Fmoc-Val-OH
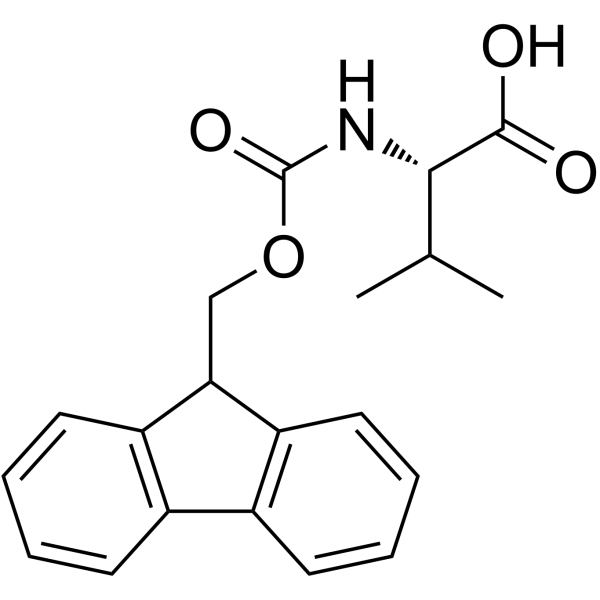
Fmoc-Val-OH structure
|
Common Name | Fmoc-Val-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68858-20-8 | Molecular Weight | 339.385 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 551.8±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H21NO4 | Melting Point | 143-147ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 287.5±25.4 °C | |
Use of Fmoc-Val-OHFmoc-L-Val-OH is a valine derivative[1]. |
| Name | (2S)-2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fmoc-L-Val-OH is a valine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 551.8±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 143-147ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H21NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 339.385 |
| Flash Point | 287.5±25.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 339.147064 |
| PSA | 79.12000 |
| LogP | 4.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.590 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Aspartate-modified doxorubicin on its N-terminal increases drug accumulation in LAT1-overexpressing tumors.
Cancer Sci. 106 , 747-56, (2015) L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1), overexpressed on the membrane of various tumor cells, is a potential target for tumor-targeting therapy. This study aimed to develop a LAT1-mediated chemotherap... |
|
|
Cell-penetrating apoptotic peptide/p53 DNA nanocomplex as adjuvant therapy for drug-resistant breast cancer.
Mol. Pharm. 11(10) , 3352-60, (2014) Drug resistance becomes a formidable challenge against effective cancer therapy. Defective apoptosis in cancer cells is a key factor responsible for chemoresistance or radioresistance. Promoting apopt... |
