Rebamipide

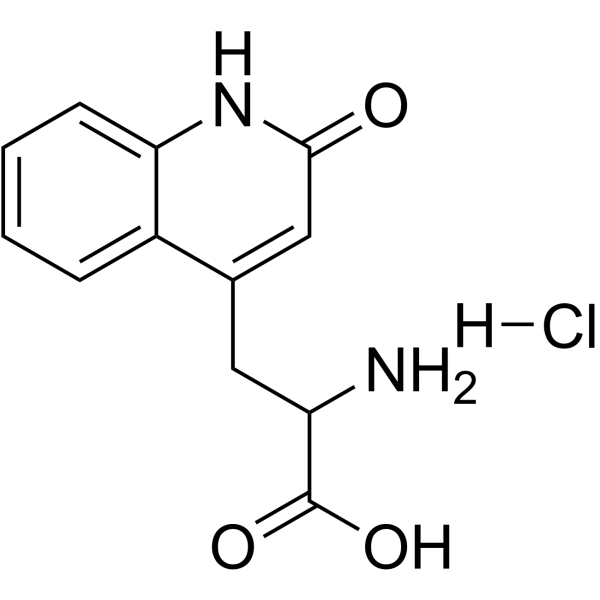
Rebamipide structure
|
Common Name | Rebamipide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90098-04-7 | Molecular Weight | 370.786 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 695.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H15ClN2O4 | Melting Point | 288-290ºC dec. | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 374.1±31.5 °C | |
Use of RebamipideRebamipide is an inducer of endogenous prostaglandin and a oxygen-derived free radical scavenger.Target: OthersRebamipide is the first anti-gastric ulcer and antigastritis drug that not only increases endogenous prostaglandin in gastric mucosa but also scavenges oxygen-derived free radicals and inhibits their production. The inhibitory effect of rebamipide on lipid peroxidation induced by a free radical initiator was also demonstrated by the in vitro system using rat gastric mucosal homogenates. These data indicate that rebamipide offers a potential for protection against reactive oxygen- and activated neutrophil-associated gastric mucosal injury by scavenging hydroxyl radical and inhibiting neutrophil activation or lipid peroxidation [1]. Rebamipide can contribute to the management of patients who are taking NSAIDs or are infected with H. pylori. Rebamipide may enhance eradication of H. pylori-infection using standard eradication therapy [2]. Rebamipide is beneficial for obtaining a better quality of ulcer healing and reduction of future ulcer relapse [3]. |
| Name | Rebamipide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Rebamipide is an inducer of endogenous prostaglandin and a oxygen-derived free radical scavenger.Target: OthersRebamipide is the first anti-gastric ulcer and antigastritis drug that not only increases endogenous prostaglandin in gastric mucosa but also scavenges oxygen-derived free radicals and inhibits their production. The inhibitory effect of rebamipide on lipid peroxidation induced by a free radical initiator was also demonstrated by the in vitro system using rat gastric mucosal homogenates. These data indicate that rebamipide offers a potential for protection against reactive oxygen- and activated neutrophil-associated gastric mucosal injury by scavenging hydroxyl radical and inhibiting neutrophil activation or lipid peroxidation [1]. Rebamipide can contribute to the management of patients who are taking NSAIDs or are infected with H. pylori. Rebamipide may enhance eradication of H. pylori-infection using standard eradication therapy [2]. Rebamipide is beneficial for obtaining a better quality of ulcer healing and reduction of future ulcer relapse [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 695.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 288-290ºC dec. |
| Molecular Formula | C19H15ClN2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 370.786 |
| Flash Point | 374.1±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 370.072021 |
| PSA | 99.26000 |
| LogP | 2.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.634 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| HS Code | 2933790090 |
|---|
|
~96% 
Rebamipide CAS#:90098-04-7 |
| Literature: OTSUKA PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD. Patent: WO2006/59781 A1, 2006 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 11-12 ; |
|
~94% 
Rebamipide CAS#:90098-04-7 |
| Literature: Lee, Byoung-suk; Chun, Myung-Hee Patent: US2003/87930 A1, 2003 ; |
|
~50% 
Rebamipide CAS#:90098-04-7 |
| Literature: Uchida; Tabusa; Komatsu; Morita; Kanbe; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1985 , vol. 33, # 9 p. 3775 - 3786 |
|
~% 
Rebamipide CAS#:90098-04-7 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 33, # 9 p. 3775 - 3786 |
|
~% 
Rebamipide CAS#:90098-04-7 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 33, # 9 p. 3775 - 3786 |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933499090. other compounds containing in the structure a quinoline or isoquinoline ring-system (whether or not hydrogenated), not further fused. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
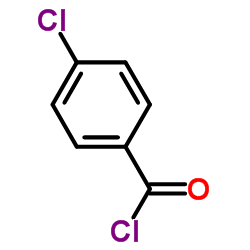
| 1H-benzimidazol-2-yl(4-chlorophenyl)methanone |
| 2-(4-chlorobenzoylamino)-3-[2(1H)-quinolinone-4-yl]propionic acid |
| 4-quinolinepropanoic acid, α-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]-2-hydroxy- |
| Mucosta |
| Proamipide |
| 2-(4-Chlorobenzoylamino)-3-[2(1H)-quinolinon-4-yl]propionic acid |
| 2-(4-Chlorobenzoylamino)-3-(1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-quinolyl)propionic acid |
| 2-(4-chlorobenzamido)-3-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinolin-4-yl)propanoic acid |
| REBAMIPIDEREBAMIPIDE |
| (R)-2-(4-chlorobenzamido)-3-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinolin-4-yl)propanoic acid |
| N-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-3-(2-hydroxyquinolin-4-yl)alanine |
| N-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-3-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-4-quinolinyl)alanine |
| REACTIVE ORANGE 122,CINO.ORANGE 122 |
| (±)-a-(p-Chlorobenzamido)-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-quinolinepropionic acid |
| N-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-3-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinolin-4-yl)alanine |
| MFCD00866895 |
| N-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-3-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinolin-4-yl)alanine |
| 2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]-3-(2-oxo-1H-quinolin-4-yl)propanoic acid |
| 2-(4-chlorobenzoyl)benzimidazole |
| Rebamipide |
| 2-(4-chlorobenzoylamino)-3-[2(1H)-quinolon-4-yl]propionic acid |
| 4-Quinolinepropanoic acid, α-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo- |
| a-[(4-Chlorobenzoyl)amino]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-quinolinepropanoic acid |
![2-amino-3-[6-bromo-2(1H)-quinolon-4-yl]propionic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/482/889573-80-2.png)