10205-71-7
CAS#:10205-71-7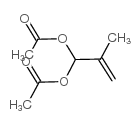 CAS#:10476-95-6
CAS#:10476-95-6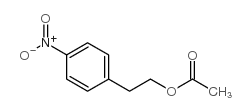 CAS#:104-30-3
CAS#:104-30-3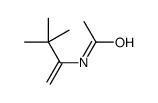 CAS#:107047-18-7
CAS#:107047-18-7 CAS#:106782-84-7
CAS#:106782-84-7
