Vesnarinone
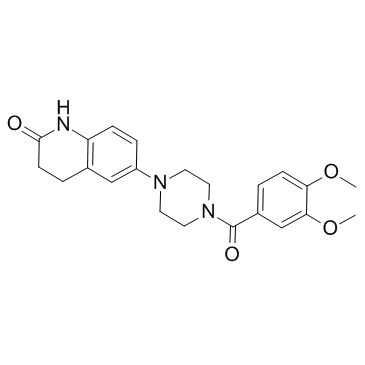
Vesnarinone structure
|
Common Name | Vesnarinone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 81840-15-5 | Molecular Weight | 395.45200 | |
| Density | 1.246g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 678.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H25N3O4 | Melting Point | 238.1-239.5° (Tominaga); mp 238.1-239.8° (Shimizu) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 364ºC | |
Use of VesnarinoneVesnarinone is a quinolinone derivative, and its pharmacodynamic effects include inhibition of phosphodiesterase III (PDE3) activity, increases in calcium flux and decreases in potassium flux.IC50 value: 1.1 μM (for HERG current)Target: PDE3in vitro: HERG current is inhibited by Vesnarinone with an IC50 of 1.1 μM, whereas KvLQT1/minK current is not significantly depressed by Vesnarinone even at 30 μM. The IC50 value for Vesnarinone inhibition of HERG channels is 1 μM. The IC50 for Vesnarinone inhibition of PDE is reported to be 300 μM. [1] Vesnarinone is a novel cytokine inhibitor, for the treatment of lung fibrosis using a murine model of bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Vesnarinone inhibits BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis, at least in part, by the inhibition of acute lung injuries in the early phase. [2] Vesnarinone is a new and novel inotropic drug that has unique and complex mechanisms of action. Vesnarinone inhibits phosphodiesterase, thereby leading to increased intracellular calcium, and also affects numerous myocardial ion channels, resulting in the prolongation of the opening time of sodium channels and the decrease in the delayed outward and inward rectifying potassium current. Vesnarinone has also demonstrated significant effects on cytokine production, which may account for some of its observed clinical benefits.[3] Vesnarinone plays an important role in the regulation of cytokines and suggest that the reduction of cytokine release may contribute to the beneficial effects of the drug in the treatment of heart failure. Vesnarinone inhibits the production of TFN-a and IFN-y by LPS stimulated whole blood from patients with heart failure and from healthy volunteers. [4]in vivo: Vesnarinone reduces the circulating levels of TNF-α. Cumulative evidence showed that a variety of cytokine are involved in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. [2] |
| Name | 6-[4-(3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3,4-dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Vesnarinone is a quinolinone derivative, and its pharmacodynamic effects include inhibition of phosphodiesterase III (PDE3) activity, increases in calcium flux and decreases in potassium flux.IC50 value: 1.1 μM (for HERG current)Target: PDE3in vitro: HERG current is inhibited by Vesnarinone with an IC50 of 1.1 μM, whereas KvLQT1/minK current is not significantly depressed by Vesnarinone even at 30 μM. The IC50 value for Vesnarinone inhibition of HERG channels is 1 μM. The IC50 for Vesnarinone inhibition of PDE is reported to be 300 μM. [1] Vesnarinone is a novel cytokine inhibitor, for the treatment of lung fibrosis using a murine model of bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Vesnarinone inhibits BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis, at least in part, by the inhibition of acute lung injuries in the early phase. [2] Vesnarinone is a new and novel inotropic drug that has unique and complex mechanisms of action. Vesnarinone inhibits phosphodiesterase, thereby leading to increased intracellular calcium, and also affects numerous myocardial ion channels, resulting in the prolongation of the opening time of sodium channels and the decrease in the delayed outward and inward rectifying potassium current. Vesnarinone has also demonstrated significant effects on cytokine production, which may account for some of its observed clinical benefits.[3] Vesnarinone plays an important role in the regulation of cytokines and suggest that the reduction of cytokine release may contribute to the beneficial effects of the drug in the treatment of heart failure. Vesnarinone inhibits the production of TFN-a and IFN-y by LPS stimulated whole blood from patients with heart failure and from healthy volunteers. [4]in vivo: Vesnarinone reduces the circulating levels of TNF-α. Cumulative evidence showed that a variety of cytokine are involved in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. [2] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.246g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 678.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 238.1-239.5° (Tominaga); mp 238.1-239.8° (Shimizu) |
| Molecular Formula | C22H25N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 395.45200 |
| Flash Point | 364ºC |
| Exact Mass | 395.18500 |
| PSA | 71.11000 |
| LogP | 2.69180 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~% 
Vesnarinone CAS#:81840-15-5 |
| Literature: Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Patent: US4415572 A1, 1983 ; |
|
~% 
Vesnarinone CAS#:81840-15-5 |
| Literature: Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Patent: US4415572 A1, 1983 ; |
|
~68% 
Vesnarinone CAS#:81840-15-5 |
| Literature: Tominaga; Yo; Ogawa; Yamashita; Yabuuchi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 6 p. 2100 - 2110 |
|
~% 
Vesnarinone CAS#:81840-15-5 |
| Literature: Tominaga; Yo; Ogawa; Yamashita; Yabuuchi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 6 p. 2100 - 2110 |
|
~% 
Vesnarinone CAS#:81840-15-5 |
| Literature: Tominaga; Yo; Ogawa; Yamashita; Yabuuchi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 6 p. 2100 - 2110 |
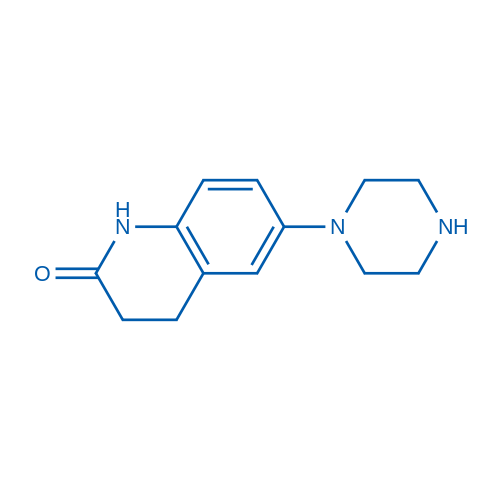
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| vesnarinone |
| Piteranometozine |
| 6-[4-(3,4-dimethoxy-benzoyl)-1-piperazinyl]-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril |
| Arkin-Z |
| 3,4-dihydro-6-[4-(3,4-dimethoxybenzoyl)-1-piperazinyl]-2(1H)-quinoline |
| DRG-0210 |
| OPC8212 |
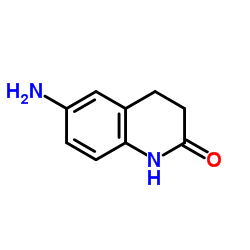
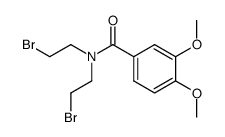
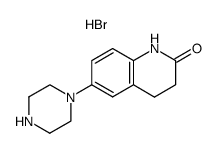
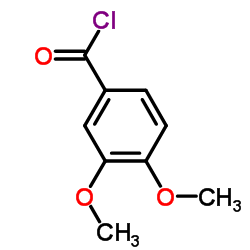
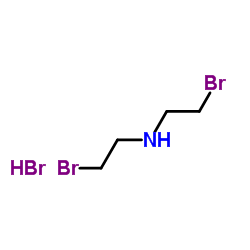
 CAS#:3943-77-9
CAS#:3943-77-9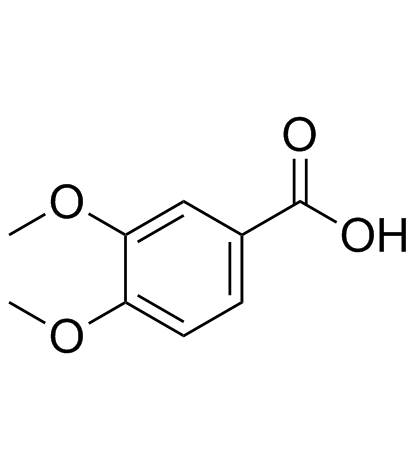 CAS#:93-07-2
CAS#:93-07-2