Native Electrophorus electricus (electric eel) Acetylcholinesterase
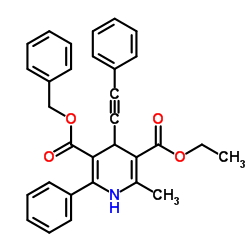
Native Electrophorus electricus (electric eel) Acetylcholinesterase structure
|
Common Name | Native Electrophorus electricus (electric eel) Acetylcholinesterase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9000-81-1 | Molecular Weight | 477.550 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 643.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H27NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 342.7±31.5 °C | |
Use of Native Electrophorus electricus (electric eel) AcetylcholinesteraseAcetylcholinesterase (ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7) is a cholinergic enzyme mainly found in neuromuscular junctions and cholinergic type chemical synapses, and is often used in biochemical research. Acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the breakdown or hydrolysis of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that act as neurotransmitters into acetate and choline. Acetylcholinesterase's main role is to terminate neuronal transmission and signaling between synapses to prevent ACh spread and activation of nearby receptors[1]. |
| Name | Acetylcholinesterase |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acetylcholinesterase (ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7) is a cholinergic enzyme mainly found in neuromuscular junctions and cholinergic type chemical synapses, and is often used in biochemical research. Acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the breakdown or hydrolysis of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that act as neurotransmitters into acetate and choline. Acetylcholinesterase's main role is to terminate neuronal transmission and signaling between synapses to prevent ACh spread and activation of nearby receptors[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 643.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C31H27NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 477.550 |
| Flash Point | 342.7±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 477.194000 |
| LogP | 7.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.639 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.
Nat. Genet. 36 , 40-5, (2004) As a base for human transcriptome and functional genomics, we created the "full-length long Japan" (FLJ) collection of sequenced human cDNAs. We determined the entire sequence of 21,243 selected clone... |
|
|
The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).
Genome Res. 14 , 2121-7, (2004) The National Institutes of Health's Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) project was designed to generate and sequence a publicly accessible cDNA resource containing a complete open reading frame (ORF) for... |
|
|
Elevated temperatures increase the toxicity of pesticide mixtures to juvenile coho salmon.
Aquat. Toxicol. 146 , 38-44, (2014) Pesticide mixtures and elevated temperatures are parallel freshwater habitat stressors for Pacific salmon in the western United States. Certain combinations of organophosphate (OP) insecticides are kn... |
| Acetylcholine esterase |
| Acetylcholinesterases |
| AcCholE |
| True cholinesterase |
| 5-Benzyl 3-ethyl 2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
| Acetylcholine hydrolase |
| Acetylcholine acetylhydrolase |
| Choline esterase |
| 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(2-phenylethynyl)-, 3-ethyl 5-(phenylmethyl) ester |
| Acetyl beta-methylcholinesterase |
| Cholinesterase |
| Acetyl choline esterase |
| MFCD00081268 |
| Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) |
| EINECS 232-559-3 |
| Cholinesterase I |
| Acetylthiocholinesterase |
| E.C. 3.1.1.7 |
| 5-Benzyl 3-ethyl 2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate |
| Native Electrophorus electricus (electric eel) Acetylcholinesterase |

