Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium
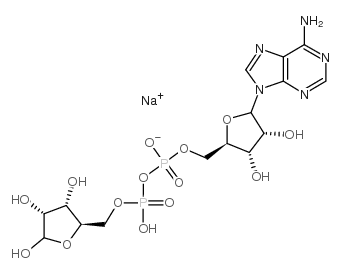
Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium structure
|
Common Name | Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68414-18-6 | Molecular Weight | 581.29800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H22N5NaO14P2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodiumAdenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium (ADP ribose sodium) is a nicotinamide adenine nucleotide (NAD+) metabolite. Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium is the most potent and primary intracellular Ca2+-permeable cation TRPM2 channel activator. Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium also can enhance autophagy[1][2]. |
| Name | [[5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] (2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-oxopentyl) hydrogen phosphate,sodium |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium (ADP ribose sodium) is a nicotinamide adenine nucleotide (NAD+) metabolite. Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium is the most potent and primary intracellular Ca2+-permeable cation TRPM2 channel activator. Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium also can enhance autophagy[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TRPM2 channel[1][2] Autophagy[1] |
| In Vitro | In mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), H2O2 treatment demonstrates that the activation of poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) produced Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose (ADP ribose), which is an activating signal for TRPM2 channels, thereby promoting Ca2+ elevation through extracellular Ca2+ influx and (or) lysosomal Ca2+ release. This process eventually activates early or late autophagy in response to different degrees of oxidative stress[1][1]. TRPM2 channels are activated by binding of Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose (ADP ribose) to the intracellular NUDT9-homology (NUDT9-H) domain unique to TRPM2 and located at its C terminus. In addition to ADPR, intracellular Ca2+ is an essential coactivator: TRPM2 channels open only in the combined presence of both ligands[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C15H22N5NaO14P2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 581.29800 |
| Exact Mass | 581.05400 |
| PSA | 313.97000 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26;S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Aspirin inhibits expression of sFLT1 from human cytotrophoblasts induced by hypoxia, via cyclo-oxygenase 1.
Placenta 36(4) , 446-53, (2015) Elevated circulating soluble FLT1 (sFLT1) levels seen in preeclampsia may play a role in its development. Aspirin is recommended for prevention of preeclampsia. We hypothesized that aspirin may inhibi... |
|
|
Sclerotium rolfsii lectin induces stronger inhibition of proliferation in human breast cancer cells than normal human mammary epithelial cells by induction of cell apoptosis.
PLoS ONE 9(11) , e110107, (2014) Sclerotium rolfsii lectin (SRL) isolated from the phytopathogenic fungus Sclerotium rolfsii has exquisite binding specificity towards O-linked, Thomsen-Freidenreich (Galβ1-3GalNAcα1-Ser/Thr, TF) assoc... |
|
|
Alpha-fetoprotein, identified as a novel marker for the antioxidant effect of placental extract, exhibits synergistic antioxidant activity in the presence of estradiol.
PLoS ONE 9(6) , e99421, (2014) Placenta, as a reservoir of nutrients, has been widely used in medical and cosmetic materials. Here, we focused on the antioxidant properties of placental extract and attempted to isolate and identify... |
| Adenosine 5'-diphosphoribose sodium salt |
| Adenosine 5 inverted exclamation marka-diphosphoribose sodium salt |
| MFCD00136017 |