121009-77-6
| Name | (3R,5R)-7-{(1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-8-[(2,2-Dimethylbutanoyl)oxy]-2,6-di methyl-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-1-naphthalenyl}-3,5-dihydroxyheptan oic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
simvasterol
Zocord Rechol [14C]-Simvastatin acid ZOCOR [3H]-Simvastatin 7-[1,2,6,7,8,8a(R)-hexahydro-2(S),6(R)-dimethyl-8(S)-[[2,2-dimethyl-butanoyl]oxy]-1(S)-naphthyl]-3(R),5(R)-dihydroxyheptanoic acid Lipex Denan Lipovas simvastatin acid Eucor [14C]-Simvastatin Simcor simvastatin hydroxy acid [3H]-Simvastatin acid |
| Description | Simvastatin acid (Tenivastatin) is an orally active HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) inhibitor. Simvastatin acid can reduce cholesterol synthesis and lower blood cholesterol levels[1]. Simvastatin acid shows anti-proliferation activities against cancer cells and induces apoptosis[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HMG-CoA reductase[1] |
| In Vitro | Simvastatin acid (32 and 64 μM; 24, 48, and 72 h) inhibits tumor cell growth, arrests in the G0/G1 phase[2]. Simvastatin acid (32 and 64 μM; 48 h) induces apoptosis in HepG2 and Huh7 cells[2]. Cell Proliferation Assay[2] Cell Line: HepG2 and Huh7 cells Concentration: 32 and 64 μM Incubation Time: 24, 48, and 72 hours Result: Inhibited tumor cell growth as compared to controls (ctrl, p<0.05). Apoptosis Analysis[2] Cell Line: HepG2 and Huh7 cells Concentration: 32 and 64 μM Incubation Time: 48 hours Result: Increased early apoptosis from 9.2% in non-treated ctrl cells to 18.2% (32 μM) and 19.8% (64 μM), respectively, increased late apoptosis from 35.0% in ctrl cells to 56.9% (32 μM) and 48.0% (64 μM), respectively, in HepG2 cells. Cell Cycle Analysis[2] Cell Line: HepG2 and Huh7 cells Concentration: 32 and 64 μM Incubation Time: 24, 48, and 72 hours Result: Exhibited downregulation of CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and cyclins D1 and E as compared to ctrl tumor cells. |
| In Vivo | Simvastatin acid (oral gavage; 15 and 30 mg/kg; once daily; 14 d) treatment attenuats oxidative damage, TNF-a and IL-6 levels, and restores itochondrial enzyme complex activities[3]. Animal Model: Male wistar rats with oxidative damage by Intrastriatal 6-OHDA administration[3] Dosage: 15 and 30 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage; once daily; 14 days Result: Attenuated oxidative damage (reduced MDA, nitrite levels and restoration of reduced GSH) , attenuated TNF-a and IL-6 levels, and restored itochondrial enzyme complex activities as compared to 6-OHDA group. |
| References |
| Density | 1.13g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 607ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C25H40O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 436.58200 |
| Flash Point | 198.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 436.28200 |
| PSA | 104.06000 |
| LogP | 4.10570 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.89E-17mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.536 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
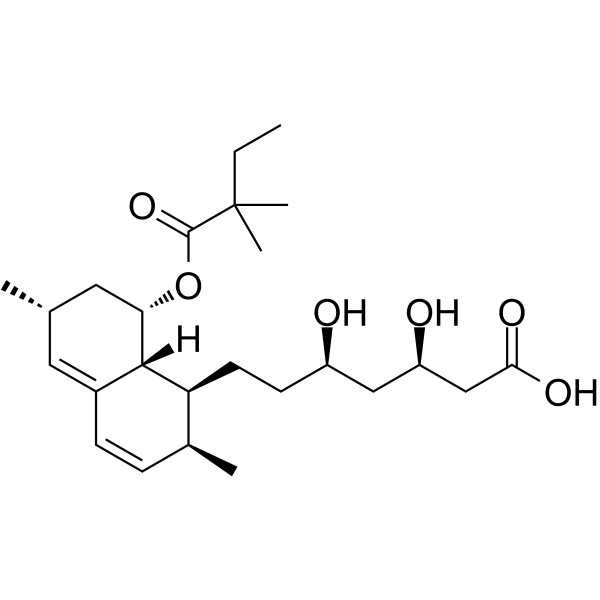
![N-butyl-7-[1,2,6,7,8,8a(R)-hexahydro-2(S),6(R)-dimethyl-8(S)-[[2,2-dimethylbutanoyl]oxy]-1(S)-naphthyl]-3(R),5(R)-dihydroxyheptanoic acid amide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/081/134970-33-5.png)
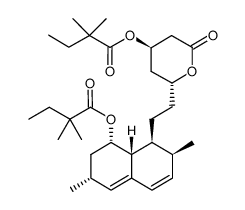
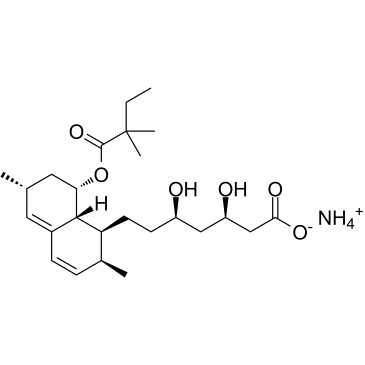
![3-[(2,2-Dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)thio]propanoic acid methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/155/938063-63-9.png)
