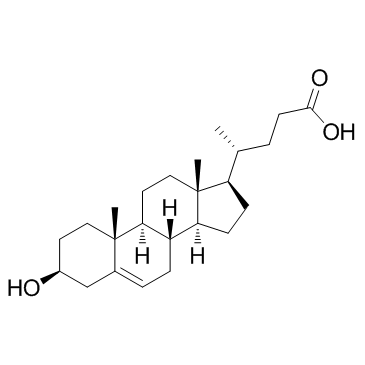
DMHCA
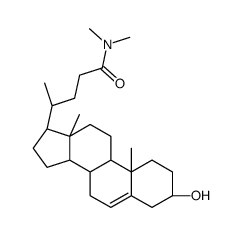
DMHCA structure
|
Common Name | DMHCA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79066-03-8 | Molecular Weight | 401.62500 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H43NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of DMHCADMHCA, a potent and selective LXR agonist, specifically activates the cholesterol efflux arm of the LXR pathway without stimulating triglyceride synthesis. DMHCA has anti-inflammatory effects and can be used for the research of cholesterol homeostasis diabetes[1]. |
| Name | (3β)-3-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethylchol-5-en-24-amide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DMHCA, a potent and selective LXR agonist, specifically activates the cholesterol efflux arm of the LXR pathway without stimulating triglyceride synthesis. DMHCA has anti-inflammatory effects and can be used for the research of cholesterol homeostasis diabetes[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: LXR[1] |
| In Vitro | In ex vivo treatment of diabetic CD34+ cells, DMHCA (10 µM; 16-18 hours) restores the fluidity of the membranes to baseline nondiabetic levels[1]. DMHCA restores the levels of BM-derived TNF-α and IL-3 to baseline and significantly reduces CCL-2 production by >50% in the BM supernatants and the systemic circulation compares to the control mice. DMHCA also increases the number of CACs in the BM and peripheral circulation and upregulates the egression of vascular reparative cells into the peripheral circulation[1]. In the PAGA analysis, DMHCA treatment enhances the overall production and robustness of erythrocyte progenitors. DMHCA enhances flux down the erythrocyte progenitor lineage. It also DMHCA increase in erythrocyte progenitor density in BM cells. DMHCA not only expands the proportion of erythrocyte progenitors but also increases the expression of the hemoglobin beta adult chain (HBB-BT)[1]. |
| In Vivo | DMHCA (oral administration; 6 months; chow 8mg/kg body weight /day) restores cholesterol homeostasis in diabetic retina. It significantly increases endogenous LXR ligands, desmosterol, and total oxysterols in the diabetic retina[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H43NO2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 401.62500 |
| Exact Mass | 401.32900 |
| PSA | 40.54000 |
| LogP | 5.43080 |
|
~85% 
DMHCA CAS#:79066-03-8 |
| Literature: Karaki, Fumika; Ohgane, Kenji; Dodo, Kosuke; Hashimoto, Yuichi Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2013 , vol. 21, # 17 p. 5297 - 5309 |
|
~% 
DMHCA CAS#:79066-03-8 |
| Literature: Spencer; Li; Russel; Collins; Bledsoe; Consler; Moore; Galardi; McKee; Watson; Parks; Lambert; Willson Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2001 , vol. 44, # 6 p. 886 - 897 |
|
~% 
DMHCA CAS#:79066-03-8 |
| Literature: Louw et al. Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 1954 , vol. 73, p. 655,660 |
| Cholenic acid dimethylamide |
| N,N-dimethyl-3-phenylpropylamine hydrochloride |
| PROPYLAMINE,N,N-DIMETHYL-3-PHENYL-,HYDROCHLORIDE |
| N,N-dimethyl-3-phenylpropylamine |
| N,N-Dimethyl-3-phenylpropylamin-hydrochlorid |
| N,N-dimethyl-3-phenylpropan-1-aminium chloride |