EHT 1864
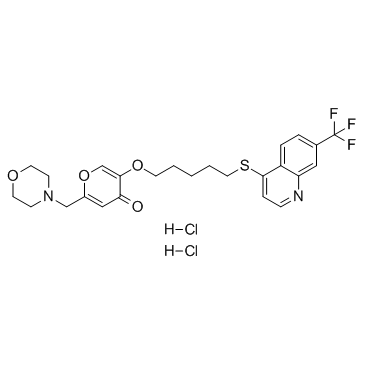
EHT 1864 structure
|
Common Name | EHT 1864 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 754240-09-0 | Molecular Weight | 581.475 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H29Cl2F3N2O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of EHT 1864EHT 1864 is a small molecule inhibitor of Rac1 signaling; modulate γ-Secretase-mediated APP processing.IC50 value:Target: Rac1 inhibitorin vitro: EHT 1864 blocks Aβ 40 and Aβ 42 production but does not impact sAPPα levels and does not inhibit γ-secretase. Rather, EHT 1864 modulates APP processing at the level of γ-secretase to prevent Aβ40 and Aβ42 generation. This effect does not result from a direct inhibition of the γ-secretase activity and is specific for APP cleavage, since EHT 1864 does not affect Notch cleavage [1]. EHT 1864 specifically inhibited Rac1-dependent platelet-derived growth factor-induced lamellipodia formation. Furthermore, our biochemical analyses with recombinant Rac proteins found that EHT 1864 possesses high affinity binding to Rac1, as well as the related Rac1b, Rac2, and Rac3 isoforms, and this association promoted the loss of bound nucleotide, inhibiting both guanine nucleotide association and Tiam1 Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor-stimulated exchange factor activity in vitro [2].in vivo: EHT1864 significantly reduces Aβ 40 and Aβ 42 levels in guinea pig brains at a threshold that is compatible with delaying plaque accumulation and/or clearing the existing plaque in brain [1]. |
| Name | 2-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-5-[5-[7-(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]sulfanylpentoxy]pyran-4-one,dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | EHT 1864 is a small molecule inhibitor of Rac1 signaling; modulate γ-Secretase-mediated APP processing.IC50 value:Target: Rac1 inhibitorin vitro: EHT 1864 blocks Aβ 40 and Aβ 42 production but does not impact sAPPα levels and does not inhibit γ-secretase. Rather, EHT 1864 modulates APP processing at the level of γ-secretase to prevent Aβ40 and Aβ42 generation. This effect does not result from a direct inhibition of the γ-secretase activity and is specific for APP cleavage, since EHT 1864 does not affect Notch cleavage [1]. EHT 1864 specifically inhibited Rac1-dependent platelet-derived growth factor-induced lamellipodia formation. Furthermore, our biochemical analyses with recombinant Rac proteins found that EHT 1864 possesses high affinity binding to Rac1, as well as the related Rac1b, Rac2, and Rac3 isoforms, and this association promoted the loss of bound nucleotide, inhibiting both guanine nucleotide association and Tiam1 Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor-stimulated exchange factor activity in vitro [2].in vivo: EHT1864 significantly reduces Aβ 40 and Aβ 42 levels in guinea pig brains at a threshold that is compatible with delaying plaque accumulation and/or clearing the existing plaque in brain [1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C25H29Cl2F3N2O4S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 581.475 |
| Exact Mass | 580.117737 |
| PSA | 90.10000 |
| LogP | 6.92230 |
| Appearance of Characters | white to beige |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: soluble10mg/mL, clear |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Gq-mediated Akt translocation to the membrane: a novel PIP3-independent mechanism in platelets.
Blood 125(1) , 175-84, (2015) Akt is an important signaling molecule regulating platelet aggregation. Akt is phosphorylated after translocation to the membrane through Gi signaling pathways by a phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphos... |
|
|
Instructive roles for cytokine-receptor binding parameters in determining signaling and functional potency.
Sci. Signal. 8 , ra114, (2015) Cytokines dimerize cell surface receptors to activate signaling and regulate many facets of the immune response. Many cytokines have pleiotropic effects, inducing a spectrum of redundant and distinct ... |
|
|
An integrated imaging approach to the study of oxidative stress generation by mitochondrial dysfunction in living cells.
Environ. Health Perspect. 118 , 902-8, (2010) The mechanisms of action of many environmental agents commonly involve oxidative stress resulting from mitochondrial dysfunction. Zinc is a common environmental metallic contaminant that has been impl... |
| 4H-Pyran-4-one, 2-(4-morpholinylmethyl)-5-[[5-[[7-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinolinyl]thio]pentyl]oxy]-, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| 2-(4-Morpholinylmethyl)-5-[(5-{[7-(trifluoromethyl)-4-quinolinyl]sulfanyl}pentyl)oxy]-4H-pyran-4-one dihydrochloride |
| 2-(Morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-5-[(5-{[7-(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]sulfanyl}pentyl)oxy]-4H-pyran-4-one dihydrochloride |
| eht 1864 |
| EHT-1864 |