Kamebakaurine
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 19:30:49
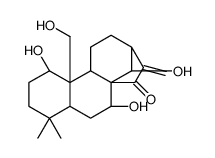
Kamebakaurine structure
|
Common Name | Kamebakaurine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73981-34-7 | Molecular Weight | 350.44900 | |
| Density | 1.3g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 563.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O5 | Melting Point | 7ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 308.6ºC | |
Use of KamebakaurineKamebakaurin is a natural compound isolated from Isodon japonicus. Kamebakaurin is a potent inhibitor of NF-κB activation by directly targeting DNA-binding activity of p50[1]. |
| Name | kamebakaurin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Kamebakaurin is a natural compound isolated from Isodon japonicus. Kamebakaurin is a potent inhibitor of NF-κB activation by directly targeting DNA-binding activity of p50[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 563.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 7ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 350.44900 |
| Flash Point | 308.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 350.20900 |
| PSA | 97.99000 |
| LogP | 1.03920 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
| 1,7,14,20-Tetrahydroxykaur-16-en-15-one (1alpha,7alpha,14R) |
| Kaur-16-en-15-one,1,7,14,20-tetrahydroxy-,(1alpha,7alpha,14R) |