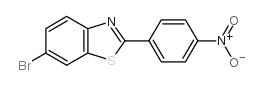
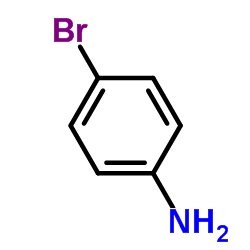
566169-97-9
| Name | 4-(6-bromo-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)aniline |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine |
| Description | 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine is a β-amyloid PET (positron emission tomography) tracer that can be used in the diagnosis of neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Down's syndrome. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
β-amyloid[1] |
| In Vitro | 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine (compound 6l) plus ultraviolet A (UVA) can induce caspase-3 activity, poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase cleavage, M30 positive CytoDeath staining, and subsequent apoptotic cell death. Treatment of A375 cells with 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine plus UVA results in a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨmt), oxidative phosphorylation system (OXPHOS) subunits, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) but an increase in mitochondrial DNA 4977-bp deletion via reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations also show major ultrastructural alterations of mitochondria[2]. |
| In Vivo | 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine plus UVA is shown to reduce murine melanoma size in a mouse model. 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine-PDT may serve as a potential ancillary modality for the treatment of melanoma[2]. |
| Cell Assay | For fluorescence Measurement of Uptake of 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine, cultured A375 cells are seeded on glass coverslips with a density of 2×104 cells/well in 24-well plate for 24 h until cell attachment. Then the cells are exposed to 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine at 5 μM for indicated times in the dark. The cells are washed twice with PBS and are then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 4°C for 30 min. The qualitative expression of cell fluorescence is determined using a Leica inverted microscope[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] A total of 5×106 B16 cells are inoculated into female ICR mice (about 19-21 g, 7 weeks). The subcutaneous inoculation of tumor cells resulted in tumor generation at the injection site. When tumors reached about 4×4 mm2 in diameter, mice are separated into groups. Each group had four mice in each experiment; 4 mg/kg of 4-(6-Bromo-2-benzothiazolyl)benzenamine is injected into the tumor site, and then tumor is exposed to different doses of UVA on the day after injection. Tumor volume is measured by calipers every 5 days after agent injection, and tumor volume is calculated[2] |
| References |
[1]. Klunk W, et al. Benzothiazole derivative compounds, compositions and uses. WO2004083195 A1 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H9BrN2S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 305.19300 |
| Exact Mass | 303.96700 |
| PSA | 67.15000 |
| LogP | 4.88920 |
|
~89% 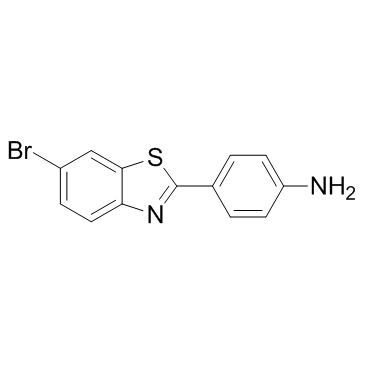
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: SNU Randamp;DB FOUNDATION; KIM, Sang Eun; LEE, Byung Chul; KIM, Ji Sun; CHUN, Young Sin Patent: WO2010/53218 A1, 2010 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 30; 31 ; |
|
~91% 
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: SNU RandDB FOUNDATION Patent: US2011/250136 A1, 2011 ; |
|
~% 
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: Mathis, Chester A; Wang, Yanming; Holt, Daniel P; Huang, Guo-Feng; Debnath, Manik L; Klunk, William E Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 13 p. 2740 - 2754 |
|
~% 
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: Mathis, Chester A; Wang, Yanming; Holt, Daniel P; Huang, Guo-Feng; Debnath, Manik L; Klunk, William E Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 13 p. 2740 - 2754 |
|
~% 
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: Mathis, Chester A; Wang, Yanming; Holt, Daniel P; Huang, Guo-Feng; Debnath, Manik L; Klunk, William E Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 13 p. 2740 - 2754 |
|
~% 
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: Mathis, Chester A; Wang, Yanming; Holt, Daniel P; Huang, Guo-Feng; Debnath, Manik L; Klunk, William E Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 13 p. 2740 - 2754 |
|
~% 
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: Lee, Byung Chul; Kim, Ji Sun; Kim, Bom Sahn; Son, Ji Yeon; Hong, Soo Kyung; Park, Hyun Soo; Moon, Byung Seok; Jung, Jae Ho; Jeong, Jae Min; Kim, Sang Eun Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 19, # 9 p. 2980 - 2990 |
|
~% 
566169-97-9 |
| Literature: Lee, Byung Chul; Kim, Ji Sun; Kim, Bom Sahn; Son, Ji Yeon; Hong, Soo Kyung; Park, Hyun Soo; Moon, Byung Seok; Jung, Jae Ho; Jeong, Jae Min; Kim, Sang Eun Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2011 , vol. 19, # 9 p. 2980 - 2990 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |