对羟基苯乙醇
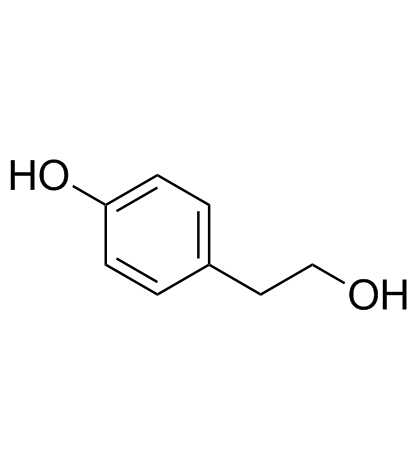
对羟基苯乙醇结构式

|
常用名 | 对羟基苯乙醇 | 英文名 | 4-Hydroxyphenyl ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 501-94-0 | 分子量 | 138.16 | |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 375.2±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C8H10O2 | 熔点 | 89-92 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 180.7±23.7 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
对羟基苯乙醇用途Tyrosol 是苯乙醇的衍生物。Tyrosol 减弱来自星形胶质细胞的促炎细胞因子,且降低 NF-κB 活化。具有抗氧化和抗炎作用[1]。 |
| 中文名 | 对羟基苯乙醇 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol |
| 中文别名 | 2-(4-羟苯基)乙醇 | 4-羟基苯乙醇 | 酪醇 | 对羟苯基乙醇 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Tyrosol 是苯乙醇的衍生物。Tyrosol 减弱来自星形胶质细胞的促炎细胞因子,且降低 NF-κB 活化。具有抗氧化和抗炎作用[1]。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 体外研究 | 酪醇(1.6 mM)显着增加暴露于氧葡萄糖剥夺(OGD)的培养星形胶质细胞的细胞活力[1]。酪醇(1.6 mM)通过调节Janus N末端激酶(JNK)减弱星形胶质细胞释放的TNF-α和IL-6水平[1]。由于酪氨酸(1.6mM)减弱GFAP(胶质原纤维酸性蛋白)的表达水平和STAT3的磷酸化[1],因此星形胶质细胞的细胞因子减少可能是由于其抑制星形胶质细胞活化和调节STAT3信号通路。酪醇可以防止OGD暴露的星形胶质细胞中IκBα的降解和IκBα磷酸化的增加,从而导致缺血期间NF-κB功能的抑制[1]。 |
| 体内研究 | 足底注射角叉菜胶导致爪厚度显着增加,在注射后2小时达到峰值。当在用角叉菜胶处理之前注射酪醇(0.5mg/kg)或酪醇硫酸盐时,这种效果降低。在以0.5mg/kg的剂量施用酪醇并且以0.1mg/kg的剂量施用酪醇-硫酸盐之后获得类似的爪水肿的AUC值。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 375.2±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 89-92 °C(lit.) |
| 分子式 | C8H10O2 |
| 分子量 | 138.16 |
| 闪点 | 180.7±23.7 °C |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 0.04 |
| 外观性状 | 灰白色至淡米色晶体或结晶 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.598 |
| 储存条件 | 密封保存,放置在通风,干燥的环境中 |
| 稳定性 | 1. 按规格使用和贮存,不会发生分解,避免与氧化物接触。 2. 存在于烟气中。 |
| 水溶解性 | slightly soluble |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:39.21 2、 摩尔体积(cm3/mol):118.1 3、 等张比容(90.2K):315.6 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):50.8 5、 极化率(10-24cm3):15.54 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):无 2.氢键供体数量:2 3.氢键受体数量:2 4.可旋转化学键数量:2 5.互变异构体数量:2 6.拓扑分子极性表面积40.5 7.重原子数量:10 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:85.3 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:无色晶体 2. 密度(g/ m3,20/4℃):1.168 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/cm3,空气=1):4.76 4. 熔点(ºC):88~91 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):287.8,195ºC(2399pa) 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa):未确定 7. 折射率:未确定 8. 闪点(ºC):143.2 9. 比旋光度(º):未确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):未确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):未确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):未确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):55.7 14. 临界温度(ºC):未确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):未确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:未确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):未确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):未确定 19. 溶解性:溶于水 |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Warning |
| 危害声明 | H315-H319-H335 |
| 警示性声明 | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| 个人防护装备 | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi:Irritant |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R36/37/38 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S26-S37/39-S24/25 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
| 海关编码 | 2907299090 |
| 对羟基苯乙醇上游产品 9 | |
|---|---|
| 对羟基苯乙醇下游产品 8 | |
可用对羟基苯乙酮用脂肪腈氧化,然后水解得(对羟苯基)乙二醛,将后者还原即得该品。
| 海关编码 | 2907299090 |
|---|---|
| 中文概述 | 2907299090 其他多元酚,酚醇。监管条件:AB(入境货物通关单,出境货物通关单)。增值税率:17.0%。退税率:9.0%。最惠国关税:5.5%。普通关税:30.0% |
| 申报要素 | 品名, 成分含量, 用途 |
| 监管条件 | A.入境货物通关单 B.出境货物通关单 |
| 检验检疫 | R.进口食品卫生监督检验 S.出口食品卫生监督检验 M.进口商品检验 N.出口商品检验 |
| Summary | 2907299090 polyphenols; phenol-alcohols。supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
Effect of different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition and sensory characteristics of Syrah red wines fermented using different yeast strains.
Food Chem. 179 , 116-26, (2015) The effect of high levels of the polysaccharide Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strain (HPS) and another conventional yeast strain (FERM) on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition of Syrah red win... |
|
|
Effect of selected Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains and different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and polyphenolic composition and sensorial characteristics of Cabernet Sauvignon red wines.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 , 2132-44, (2015) The objective of this work was to study the effect of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains with different capabilities of polysaccharide liberation during alcoholic fermentation in addition to s... |
|
|
Multicommuted flow injection method for fast photometric determination of phenolic compounds in commercial virgin olive oil samples.
Talanta 147 , 531-6, (2015) A multicommuted flow injection method has been developed for the determination of phenolic species in virgin olive oil samples. The method is based on the inhibitory effect of antioxidants on a stable... |
| 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)phenol |
| 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethyl Alcohol |
| 4-Hydroxyphenylethanol |
| β-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol |
| 4-[(2S)-2-Amino-3-hydroxypropyl]phenol |
| (S)-4-(2-Amino-3-hydroxypropyl)phenol |
| b-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol |
| Benzenepropanol, β-amino-4-hydroxy-, (βS)- |
| tyrosinol |
| 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)benzolol |
| phenethyl alcohol, 4-hydroxy- |
| p-Hydroxyphenethyl alcohol |
| Benzenepropanol, β-amino-4-hydroxy-, (S)- |
| UNII-1AK4μ3SNX |
| 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol |
| Ethanol, 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)- |
| 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethan-1-ol |
| (S)-b-Amino-4-hydroxybenzenepropanol |
| 4-hydroxybenzeneethanol |
| MFCD00002902 |
| β-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol |
| 4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcohol |
| EINECS 207-930-8 |
| Benzeneethanol, 4-hydroxy- |
| p-Hydroxyphenylethanol |
| 4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcohol,Tyrosol,p-HPEA |
| 4-Hydroxyphenylethyl alcohol |
| b-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol |
| 4-Hydroxyphenyl ethanol |
| Tyrosol |

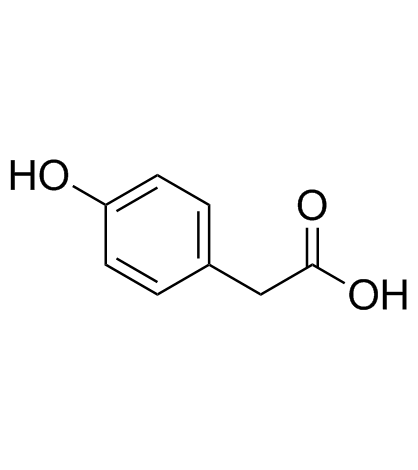 CAS号156-38-7
CAS号156-38-7 CAS号14199-15-6
CAS号14199-15-6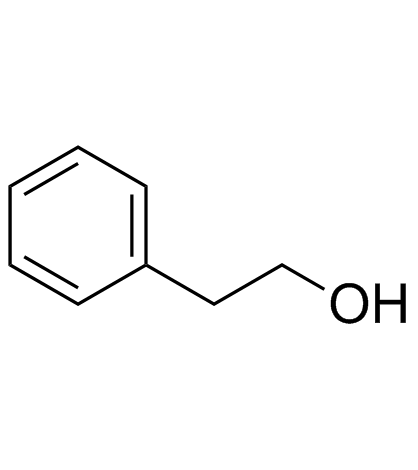 CAS号60-12-8
CAS号60-12-8![4-[2-(2-chloroacetyl)oxoethyl]phenyl-2-chloroacetate结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/042/1223454-88-3.png) CAS号1223454-88-3
CAS号1223454-88-3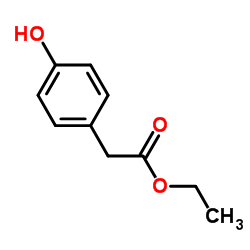 CAS号17138-28-2
CAS号17138-28-2 CAS号104-01-8
CAS号104-01-8 CAS号14140-15-9
CAS号14140-15-9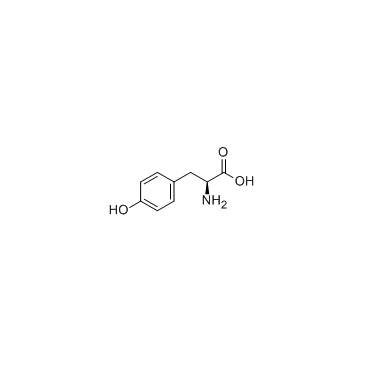 CAS号60-18-4
CAS号60-18-4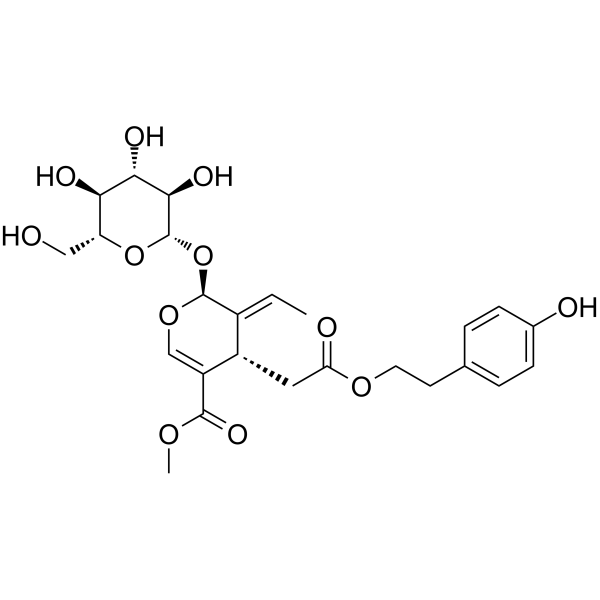 CAS号35897-92-8
CAS号35897-92-8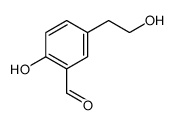 CAS号110005-81-7
CAS号110005-81-7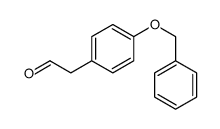 CAS号40167-10-0
CAS号40167-10-0 CAS号56718-71-9
CAS号56718-71-9 CAS号181115-01-5
CAS号181115-01-5 CAS号28145-35-9
CAS号28145-35-9 CAS号93221-48-8
CAS号93221-48-8 CAS号81024-42-2
CAS号81024-42-2 CAS号836-43-1
CAS号836-43-1
