alpha-Amylase
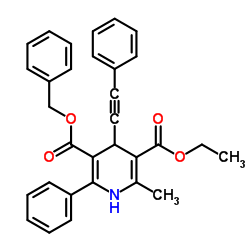
alpha-Amylase structure
|
Common Name | alpha-Amylase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9000-85-5 | Molecular Weight | 477.550 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 643.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H27NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 342.7±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of alpha-AmylaseBacterial α-Amylase catalyses the hydrolysis of internal α-1,4-glycosidic linkages in starch in low molecular weight products, such glucose, maltose and maltotriose units. Bacterial α-Amylase is often used in biochemical studies[1]. |
| Name | 5-Benzyl 3-ethyl 2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bacterial α-Amylase catalyses the hydrolysis of internal α-1,4-glycosidic linkages in starch in low molecular weight products, such glucose, maltose and maltotriose units. Bacterial α-Amylase is often used in biochemical studies[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 细菌 α-淀粉酶的最适温度范围为 25-100℃,最适 pH 范围为 1-11.5[1]。 |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 643.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C31H27NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 477.550 |
| Flash Point | 342.7±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 477.194000 |
| LogP | 7.16 |
| Appearance of Characters | suspension | yellow-brown |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.639 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,B,Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 42-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 36-36/37-24-22-2-26-45-23-36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BU7432500 |
|
Structural features of soluble cereal arabinoxylan fibers associated with a slow rate of in vitro fermentation by human fecal microbiota.
Carbohydr. Polym. 130 , 191-7, (2015) Most soluble dietary fibers ferment rapidly in the proximal colon, potentially causing discomfort and poor tolerability. Alkali-extracted arabinoxylan isolates from corn, wheat, rice and sorghum brans... |
|
|
In vitro and in vivo effects of standardized extract and fractions of Phaleria macrocarpa fruits pericarp on lead carbohydrate digesting enzymes.
BMC Complement Altern. Med. 13 , 39, (2013) One vital therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus is the use of agents that can decrease postprandial hyperglycaemia by inhibiting carbohydrate digesting enzymes. The presen... |
|
|
Combined effects of green tea extracts, green tea polyphenols or epigallocatechin gallate with acarbose on inhibition against α-amylase and α-glucosidase in vitro.
Molecules 18(9) , 11614-23, (2013) Green tea, green tea polyphenols and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) are confirmed to have beneficial effects in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, and a possible mechanism can be ascribed to their i... |
| MFCD05861376 |
| 5-Benzyl 3-ethyl 2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
| MFCD01867626 |
| 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(2-phenylethynyl)-, 3-ethyl 5-(phenylmethyl) ester |
| 5-Benzyl 3-ethyl 2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate |
| alpha-Amylase |