半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐
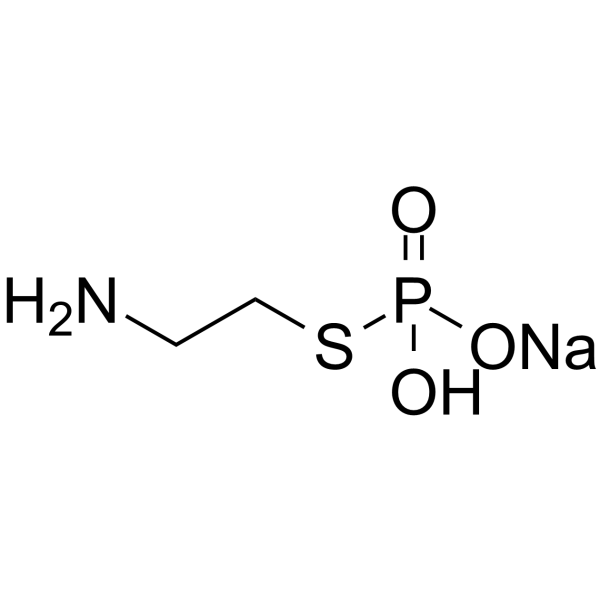
半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐结构式

|
常用名 | 半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐 | 英文名 | Ethanethiol, 2-amino-,1-(dihydrogen phosphate), sodium salt (1:1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 3724-89-8 | 分子量 | 179.11000 | |
| 密度 | 1.597g/cm3 | 沸点 | 384.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C2H7NNaO3PS | 熔点 | 220ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 186.2ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐用途半胱胺S-磷酸(半胱氨酸)钠可通过人碱性磷酸酶水解成半胱氨。半胱胺是研究肾病性半胱氨酸病的口服活性剂和抗氧化剂[1][2]。 |
| 中文名 | 半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | sodium,2-aminoethylsulfanyl(hydroxy)phosphinate |
| 中文别名 | 半胱胺S-磷酸钠盐 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | 半胱胺S-磷酸(半胱氨酸)钠可通过人碱性磷酸酶水解成半胱氨。半胱胺是研究肾病性半胱氨酸病的口服活性剂和抗氧化剂[1][2]。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.597g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 384.2ºC at 760mmHg |
| 熔点 | 220ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
| 分子式 | C2H7NNaO3PS |
| 分子量 | 179.11000 |
| 闪点 | 186.2ºC |
| 精确质量 | 178.97800 |
| PSA | 121.49000 |
| LogP | 0.90950 |
| 储存条件 | 低温,阴凉通风处保存 |
| 分子结构 | 摩尔折射率:无可用 摩尔体积( m 3/mol ):无可用 等张比容( 90.2K ):无可用 表面张力( dyne/cm ):无可用 介电常数( F/m ):无可用 偶极距( D ):无可用 极化率( 10 -24cm 3 ):无可用 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):无 2.氢键供体数量:2 3.氢键受体数量:5 4.可旋转化学键数量:3 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积112 7.重原子数量:9 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:112 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:2 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:未确定 2. 密度(g/mLat 25°C):未确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):未确定 4. 熔点(ºC):220 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):未确定 6. 沸点(ºC,16mmHg):未确定 7. 折射率(n20/D):未确定 8. 闪点(ºC):未确定 9. 比旋光度(º):未确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):未确定 11. 蒸气压(mmHg,37ºC):未确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,114.4 ºC):未确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):未确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):未确定 15. 临界压力(MPa):未确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:未确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):未确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):未确定 19. 溶解性:未确定 |
|
半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐毒理学数据: 急性毒性:大鼠腹膜腔LD50:555mg/kg;大鼠肌肉LD50:505mg/kg;小鼠经口LD50:1433mg/kg;小鼠腹膜腔LD50:806mg/kg;小鼠肌肉LD50:1003mg/kg;豚鼠腹膜腔LD50:358mg/kg; 半胱胺S-磷酸盐 钠盐生态学数据: 该物质对环境可能有危害,建议不要让其进入环境 |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Warning |
| 危害声明 | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| 警示性声明 | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| 个人防护装备 | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xn: Harmful; |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | 22-36/37/38 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S26;S36 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
| RTECS号 | TE6483500 |
|
A comparison of the effectiveness of cysteamine and phosphocysteamine in elevating plasma cysteamine concentration and decreasing leukocyte free cystine in nephropathic cystinosis.
Pediatr. Res. 23(6) , 616-20, (1988) Cysteamine (beta-mercaptoethylamine, MEA) is currently used to treat children with nephropathic cystinosis. In this study MEA was compared to phosphocysteamine (MEAP), a phosphorothioester that tastes... |
|
|
The treatment of cystinosis with cysteamine and phosphocysteamine in the United Kingdom and Eire.
Pediatr. Nephrol. 9(6) , 685-9, (1995) Fifty-nine patients with cystinosis were treated with cysteamine or phosphocysteamine in the United Kingdom up to May 1990. Treatment was started at a median age of 3.2 years (range 0.6-24.8 years) an... |
|
|
Combination small molecule PPT1 mimetic and CNS-directed gene therapy as a treatment for infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 35(5) , 847-57, (2012) Infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (INCL) is a profoundly neurodegenerative disease of children caused by a deficiency in the lysosomal enzyme palmitoyl protein thioesterase-1 (PPT1). There is c... |
| Phosphocysteamine |
| Tsistafos |
| MFCD00038474 |
| Cystaphos sodium salt |
| Tsistafos (cystafos) |
| Cystaphos |
| Cistaphos |
| S-(2-Aminoethyl) thiophosphate monosodium salt |
| EINECS 223-079-5 |
| Cystafos |