|
|
Design and synthesis of newN-(fluorenyl-9-methoxycarbonyl) (Fmoc)-dipeptides as anti-inflammatory agents
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44 , 1933-40, (2009) Twenty-four new dipeptide analogs ( 1– 24) of aurantiamide acetate were designed, synthesized, and assayed for effects on superoxide anion generation and elastase release by human neutrophils in respo... |
| L-Valine, N-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]- |
| N-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-L-valine |
| N-Fmoc-Val-OH (N-Fmoc-L-valine) |
| FMco-Val-OH |
| N-FMOC-L-VAL |
| FMOC-L-VAL-OH |
| FMOC-VAL |
| FMOC-VAL-OH |
| MFCD00037124 |
| N-((9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl)-L-valine |
| FMOC-VALINE |
| FMOC-L-VALINE |
| N-Fmoc-L-valine |
| FMOC-L-VAL |
| N-FMOC-VAL-OH |
| Fmoc-Valine-OH |
| EINECS 272-515-0 |
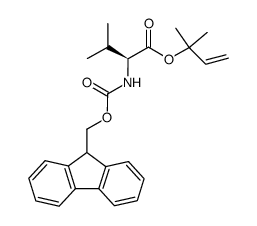 CAS#:851713-90-1
CAS#:851713-90-1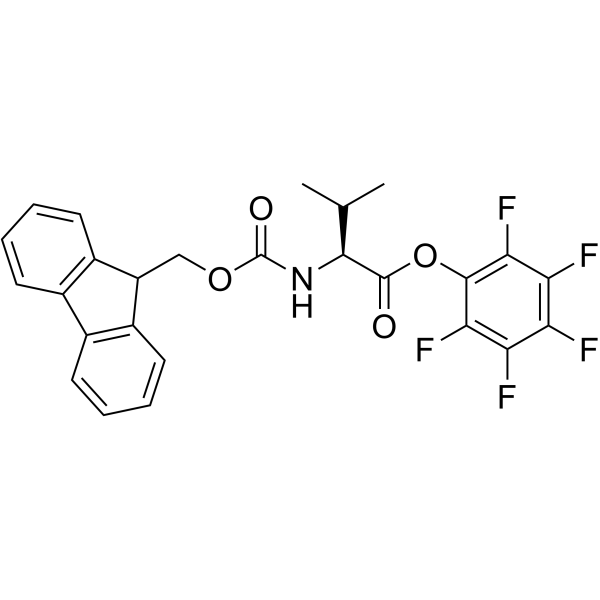 CAS#:86060-87-9
CAS#:86060-87-9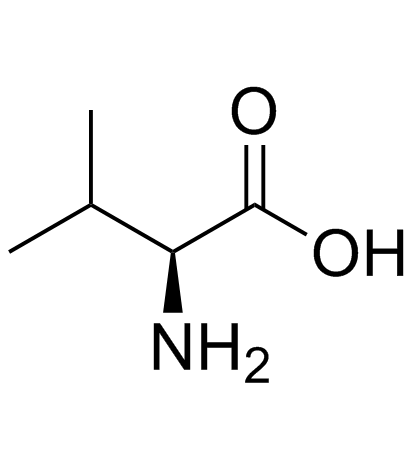 CAS#:72-18-4
CAS#:72-18-4 CAS#:82911-69-1
CAS#:82911-69-1 CAS#:28920-43-6
CAS#:28920-43-6 CAS#:100803-86-9
CAS#:100803-86-9 CAS#:88744-04-1
CAS#:88744-04-1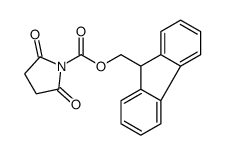 CAS#:102774-86-7
CAS#:102774-86-7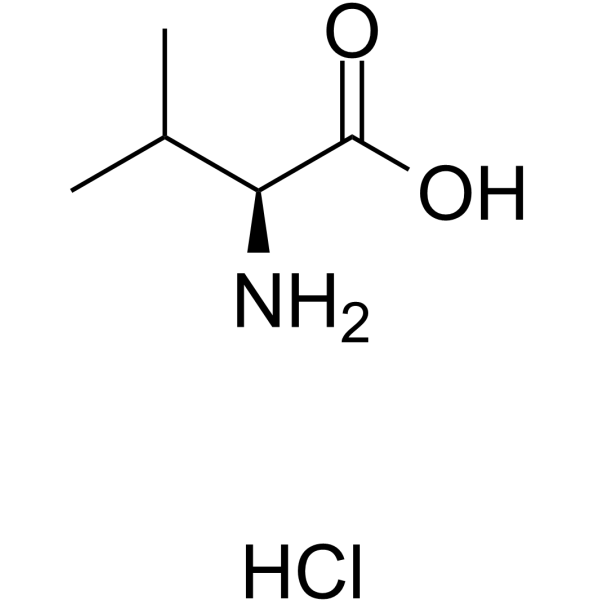 CAS#:17498-50-9
CAS#:17498-50-9 CAS#:143744-88-1
CAS#:143744-88-1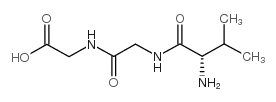 CAS#:21835-35-8
CAS#:21835-35-8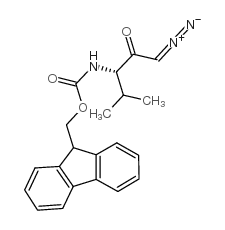 CAS#:193148-58-2
CAS#:193148-58-2 CAS#:4425-82-5
CAS#:4425-82-5 CAS#:260254-74-8
CAS#:260254-74-8 CAS#:3061-91-4
CAS#:3061-91-4 CAS#:69558-55-0
CAS#:69558-55-0 CAS#:75957-56-1
CAS#:75957-56-1
