Flumatinib mesylate
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 08:16:02
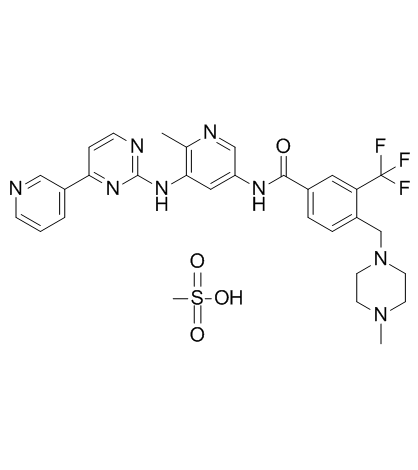
Flumatinib mesylate structure
|
Common Name | Flumatinib mesylate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 895519-91-2 | Molecular Weight | 658.694 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H33F3N8O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Flumatinib mesylateFlumatinib mesylate (HH-GV-678 mesylate), a derivative of imatinib, is a multi-kinase inhibitor with IC50 Values of 1.2 nM, 307.6 nM and 2662 nM for c-Abl, PDGFRβ and c-Kit respectively.IC50 Value: 1.2 nM (c-Abl); 307.6 nM(PDGFRβ); 2662 nM (c-Kit) [1]Target: c-Abl; c-Kit; PDGRFβin vitro: HH-GV-678 can predominantly inhibit the autophosphorylation of Bcr-Abl in K562 cell. In higher concentration, HH-GV-678 can inhibit the phosphorylation of c-Kit in Mo7e cell and the phosphorylation of PDGFR in Swiss3T3 cell, however, HH-GV-678 has no or little effect on other tyrosine kinase including EGFR/KDR/c-Src andHER2 [1]. Flumatinib effectively overcame the drug resistance of certain KIT mutants with activation loop mutations (i.e., D820G, N822K, Y823D, and A829P) [2].in vivo: The purpose of this study was to identify the metabolites of flumatinib in CML patients, with the aim of determining the main metabolic pathways offlumatinib in humans after oral administration. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry revealed 34 metabolites; 7 primary metabolites were confirmed by comparison with synthetic reference standards. The results show that the parent drugflumatinib was the main form recovered in human plasma, urine, and feces. The main metabolites of flumatinib in humans were the products of N-demethylation, N-oxidation, hydroxylation, and amide hydrolysis [3]. |
| Name | methanesulfonic acid,4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-N-[6-methyl-5-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]pyridin-3-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Flumatinib mesylate (HH-GV-678 mesylate), a derivative of imatinib, is a multi-kinase inhibitor with IC50 Values of 1.2 nM, 307.6 nM and 2662 nM for c-Abl, PDGFRβ and c-Kit respectively.IC50 Value: 1.2 nM (c-Abl); 307.6 nM(PDGFRβ); 2662 nM (c-Kit) [1]Target: c-Abl; c-Kit; PDGRFβin vitro: HH-GV-678 can predominantly inhibit the autophosphorylation of Bcr-Abl in K562 cell. In higher concentration, HH-GV-678 can inhibit the phosphorylation of c-Kit in Mo7e cell and the phosphorylation of PDGFR in Swiss3T3 cell, however, HH-GV-678 has no or little effect on other tyrosine kinase including EGFR/KDR/c-Src andHER2 [1]. Flumatinib effectively overcame the drug resistance of certain KIT mutants with activation loop mutations (i.e., D820G, N822K, Y823D, and A829P) [2].in vivo: The purpose of this study was to identify the metabolites of flumatinib in CML patients, with the aim of determining the main metabolic pathways offlumatinib in humans after oral administration. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry revealed 34 metabolites; 7 primary metabolites were confirmed by comparison with synthetic reference standards. The results show that the parent drugflumatinib was the main form recovered in human plasma, urine, and feces. The main metabolites of flumatinib in humans were the products of N-demethylation, N-oxidation, hydroxylation, and amide hydrolysis [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C30H33F3N8O4S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 658.694 |
| Exact Mass | 658.229736 |
| PSA | 165.41000 |
| LogP | 5.92170 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-(6-methyl-5-{[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino}-3-pyridinyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide methanesulfonate (1:1) |
| Benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[6-methyl-5-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-3-pyridinyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)-, methanesulfonate (1:1) |
| Flumatinib mesylate |
| Flumatinib (mesylate) |