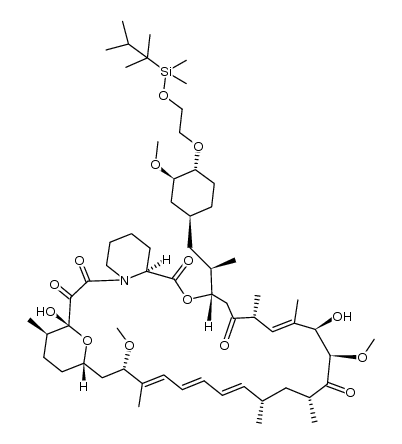
159351-69-6
| Name | everolimus |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
SDZRAD
Certican Zortress Afinitor RAD-001 CERTICAN(R) 42-O-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-rapamycin Everolimus Certica |
| Description | Everolimus (RAD001) is a potent mTOR inhibitor that binds to FKBP-12 to generate an immunosuppressive complex. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
mTOR:5-6 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Everolimus (RAD001) is an orally active derivative of rapamycin that inhibits the Ser/Thr kinase, mTOR[1]. In both the sensitive murine B16/BL6 melanoma (IC50, 0.7 nM) and the insensitive human cervical KB-31 (IC50, 1,778 nM), antiproliferative concentrations of Everolimus results in total dephosphorylation of S6K1 and the substrate S6 and a shift in the mobility of 4E-BP1, which is indicative of a reduced phosphorylation status[2]. Everolimus exhibits a dose-dependent inhibition in both the total cells and the stem cells from the BT474 cell line and the primary breast cancer cells, albeit with different degrees of growth inhibition. Compare with the total cells, Everolimus is less effective in growth inhibition in the stem cells at all tested concentrations (P<0.001). The IC50 values of Everolimus for BT474 and the primary CSCs are 2,054 and 3,227 nM, or 29 times and 21 times greater than the IC50 values for their corresponding total cells, respectively[3]. |
| In Vivo | Everolimus is orally active in both mice and rats, producing an antitumor effect that is characterized by dramatic reduction in tumor growth rates as opposed to producing tumor regressions. In the rat CA20498 model, daily treatment with Everolimus (0.5 or 2.5 mg/kg) dose-dependently inhibits growth, and intermittent dosing using a higher dose of 5 mg/kg (once or twice per week) also shows similar antitumor efficacy. Inhibition by Everolimus is characterized by sustained suppression rather than regression and is not associated with any body weight loss[1]. The effect of Everolimus treatment (0.1-10 mg/kg/d) is selective and differ from the effects of PTK/ZK (100 mg/kg). With either growth factor, Everolimus dose-dependently increases the hemoglobin content (convert to blood equivalents and indicative of the number of vessels as well as vascular leakiness) but reduces the Tie-2 content (number of endothelial cells indicative of the number of vessels) and this is significant for VEGF stimulation but not bFGF stimulation. The pharmacokinetics of Everolimus in mice shows that maximum levels of only 0.1 μM are achieved in a human tumor xenograft following a single administration, whereas plasma levels reach 1 to 3 μM for ~4 h[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Tumor cells are plated into 96-well plates at densities ranging from 500 to 5,000/100 μL/well, with repeat experiments being done at an optimal cell number, typically 1,000 to 2,000 per well, and incubated overnight. Cells are exposed to Everolimus and incubated for 4 days and the cell number is determined by methylene blue staining. For this, 50 μL glutaraldehyde [20% (v/v)] is added to the wells incubated for 10 min at room temperature. The culture medium is aspirated, cells are washed with distilled water, and 100 μL methylene blue [0.05% (w/v) in water] is added and incubated for 10 min at 37°C. Stained cells are washed three times with water, 200 μL HCl [3% (v/v)] is added, and the plate shaken at room temperature for 20 min. The absorbance of each well is determined at 650 nm. The IC50 values are calculated using Softmax 2.0 software[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Everolimus, PTK/ZK, and their respective vehicles are prepared each day just before administration to animals and the administration volume is individually adjusted based on animal body weight. In C57/BL6 mice, Everolimus is administered at doses ranging from 0.1 to 10 mg/kg/d orally (10 mL/kg) and predominantly at 2.5 to 10 mg/kg because these doses provides the maximum effect. PTK/ZK is administered at 50 to 100 mg/kg/d orally. Rats[2] Wistar-Furth rats are divided into two equal groups based on body weight and treated either with vehicle or Everolimus (10 mg/kg/d orally in mice and 5 mg/kg three times per week orally in rats). Directly after the first measurement at baseline (day 0), Everolimus or vehicle is administered orally by gavage (10 mL/kg) for up to 7 days maximum with subsequent magnetic resonance measurements made within 30 min of the last dose. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 998.7±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Molecular Formula | C53H83NO14 |
| Molecular Weight | 958.224 |
| Flash Point | 557.8±37.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 957.581360 |
| PSA | 204.66000 |
| LogP | 3.35 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.548 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Hygroscopic |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in dimethysulfoxide,ethanol and chloroform. Slightly soluble in water. |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H302 + H332-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | R48/25 |
| Safety Phrases | S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1648 3 / PGII |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
|
~% 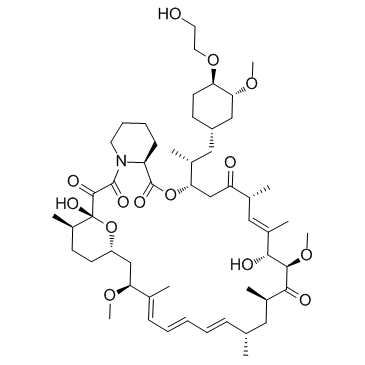
159351-69-6 |
| Literature: WO2012/103959 A1, ; Page/Page column 18 ; |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |