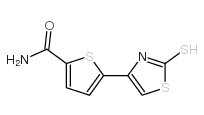
68377-92-4
| 中文名 | 阿罗洛尔 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 5-[2-[3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropyl]sulfanyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]thiophene-2-carboxamide |
| 英文别名 |
Arotinolo
5-(2-{[3-(tert-Butylamino)-2-hydroxypropyl]sulfanyl}-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)thiophene-2-carboxamide 5-[2-({2-Hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)amino]propyl}sulfanyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]-2-thiophenecarboxamide Arottnolol Arotinolol UNII:394E3P3B99 2-Thiophenecarboxamide, 5-[2-[[3-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]thio]-4-thiazolyl]- (±)-5-[2-[[3-[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]-2-hydroxypropyl]thio]-4-thiazolyl]-2-thiophenecarboxamide ARL 2-(3'-tert-Butylamino-2'-hydroxypropylthio)-4-(5'-carbamoyl-2'-thienyl)thiazole 5-[2-({3-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-2-hydroxypropyl}thio)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]thiophene-2-carboxamide |
| 描述 | Arotinolol 是一种非选择性的 α/β-肾上腺素受体 (α/β-adrenergic receptor ) 阻滞剂和一种血管扩张性 β-受体阻滞剂。Arotinolol 是一种抗高血压试剂,可用于治疗各种心血管疾病以及非心血管疾病。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点 |
IC50: α/β-adrenergic receptor |
| 体内研究 | 阿罗替洛尔(口服灌胃;200mg/kg;8周)能显著降低SHR小鼠的中心动脉压(CAP)和脉搏波速度(PWV),并能减少主动脉胶原沉积,最终改善动脉硬度[1]。动物模型:SHR小鼠[1]剂量:200mg/kg给药:灌胃;200mg/kg;每日1次;8周结果:SHR动脉硬化改善。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 599.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 148-149ºC |
| 分子式 | C15H21N3O2S3 |
| 分子量 | 371.541 |
| 闪点 | 316.6±32.9 °C |
| 精确质量 | 371.079590 |
| PSA | 170.02000 |
| LogP | 2.67 |
| 外观性状 | 白色固体 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.646 |
| 储存条件 | 2-8°C |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):2.3 2.氢键供体数量:3 3.氢键受体数量:7 4.可旋转化学键数量:8 5.互变异构体数量:2 6.拓扑分子极性表面积:170 7.重原子数量:23 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:406 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:1 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi |
|---|
|
~% 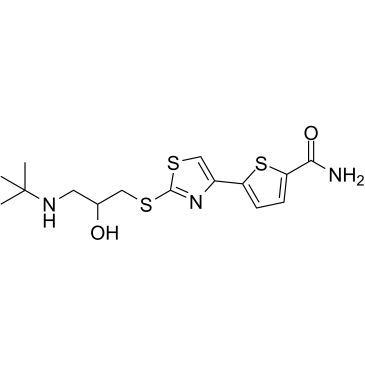
68377-92-4 |
| 文献:US3932400 A1, ; US 3932400 A |
| 上游产品 1 | |
|---|---|
| 下游产品 0 | |