102029-73-2
| Name | Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ACETHYL COENZYME A SODIUM SALT
ACETYL COENZYME A (C2:0) SODIUMPREPARED ENZYMATICA Adenosine, 5'-O-[[[[4-[[3-[[2-(acetylthio)ethyl]amino]-3-oxopropyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutoxy]hydroxyphosphinyl]oxy]hydroxyphosphinyl]-, 3'-(dihydrogen phosphate) Acetyl-Coenzym A acetyl coa C2:0 S-{1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-3,5,9-trihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-3,5-dioxido-10,14-dioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-11,15-diaza-3λ,5λ-dipho sphaheptadecan-17-yl} ethanethioate Acetyl Coenzyme A Trisodium Salt coenzyme A acetyl derivative (C2:0),sodium salt Acetyl Coenzyme A MFCD00078858 |
| Description | Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium (Acetyl-CoA trisodium) is a central metabolic intermediate. Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium is the actual molecule through which glycolytic pyruvate enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a key precursor of lipid synthesis, and is the sole donor of the acetyl groups for acetylation. Acetyl Coenzyme A trisodium acts as a potent allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase (PC)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Acetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA) is a membrane-impermeant molecule constituted by an acetyl moiety (CH3CO) linked to coenzyme A (CoA), a derivative of vitamin B5 and cysteine, through a thioester bond. As thioester bonds are energy rich, the chemical structure of acetyl-CoA facilitates the transfer of the acetyl moiety to a variety of acceptor molecules, including amino groups on proteins[1]. In most mammalian cells, Acetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA) is predominantly generated in the mitochondrial matrix by various metabolic circuitries, namely glycolysis, β-oxidation, and the catabolism of branched amino acids. Cytosolic Acetyl-coenzyme A is the precursor of multiple anabolic reactions that underlie the synthesis of fatty acids and steroids, as well as specific amino acids including glutamate, proline, and arginine[1]. |
| In Vivo | Mice deprived of food (but with access to water ad libitum) for 24 hr exhibit a significant reduction in total Acetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA) levels in several organs, including the heart and muscles, corresponding to a decrease in protein acetylation levels. However, the same experimental conditions have no major effects on Acetyl-coenzyme A concentrations in the brain and actually increase hepatic Acetyl-coenzyme A and protein acetylation levels. Ethanol intake augments Acetyl-coenzyme A levels in hepatic mitochondria[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
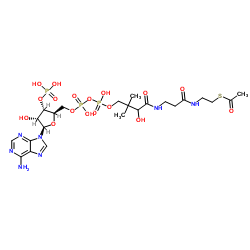
| Molecular Formula | C23H38N7O17P3S |
| Molecular Weight | 809.571 |
| Exact Mass | 809.125793 |
| PSA | 418.36000 |
| LogP | -3.89 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.718 |
| Storage condition | -20 °C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25 |
| Safety Phrases | 24-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |