Retinyl palmitate
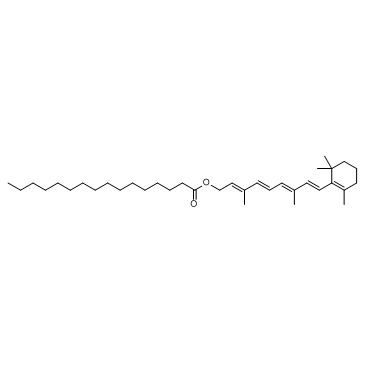
Retinyl palmitate structure
|
Common Name | Retinyl palmitate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79-81-2 | Molecular Weight | 524.860 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 607.5±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H60O2 | Melting Point | 41678ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 79.7±21.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Retinyl palmitateRetinyl palmitate is an ester of Retinol and is the major form of vitamin A found in the epidermis. Retinyl palmitate has been widely used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. |
| Name | all-trans-retinyl palmitate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Retinyl palmitate is an ester of Retinol and is the major form of vitamin A found in the epidermis. Retinyl palmitate has been widely used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Retinyl palmitate has a high molecular weight and a stable formulation. To be active, Retinyl palmitate should be enzymatically converted in the skin to retinol by cleavage of the ester linkage and must then be converted to tretinoin via oxidative processes[1]. |
| In Vivo | The topical administration of Retinyl palmitate in rats results in increased protein and collagen and an epidermal thickening[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 607.5±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 41678ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C36H60O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 524.860 |
| Flash Point | 79.7±21.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 524.459351 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 14.83 |
| Appearance of Characters | oil |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.508 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R63 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S23-S36/37/39-S45-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN1170 - class 3 - PG 2 - Ethanol, solution |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VH6860000 |
| HS Code | 2936210000 |
|
~93% 
Retinyl palmitate CAS#:79-81-2 |
| Literature: DSM IP ASSETS B.V.; BONRATH, Werner; GAA, Alex; STRITT, Claude Patent: WO2014/23772 A1, 2014 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 9 ; |
|
~78% 
Retinyl palmitate CAS#:79-81-2 |
| Literature: Eastman Chemical Company Patent: US7566795 B2, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 11 ; |
|
~73% 
Retinyl palmitate CAS#:79-81-2 |
| Literature: Zhu, Kai; Wang, Jianqiang; Wang, Yan-Hua; Liu, Hui; Han, Ping-Fang; Wei, Ping Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2011 , vol. 11, # 9 p. 7593 - 7602 |
|
~% 
Retinyl palmitate CAS#:79-81-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 64, p. 2407,2410 Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 32, p. 489,498 Vitamins Hormones, , vol. 18, p. 301 |
|
~% 
Retinyl palmitate CAS#:79-81-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association, Scientific Edition, , vol. 49, p. 458 - 462 |
| HS Code | 2936210000 |
|---|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
|
|
Lack of Impact of High Dietary Vitamin A on T Helper 2-Dependent Contact Hypersensitivity to Fluorescein Isothiocyanate in Mice.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38 , 1827-30, (2015) Overuse of vitamin A as a dietary supplement is a concern in industrialized countries. High-level dietary vitamin A is thought to shift immunity to a T helper 2 (Th2)-dominant one, resulting in the pr... |
| Retinol, O-(1-oxohexadecyl)- |
| EINECS 201-228-5 |
| O-hexadecanoylretinol |
| Retinyl palmitate |
| all-trans-retinyl palmitate |
| O-Palmitoylretinol |
| Retinol hexadecanoate |
| VITAMIN A PALMITATE |
| [(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenyl] hexadecanoate |
| MFCD00019414 |
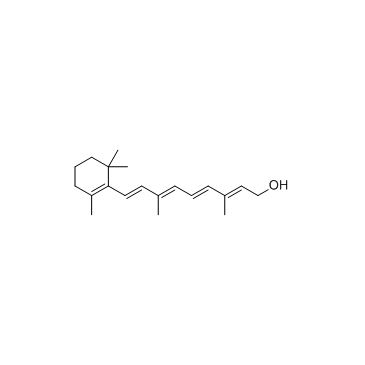
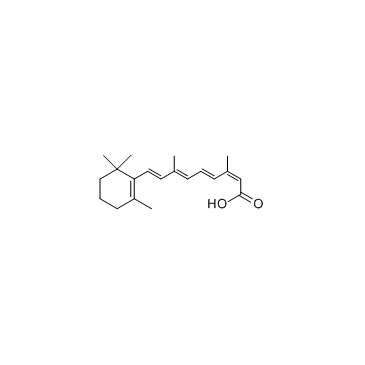 CAS#:4759-48-2
CAS#:4759-48-2 CAS#:302-79-4
CAS#:302-79-4
