CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
UQ2275000
-
CHEMICAL NAME :
-
Pyrazinecarboxamide
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
98-96-4
-
BEILSTEIN REFERENCE NO. :
-
0112306
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
199806
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
16
-
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C5-H5-N3-O
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
123.13
-
WISWESSER LINE NOTATION :
-
T6N DNJ BVZ
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
10 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Vascular - BP elevation not characterized in autonomic section
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - rat
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
3 gm/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - excitement Behavioral - ataxia
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
3 gm/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - excitement Behavioral - ataxia
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
1680 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Subcutaneous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
2973 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Mammal - dog
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
90 gm/kg/90D-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Liver - hepatitis (hepatocellular necrosis), zonal
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
328 gm/kg/78W-C
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Tumorigenic - equivocal tumorigenic agent by RTECS criteria Blood - lymphoma, including Hodgkin's disease
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TD - Toxic dose (other than lowest)
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
756 gm/kg/30W-C
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Tumorigenic - equivocal tumorigenic agent by RTECS criteria Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - tumors
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Mutation test systems - not otherwise specified
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
Cytogenetic analysis
MUTATION DATA
-
TEST SYSTEM :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
500 mg/kg
-
REFERENCE :
-
MUREAV Mutation Research. (Elsevier Science Pub. B.V., POB 211, 1000 AE Amsterdam, Netherlands) V.1- 1964- Volume(issue)/page/year: 321,1,1994 *** NIOSH STANDARDS DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE DATA *** NIOSH OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE SURVEY DATA : NOES - National Occupational Exposure Survey (1983) NOES Hazard Code - X6080 No. of Facilities: 7 (estimated) No. of Industries: 1 No. of Occupations: 2 No. of Employees: 307 (estimated) No. of Female Employees: 251 (estimated)
|
 CAS#:19847-12-2
CAS#:19847-12-2 CAS#:19847-10-0
CAS#:19847-10-0![(1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)(pyrazin-2-yl)methanone Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/315/306990-94-3.png) CAS#:306990-94-3
CAS#:306990-94-3 CAS#:109-08-0
CAS#:109-08-0 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:123-32-0
CAS#:123-32-0 CAS#:98-97-5
CAS#:98-97-5 CAS#:6164-79-0
CAS#:6164-79-0 CAS#:290-37-9
CAS#:290-37-9 CAS#:77287-34-4
CAS#:77287-34-4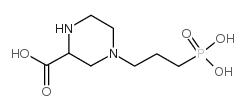 CAS#:100828-16-8
CAS#:100828-16-8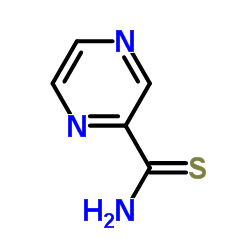 CAS#:4604-72-2
CAS#:4604-72-2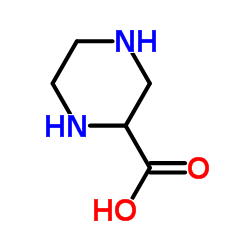 CAS#:31321-68-3
CAS#:31321-68-3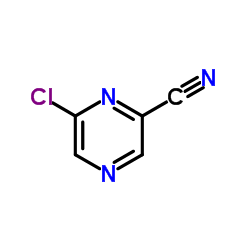 CAS#:6863-74-7
CAS#:6863-74-7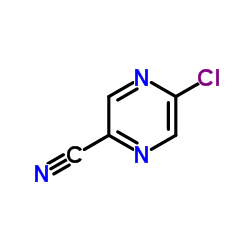 CAS#:36070-75-4
CAS#:36070-75-4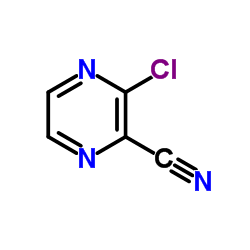 CAS#:55557-52-3
CAS#:55557-52-3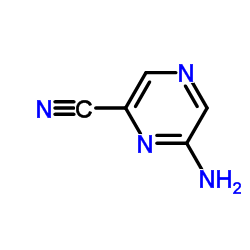 CAS#:59489-39-3
CAS#:59489-39-3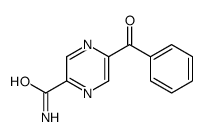 CAS#:147425-80-7
CAS#:147425-80-7 CAS#:5049-61-6
CAS#:5049-61-6
