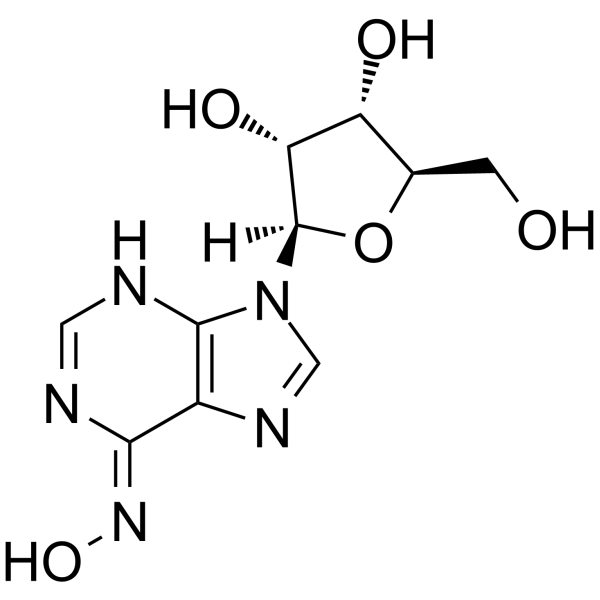
3414-62-8
| Name | 6-n-hydroxyadenosine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N6-Hydroxy-5-methyl-cytosin
N6-hydroxyadenosine N-hydroxyadenosine 5-methyl-1H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione 4-oxime 6-(hydroxyamino)-5-methylpyrimidin-2(1h)-one 5-Methyl-N(4)-hydroxycytosine |
| Description | Inosine oxime (6-Hydroxyadenosine) is an endogenous metabolite in the course of cell metabolism by cytochrome P450, by oxidative stress or by deviating nucleotide biosynthesis. Inosine oxime has toxic and mutagenic for procaryotic and eucaryotic cells[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Inosine oxime (6-Hydroxyadenosine) (1-5 nM) has reductive detoxication through direct dehydroxylamination catalyzed by adenosine deaminase to inosine and decreases inosine formation by 35% with knockdown of mARC1 in HEK-293. |
| References |
| Density | 2.12g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 703.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 283.24100 |
| Flash Point | 379.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 283.09200 |
| PSA | 149.01000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.897 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
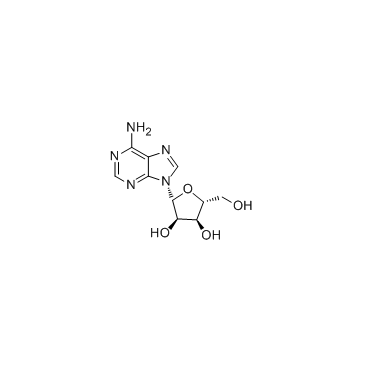
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |