UNII:4956DJR58O
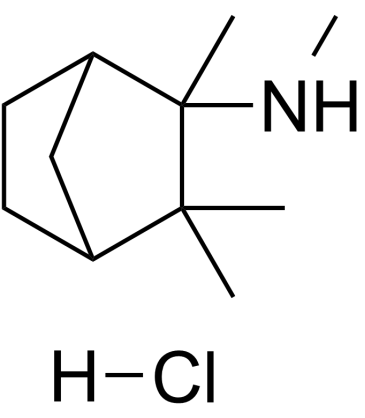
UNII:4956DJR58O structure
|
Common Name | UNII:4956DJR58O | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 826-39-1 | Molecular Weight | 203.752 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 189.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H22ClN | Melting Point | >240ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 58.1ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of UNII:4956DJR58OMecamylamine hydrochloride is an orally active, nonselective, noncompetitive nAChR antagonist that can treat various neuropsychiatric disorders. Mecamylamine hydrochloride is originally used as a ganglionic blocker in treating hypertension. Mecamylamine hydrochloride can easily crosses the blood-brain barrier[1][2]. |
| Name | Mecamylamine Hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Mecamylamine hydrochloride is an orally active, nonselective, noncompetitive nAChR antagonist that can treat various neuropsychiatric disorders. Mecamylamine hydrochloride is originally used as a ganglionic blocker in treating hypertension. Mecamylamine hydrochloride can easily crosses the blood-brain barrier[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
nAChR[1] |
| In Vitro | Mecamylamine blocks muscle nAChRs in a use- and voltagedependent manner. Mecamylamine blocks the nicotinic currents via trapping mechanism. The main feature of this block is the phenomenon of block relief, which might be revealed by combined action of depolarization and activation of nAChRs. The experimental study of the Mecamylamine action on muscle nAChRs revealed that: (1) Mecamylamine (1-20 μM) reduces evoked end-plate currents (EPC) amplitude with Hill’s constant equal to 1.2 and IC50 = 7.8 μM at holding potential –70 mV; (2) the calculated depth of its interaction with the muscle nAChR channel is almost half of the one of neuronal nAChRs (0.37 compare to 0.72 for neuronal nAChRs); (3) simultaneous membrane depolarization and repetitive activation of postsynaptic nAChRs by motor nerve stimulation produced rapid block relief dependent on the degree of depolarization, number of conditioning signals and Mecamylamine concentration, and only slightly depended on the rate of stimulation[2]. |
| In Vivo | Mecamylamine (0.5-1 mg/kg; Intraperitoneal injection; C57BL/6J mice) has antidepressant-like effects in both the TST and FST and these effects are dependent on bothβ2 andα7 subunits[3]. Animal Model: C57BL/6J mice (3-4 months) forced swim test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST)[3] Dosage: 0.5 mg/kg, 0.75 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection Result: Significantly decreased immobility time in the TST at the 1.0-mg/kg dose but did not alter baseline locomotor activity. Also significantly decreased time immobile in the FST. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 189.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >240ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C11H22ClN |
| Molecular Weight | 203.752 |
| Flash Point | 58.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 203.144073 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 3.61350 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: 122 mg/mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RB6900000 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2921300090 |
| HS Code | 2921300090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921300090 other cyclanic, cyclenic or cyclotherpenic mono- or polyamines, and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
A nicotinic receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory effect of the flavonoid rhamnetin in BV2 microglia.
Fitoterapia 98 , 11-21, (2014) The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) is a potential target in neuroinflammation. Screening a plant extract library identified Solidago nemoralis as containing methyl-quercetin derivativ... |
|
|
Profiling the role of deacylation-reacylation in the lymphatic transport of a triglyceride-mimetic prodrug.
Pharm. Res. 32(5) , 1830-44, (2015) Recent studies have demonstrated the potential for a triglyceride (TG) mimetic prodrug to promote the delivery of mycophenolic acid (MPA) to the lymphatic system. Here, the metabolic pathways that fac... |
|
|
Toxicity induced by F. poae-contaminated feed and the protective effect of Montmorillonite supplementation in broilers.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 74 , 120-30, (2014) The T-2 and HT-2 toxins, the main metabolites of Fusarium poae, induce toxicity in broilers and accumulate in tissues. Consequently, during the breeding process of broilers, diets are frequently suppl... |
| bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-amine, N,2,3,3-tetramethyl-, hydrochloride |
| EINECS 212-555-8 |
| N,2,2,3-tetramethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-amine,hydrochloride |
| N,2,3,3-tétraméthylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-amine chlorhydrate |
| 2-(Methylamino)-2,3,3-trimethylnorbornane hydrochloride |
| N,2,3,3-Tetramethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-amine hydrochloride |
| Norbornane, 2-(methylamino)-2,3,3-trimethyl-, hydrochloride |
| Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-amine, N,2,3,3-tetramethyl-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| N,2,3,3-Tetramethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-amine hydrochloride (1:1) |
| N,2,3,3-Tetramethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-aminhydrochlorid |
| Inversine hydrochloride |
| N,2,3,3-tetramethyl-2-norcamphanamine hydrochloride |
| UNII:4956DJR58O |
| MFCD00151462 |

