DL-Lysine monohydrate
Modify Date: 2024-01-11 00:50:39
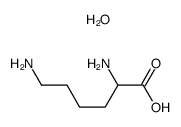
DL-Lysine monohydrate structure
|
Common Name | DL-Lysine monohydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 885701-25-7 | Molecular Weight | 164.20300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 400ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H16N2O3 | Melting Point | ca 110℃ | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 195.7ºC | |
Use of DL-Lysine monohydrateDL-Lysine monohydrate is a racemic mixture of the D-Lysine and L-Lysine. Lysine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins[1]. |
| Name | 2,6-diaminohexanoic acid,hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-Lysine monohydrate is a racemic mixture of the D-Lysine and L-Lysine. Lysine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | D-Lysine produces from L-Lysine by successive chemical racemization and microbial asymmetric degradation. L-Lysine is enantiomer of D-Lysine. D-Lysine exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. D-Lysine is a potentially toxic compound[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 400ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | ca 110℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C6H16N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.20300 |
| Flash Point | 195.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 164.11600 |
| PSA | 98.57000 |
| LogP | 0.86360 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
|---|
| 2,6-diaminohexanoic Acid Hydrate |
| L-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid |
| DL-Lysine monohydrate |