Methacrylamide
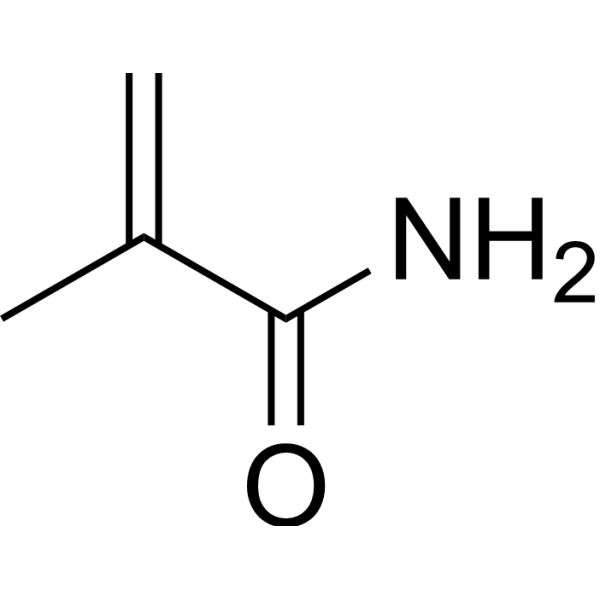
Methacrylamide structure
|
Common Name | Methacrylamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79-39-0 | Molecular Weight | 85.10 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 211.5±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO | Melting Point | 108 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 81.7±19.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of MethacrylamideMethacrylamide can be used as an excipient. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs[1]. |
| Name | methacrylamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Methacrylamide can be used as an excipient. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 211.5±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 108 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO |
| Molecular Weight | 85.10 |
| Flash Point | 81.7±19.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 85.052765 |
| PSA | 43.09000 |
| LogP | -0.23 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.438 |
| Water Solubility | 202 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | 3263 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | UC6475000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Sulfobetaine-Vinylimidazole Block Copolymers: A Robust Quantum Dot Surface Chemistry Expanding Bioimaging's Horizons.
ACS Nano 9 , 11479-89, (2015) Long-term inspection of biological phenomena requires probes of elevated intra- and extracellular stability and target biospecificity. The high fluorescence and photostability of quantum dot (QD) nano... |
|
|
Metal-free synthesis of 3,3-disubstituted oxoindoles by iodine(III)-catalyzed bromocarbocyclizations.
Chemistry 18(35) , 10834-8, (2012) "I" did it: An iodine(III)-mediated bromocarbocyclization was elaborated as an efficient tool for the synthesis of oxoindoles. This method is applicable to a variety of structurally different substrat... |
|
|
Photochemical internalization-mediated nonviral gene transfection: polyamine core-shell nanoparticles as gene carrier.
J. Biomed. Opt. 19(10) , 105009, (2014) The overall objective of the research was to investigate the utility of photochemical internalization (PCI) for the enhanced nonviral transfection of genes into glioma cells. The PCI-mediated introduc... |
| Methacrylamide |
| Methylacrylic amide |
| 2-Methylpropenamide |
| 2-Propenamide, 2-methyl- |
| Methacryamide |
| EINECS 201-202-3 |
| methylacrylamide |
| 2-methylprop-2-enamide |
| MFCD00008018 |
| Methacrylic acid amide |
| 2-Propenamide,2-methyl |
| 2-Methylacrylamide |
| methacrylic amide |
| methylbisacrylamide |
| 2-Methyl-2-propenamide |

