PQ-10
Modify Date: 2024-01-06 16:00:28
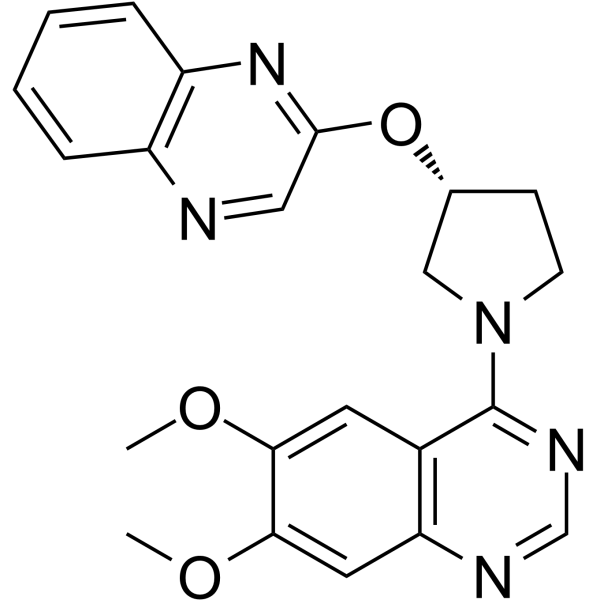
PQ-10 structure
|
Common Name | PQ-10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 927691-21-2 | Molecular Weight | 403.43400 | |
| Density | 1.333 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H39N5O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of PQ-10PQ-10 is a potent inhibitor of Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) with IC50 andED50 of 4.6 nM and 13 mg/kg, respectively. PQ-10 induces patterns of brain glucose metabolism which can be a potential translational biomarker. PQ-10 has the potential for researching psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia[1]. |
| Name | 6,7-dimethoxy-4-(3-quinoxalin-2-yloxypyrrolidin-1-yl)quinazoline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | PQ-10 is a potent inhibitor of Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) with IC50 andED50 of 4.6 nM and 13 mg/kg, respectively. PQ-10 induces patterns of brain glucose metabolism which can be a potential translational biomarker. PQ-10 has the potential for researching psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PDE10A:4.6 nM (IC50) |
| In Vivo | PQ-10 shows region-specific increases in 2-DG uptake in the globus pallidus (equivalent to the external segment of the globus pallidus in primates) and the lateral habenula in mice[1]. Animal Model: 24 –28 g male C57BL/6 mice, PDE10A WT and KO mice[1] Dosage: 0.16, 0.63, 2.5, and 10 mg/kg Administration: s.c. Result: Showed region-specific increases in 2-DG uptake in the globus pallidus (equivalent to the external segment of the globus pallidus in primates) and the lateral habenula in mice. |
| References |
| Density | 1.333 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H39N5O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 403.43400 |
| Exact Mass | 403.16400 |
| PSA | 82.49000 |
| LogP | 3.31290 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
| PQ-10 |