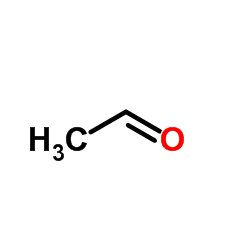
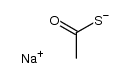
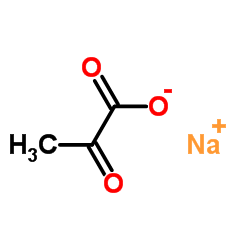
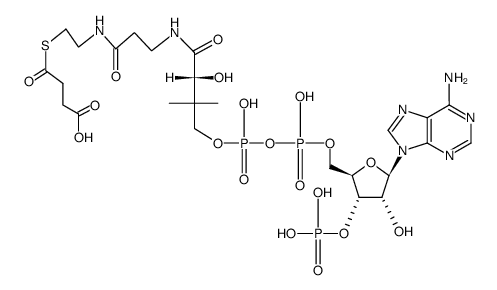
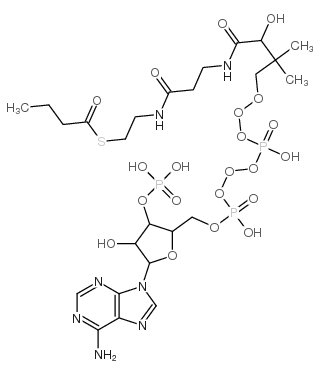
72-89-9
| Name | acetyl-CoA |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
acetylocholine
Azetylcholin ac-CoA Choline acetate S-{(9R)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-3,5,9-trihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-3,5-dioxido-10,14-dioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-11,15-diaza-3λ,5λ-diphosphaheptadecan-17-yl} ethanethioate (non-preferred name) Acetyl-CoenzymeA S-ACETYL COENZYME A acetyl CoA Acetyl-CoA,Tri-Na O-Acetylcholine S-acetylcoenzyme A [3H]-Acetylcholine Acetyl choline ion [14C]-Acetyl-Coenzyme A S-{(9R)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-3,5,9-trihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-3,5-dioxido-10,14-dioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-11,15-diaza-3λ,5λ-diphosphaheptadecan-17-yl} ethanethioate (non-preferred name) Adenosine, 5'-O-[[[[(3R)-4-[[3-[[2-(acetylthio)ethyl]amino]-3-oxopropyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutoxy]hydroxyphosphinyl]oxy]hydroxyphosphinyl]-, 3'-(dihydrogen phosphate) Coenzyme A S-Acetate Choline acetate (ester) trilithium,[2-[[[[4-[[3-(2-acetylsulfanylethylamino)-3-oxopropyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutoxy]-oxidophosphoryl]oxy-oxidophosphoryl]oxymethyl]-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxyoxolan-3-yl] hydrogen phosphate,trihydrate Acetyl coenzyme A coenzyme A, acetyl- ac-S-CoA S-{(9R)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-3,5,9-trihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-3,5-dioxido-10,14-dioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-11,15-diaza-3λ,5λ-diphosphaheptadecan-17-yl} ethanethioate S-{(9R)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-3,5,9-trihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-3,5-dioxido-10,14-dioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-11,15-diaza-3λ,5λ- diphosphaheptadecan-17-yl} ethanethioate [3H]-Acetyl-Coenzyme A (2-Acetoxyethyl)trimethylammonium Ach acetyl-S-CoA Acetylcholinum acetylCoA Acetyl-Coenzyme A [14C]-Acetylcholine Coenzyme A, S-acetate acetylcholine acetylcholine cation |
| Description | Acetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA) is a membrane-impermeant central metabolic intermediate, participates in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation metabolism. Acetyl-coenzyme A, regulates various cellular mechanisms by providing (sole donor) acetyl groups to target amino acid residues for post-translational acetylation reactions of proteins. Acetyl Coenzyme A is also a key precursor of lipid synthesis[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Acetyl coenzyme A 在饥饿的 U2OS 细胞中增加细胞质蛋白乙酰化,同时减少饥饿诱导的自噬通量。(U2OS 细胞稳定表达 GFP-LC3 并显微注射Acetyl coenzyme A; 在无营养条件下,用 100 nM BafA1 孵育 3 h 后固定)[2]。 |
| In Vivo | Acetyl coenzyme A 通过抑制适应不良的自噬来抑制压力超负荷诱导的小鼠心肌病[2][3]。被剥夺食物 (但可以随意饮水) 24 小时的小鼠在几个器官 (包括心脏和肌肉) 中表现出总 Acetyl coenzyme A 水平显着降低,对应于蛋白质乙酰化水平的降低。相同的实验条件对大脑中 Acetyl coenzyme A 的浓度没有重大影响,实际上会增加肝脏 Acetyl coenzyme A 和蛋白质乙酰化水平[4]。 |
| References |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H38N7O17P3S |
| Molecular Weight | 809.571 |
| Exact Mass | 809.125793 |
| PSA | 425.34000 |
| LogP | -3.89 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.718 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 75, p. 2520 Journal of Biological Chemistry, , vol. 203, p. 869,872, 877 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: US2013/66035 A1, ; Page/Page column ; |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Biochemische Zeitschrift, , vol. 329, p. 175 Journal of Biological Chemistry, , vol. 199, p. 65,66 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry, , vol. 67, # 10 p. 2106 - 2114 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 74, p. 3205 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Biochemistry, , vol. 51, # 13 p. 2795 - 2803 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Organic Letters, , vol. 9, # 20 p. 3877 - 3880 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Biochemistry, , vol. 50, # 39 p. 8407 - 8416 |
|
~% 
72-89-9 |
| Literature: Biochemistry, , vol. 51, # 42 p. 8422 - 8434 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |